|
Igneous Differentiation
In geology, igneous differentiation, or magmatic differentiation, is an umbrella term for the various processes by which magmas undergo bulk chemical change during the partial melting process, cooling, emplacement, or eruption. The sequence of (usually increasingly silicic) magmas produced by igneous differentiation is known as a magma series. Definitions Primary melts When a rock melts to form a liquid, the liquid is known as a ''primary melt''. Primary melts have not undergone any differentiation and represent the starting composition of a magma. In nature, primary melts are rarely seen. Some leucosomes of migmatites are examples of primary melts. Primary melts derived from the mantle are especially important and are known as ''primitive melts'' or primitive magmas. By finding the primitive magma composition of a magma series, it is possible to model the composition of the rock from which a melt was formed, which is important because we have little direct evidence of the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other Astronomical object, astronomical objects, the features or rock (geology), rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth science, Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the Relative dating, relative and Geochronology, absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Eart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquidus
The liquidus temperature, TL or Tliq, specifies the temperature above which a material is completely liquid, and the maximum temperature at which crystals can co-exist with the melt in thermodynamic equilibrium. It is mostly used for impure substances (mixtures) such as glasses, alloys and rocks. Above the liquidus temperature the material is homogeneous and liquid at equilibrium. Below the liquidus temperature, more and more crystals will form in the melt if one waits a sufficiently long time, depending on the material. Alternately, homogeneous glasses can be obtained through sufficiently fast cooling, i.e., through kinetic inhibition of the crystallization process. The crystal phase that crystallizes first on cooling a substance to its liquidus temperature is termed primary crystalline phase or primary phase. The composition range within which the primary phase remains constant is known as primary crystalline phase field. The liquidus temperature is important in the glass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rock Types
The following is a list of rock types recognized by geologists. There is no agreed number of specific types of rocks. Any unique combination of chemical composition, mineralogy, grain size, texture, or other distinguishing characteristics can describe a rock type. Additionally, different classification systems exist for each major type of rock. There are three major types of rock: igneous rock, metamorphic rock, and sedimentary rock. Igneous rocks * * * * * * ** – Basaltic lava with a crumpled appearance ** – Basaltic lava with a flowing, often ropy appearance * ** ** * * * * * ** * * * ** * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * – An ultramafic, ultrapotassic intrusive rock dominated by mafic phenocrysts in a feldspar groundmass * – A silica-undersaturated form of andesite * – An ultramafic rock, essentially a peridotite * – A silica-undersaturated granite with 90% pyroxene * – A diorite with >5% modal quartz * – An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crust (geology)
In geology, the crust is the outermost solid shell of a rocky planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. It is usually distinguished from the underlying mantle by its chemical makeup; however, in the case of icy satellites, it may be distinguished based on its phase (solid crust vs. liquid mantle). The crusts of Earth, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Io, the Moon and other planetary bodies formed via igneous processes and were later modified by erosion, impact cratering, volcanism, and sedimentation. Most terrestrial planets have fairly uniform crusts. Earth, however, has two distinct types: continental crust and oceanic crust. These two types have different chemical compositions and physical properties and were formed by different geological processes. Types of crust Planetary geologists divide crust into three categories based on how and when it formed. Primary crust / primordial crust This is a planet's "original" crust. It forms from solidification of a magma ocean. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felsic
In geology, felsic is a modifier describing igneous rocks that are relatively rich in elements that form feldspar and quartz.Marshak, Stephen, 2009, ''Essentials of Geology,'' W. W. Norton & Company, 3rd ed. It is contrasted with mafic rocks, which are relatively richer in magnesium and iron. Felsic refers to silicate minerals, magma, and rocks which are enriched in the lighter elements such as silicon, oxygen, aluminium, sodium, and potassium. Felsic magma or lava is higher in viscosity than mafic magma/lava. Felsic rocks are usually light in color and have specific gravities less than 3. The most common felsic rock is granite. Common felsic minerals include quartz, muscovite, orthoclase, and the sodium-rich plagioclase feldspars (albite-rich). Terminology In modern usage, the term ''acid rock'', although sometimes used as a synonym, normally now refers specifically to a high-silica-content (greater than 63% SiO2 by weight) volcanic rock, such as rhyolite. Older, broader ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solidus (chemistry)
In chemistry, materials science, and physics, the solidus is the locus of temperatures (a curve on a phase diagram) below which a given substance is completely solid (crystallized). The solidus temperature, TS or Tsol, specifies the temperature below which a material is completely solid, and the minimum temperature at which a melt can co-exist with crystals in thermodynamic equilibrium. The solidus is applied, among other materials, to metal alloys, ceramics, and natural rocks and minerals. The solidus quantifies the temperature at which melting of a substance ''begins'', but the substance is not necessarily melted ''completely'', i.e., the solidus is not necessarily a melting point. For this distinction, the solidus may be contrasted to the liquidus. The solidus is always less than or equal to the liquidus, but they need not coincide. If a gap exists between the solidus and liquidus it is called the freezing range, and within that gap, the substance consists of a mixture of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
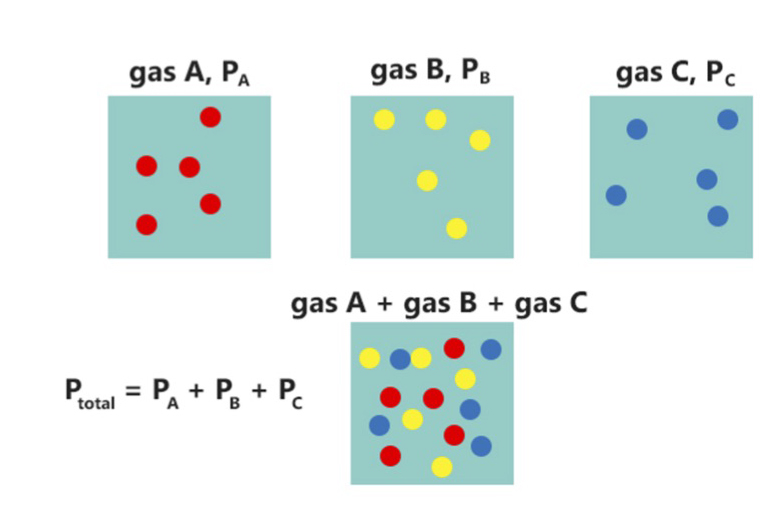
Partial Pressure
In a mixture of gases, each constituent gas has a partial pressure which is the notional pressure of that constituent gas as if it alone occupied the entire volume of the original mixture at the same temperature. The total pressure of an ideal gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture ( Dalton's Law). The partial pressure of a gas is a measure of thermodynamic activity of the gas's molecules. Gases dissolve, diffuse, and react according to their partial pressures but not according to their concentrations in gas mixtures or liquids. This general property of gases is also true in chemical reactions of gases in biology. For example, the necessary amount of oxygen for human respiration, and the amount that is toxic, is set by the partial pressure of oxygen alone. This is true across a very wide range of different concentrations of oxygen present in various inhaled breathing gases or dissolved in blood; consequently, mixture ratios, like that of breat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) feldspars and the ''alkali'' (potassium-sodium) feldspars. Feldspars make up about 60% of the Earth's crust, and 41% of the Earth's continental crust by weight. Feldspars crystalize from magma as both intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks and are also present in many types of metamorphic rock. Rock formed almost entirely of calcic plagioclase feldspar is known as anorthosite. Feldspars are also found in many types of sedimentary rocks. Compositions The feldspar group of minerals consists of tectosilicates, silicate minerals in which silicon ions are linked by shared oxygen ions to form a three-dimensional network. Compositions of major elements in common feldspars can be expressed in terms of three endmembers: * potassium feldspar (K- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers. Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or '' granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranites) contain almost no dark minerals. Granite is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyroxene
The pyroxenes (commonly abbreviated to ''Px'') are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula , where X represents calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron (Fe II) or magnesium (Mg) and more rarely zinc, manganese or lithium, and Y represents ions of smaller size, such as chromium (Cr), aluminium (Al), magnesium (Mg), cobalt (Co), manganese (Mn), scandium (Sc), titanium (Ti), vanadium (V) or even iron (Fe II) or (Fe III). Although aluminium substitutes extensively for silicon in silicates such as feldspars and amphiboles, the substitution occurs only to a limited extent in most pyroxenes. They share a common structure consisting of single chains of silica tetrahedra. Pyroxenes that crystallize in the monoclinic system are known as clinopyroxenes and those that crystallize in the orthorhombic system are known as orthopyroxenes. The name ''pyroxene'' is derived from the Ancient Greek words for 'f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enstatite
Enstatite is a mineral; the magnesium endmember of the pyroxene silicate mineral series enstatite (MgSiO3) – ferrosilite (FeSiO3). The magnesium rich members of the solid solution series are common rock-forming minerals found in igneous and metamorphic rocks. The intermediate composition, , has historically been known as hypersthene, although this name has been formally abandoned and replaced by orthopyroxene. When determined petrographically or chemically the composition is given as relative proportions of enstatite (En) and ferrosilite (Fs) (e.g., En80Fs20). Polymorphs and varieties Most natural crystals are orthorhombic ( space group P''bca'') although three polymorphs are known. The high temperature, low pressure polymorphs are protoenstatite and protoferrosilite (also orthorhombic, space group P''bcn'') while the low temperature forms, clinoenstatite and clinoferrosilite, are monoclinic (space group P2''1/c''). Weathered enstatite with a small amount of iron tak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers quickly on the surface. For this reason, olivine has been proposed as a good candidate for accelerated weathering to sequester carbon dioxide from the Earth's oceans and atmosphere, as part of climate change mitigation. Olivine also has many other historical uses, such as the gemstone peridot (or chrysolite), as well as industrial applications like metalworking processes. The ratio of magnesium to iron varies between the two endmembers of the solid solution series: forsterite (Mg-endmember: ) and fayalite (Fe-endmember: ). Compositions of olivine are commonly expressed as molar percentages of forsterite (Fo) and fayalite (Fa) (''e.g.'', Fo70Fa30). Forsterite's melting temperature is unusually high at atmospheric pressure, almost , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |