|
Išhtup-Išar
Ishtup-Ishar (Ištup-Išar) () was a king (Lugal) of the second Mariote kingdom. The king's name was traditionally read as Išhtup-šar, with šar being a common divine element in personal names attested in the region. However, the king's name is read as Ishtup-Ishar by Alfonso Archi, Ishar being an important justice deity worshiped in Mari and Ebla. In a letter written by the later Mariote king Enna-Dagan, Ishar is attested conquering and destroying the Eblaite cities of Lalanium and Emar Emar (, ), is an archaeological site at Tell Meskene in the Aleppo Governorate of northern Syria. It sits in the great bend of the mid-Euphrates, now on the shoreline of the man-made Lake Assad near the town of Maskanah. It has been the sourc .... See also * Eblaite-Mariote war Citations 25th-century BC monarchs 24th-century BC monarchs Kings of Mari {{MEast-royal-stub 3rd-millennium BC births 3rd-millennium BC deaths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Kings Of Mari
The city of Mari, Syria, Mari in modern Syria was ruled by several dynasties in the Bronze Age. The history of the city is divided into three kingdoms. First kingdom The ''Sumerian King List (SKL)'' records a dynasty of six kings from Mari enjoying hegemony between the dynasty of Adab (city), Adab and the dynasty of Kish (Sumer), Kish. The names of the Mariote kings were damaged on the early copies of the list, and those kings were correlated with historical kings that belonged to the second kingdom. However, an undamaged copy of the list that date to the Old Babylonian period was discovered in Tell Leilan, Shubat-Enlil, and the names bears no resemblance to any of the historically attested monarchs of the second kingdom, indicating that the compilers of the list had an older and probably a legendary dynasty in mind, that predate the second kingdom. Second kingdom The chronological order of the kings from the second kingdom era is highly uncertain; nevertheless, it is assumed that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
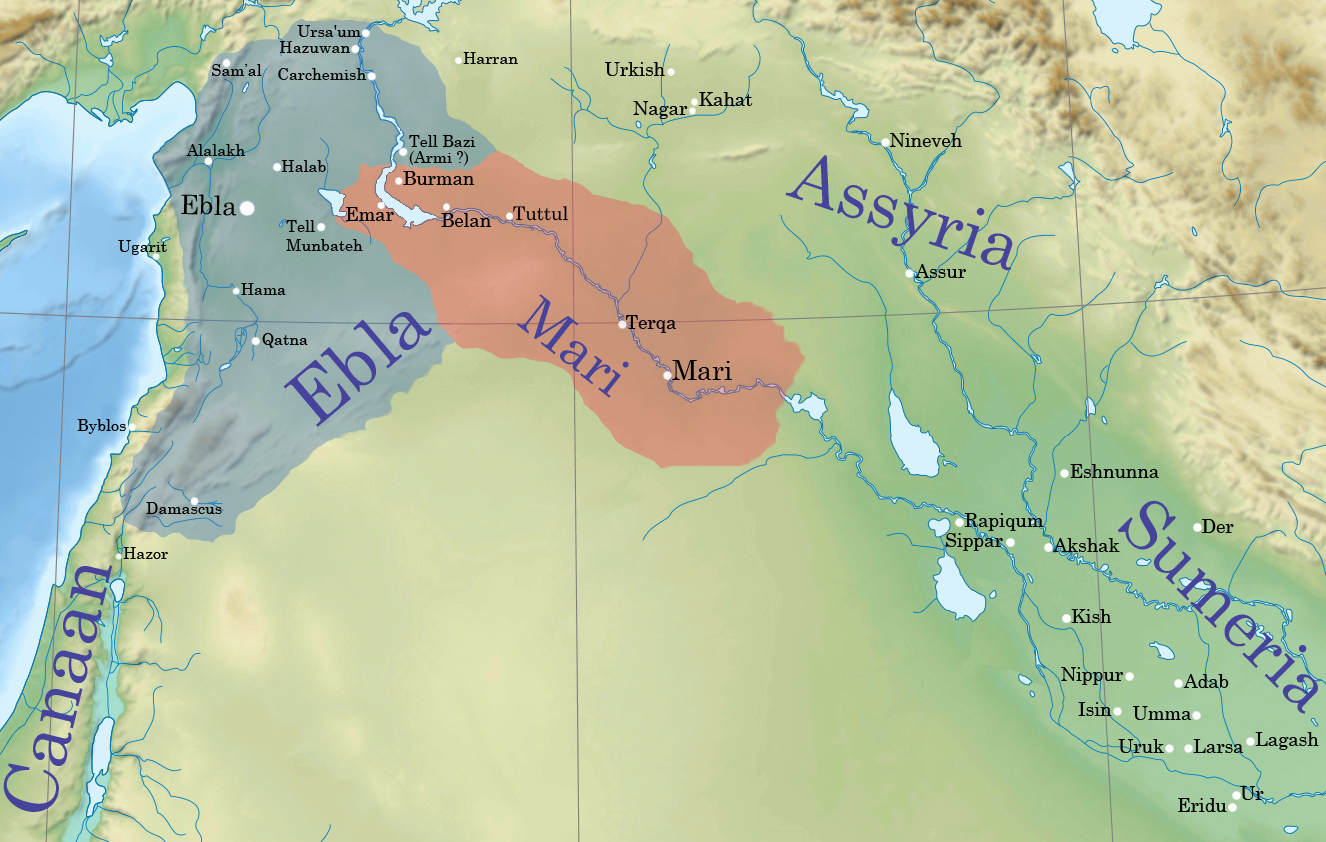
Mari, Syria
Mari (Cuneiform: , ''ma-riki'', modern Tell Hariri; ) was an ancient Semitic people, Semitic city-state in modern-day Syria. Its remains form a Tell (archaeology), tell 11 kilometers north-west of Abu Kamal on the Euphrates, Euphrates River western bank, some 120 kilometers southeast of Deir ez-Zor. It flourished as a trade center and hegemonic state between 2900 BC and 1759 BC. The city was built in the middle of the Euphrates trade routes between Sumer in the south and the Ebla, Eblaite kingdom and the Levant in the west. Mari was first abandoned in the middle of the 26th century BC but was rebuilt and became the capital of a hegemonic East Semitic languages, East Semitic state before 2500 BC. This second Mari engaged in a long war with its rival Ebla and is known for its strong affinity with Sumerian culture. It was destroyed in the 23rd century BC by the Akkadians, who allowed the city to be rebuilt and appointed a military governor (''Shakkanakku''). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saʿumu
Saʿumu (died 2400 BC) was a king (Lugal) of the second Mari, Syria#The second kingdom, Mariote kingdom who reigned c. 2416–2400 BC. Some scholars, such as Joseph Martin Pagan, Joseph Pagan, interpreted the king's name as derived from the root "ś-y-m", a cognate of the Akkadian language, Akkadian word "šâmu-m", meaning "to buy". In a letter written by the later Mariote king Enna-Dagan, Saʿumu is attested launching a major attack on the Eblaites. The king's campaigns recorded in the letter were concentrated in the middle Euphrates valley east of Emar, where he defeated the cities of Tibalat and Ilwani, leaving ruins in the mountainous area of Angai. Saʿumu continued his war defeating the cities of Ra'ak, Nirum, Ashaldu and Badul, leaving ruins in the borders of Nahal, Syria, Nahal's region. See also *Mari, Syria#Mari–Ebla war, Eblaite-Mariote war Notes Citations 25th-century BC monarchs Kings of Mari {{MEast-royal-stub 3rd-millennium BC births 3rd-mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iblul-Il
Iblul-Il (died 2380 BC) was the most energetic king (Lugal) of the second Mari, Syria#The second kingdom, Mariote kingdom, noted for his extensive campaigns in the middle Euphrates valley against the Ebla#Archive period, Eblaites, and in the upper Tigris region against various opponents, which asserted the Mariote supremacy in the Syrian north. Reign Sources Iblul-Il is attested in Mari, where statues bearing his name were excavated in 1952 from the city's temples. However, the deeds of the king are recorded in a letter sent to Ebla by Enna-Dagan, a successor of Iblul-Il. Campaigns Iblul-Il campaigned extensively against Ebla and its vassals and allies. The offensive was probably due to Ebla's increasing militaristic character, and was meant to block the trade route between Kish (Sumer), Kish, Tell Brak#Kingdom of Nagar, Nagar, and Ebla. Iblul-Il was a contemporary of Ebla's king Igrish-Halam, and is mentioned in the letter of Enna-Dagan campaigning in the middle Euphrates defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lugal
( Sumerian: ) is the Sumerian term for "king, ruler". Literally, the term means "big man." In Sumerian, ''lú'' " 𒇽" is "man" and ''gal'' " 𒃲" is "great", or "big." It was one of several Sumerian titles that a ruler of a city-state could bear (alongside '' en'' and '' ensi'', the exact difference being a subject of debate). The sign eventually became the predominant logograph for "King" in general. In the Sumerian language, is used to mean an owner (e.g. of a boat or a field) or a head (of a unit such as a family). As a cuneiform logograph (Sumerogram) LUGAL (Unicode: 𒈗, rendered in Neo Assyrian). Cuneiform The cuneiform sign LUGAL 𒈗 (Borger nr. 151, Unicode U+12217) serves as a determinative in cuneiform texts ( Sumerian, Akkadian and Hittite), indicating that the following word is the name of a king. In Akkadian orthography, it may also be a syllabogram ''šàr'', acrophonically based on the Akkadian for "king", ''šarrum''. Unicode also includes the cuneif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfonso Archi
Alphons (Latinized ''Alphonsus'', ''Adelphonsus'', or ''Adefonsus'') is a male given name recorded from the 8th century (Alfonso I of Asturias, r. 739–757) in the Christian successor states of the Visigothic Kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula. In the later medieval period it became a standard name in the Hispanic and Portuguese royal families. It is derived from a Gothic name, or a conflation of several Gothic names; from ''*Aþalfuns'', composed of the elements '' aþal'' "noble" and ''funs'' "eager, brave, ready", and perhaps influenced by names such as ''*Alafuns'', ''*Adefuns'' and ''* Hildefuns''. It is recorded as ''Adefonsus'' in the 9th and 10th century, and as ''Adelfonsus'', ''Adelphonsus'' in the 10th to 11th. The reduced form ''Alfonso'' is recorded in the late 9th century, and the Portuguese form ''Afonso'' from the early 11th and ''Anfós'' in Catalan from the 12th century until the 15th. Variants of the name include: '' Alonso'' (Spanish), ''Alfonso'' (Spanish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Išḫara
Išḫara was a goddess originally worshipped in Ebla and other nearby settlements in the north of modern Syria in the third millennium BCE. The origin of her name is disputed, and due to lack of evidence supporting Hurrian or Semitic etymologies it is sometimes assumed it might have originated in a linguistic substrate. In Ebla, she was considered the tutelary goddess of the royal family. An association between her and the city is preserved in a number of later sources from other sites as well. She was also associated with love, and in that role is attested further east in Mesopotamia as well. Multiple sources consider her the goddess of the institution of marriage, though she could be connected to erotic love as well, as evidenced by incantations. She was also linked to oaths and divination. She was associated with reptiles, especially mythical '' bašmu'' and ''ḫulmiẓẓu'', and later on with scorpions as well, though it is not certain how this connection initially devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebla
Ebla (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', , modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a Tell (archaeology), tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was an important center throughout the and in the first half of the Its discovery proved the Levant was a center of ancient, centralized civilization equal to Ancient Egypt, Egypt and Mesopotamia and ruled out the view that the latter two were the only important centers in the Ancient Near East, Near East during the Early Bronze Age. The first Eblaite kingdom has been described as the first recorded world power. Starting as a small settlement in the Early Bronze Age ( ), Ebla developed into a trading empire and later into an expansionist power that imposed its hegemony over much of northern and eastern Syria. Ebla was destroyed during the It was then rebuilt and was mentioned in the records of the Third Dynasty of Ur. The second Ebla w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emar
Emar (, ), is an archaeological site at Tell Meskene in the Aleppo Governorate of northern Syria. It sits in the great bend of the mid-Euphrates, now on the shoreline of the man-made Lake Assad near the town of Maskanah. It has been the source of many cuneiform tablets, making it rank with Ugarit, Mari and Ebla among the most important archaeological sites of Syria. In these texts, dating from the 14th century BC to the fall of Emar in 1187 BC, and in excavations in several campaigns since the 1970s, Emar emerges as an important Bronze Age trade center, occupying a liminal position between the power centers of Upper Mesopotamia and AnatoliaSyria. Unlike other cities, the tablets preserved at Emar, most of them in Akkadian and of the thirteenth century BC, are not royal or official, but record private transactions, judicial records, dealings in real estate, marriages, last wills, formal adoptions. In the house of a priest, a library contained literary and lexical texts in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
25th-century BC Monarchs
The 5th century is the time period from AD 401 (represented by the Roman numerals CDI) through AD 500 (D) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The 5th century is noted for being a period of migration and political instability throughout Eurasia. It saw the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, which came to a formal end in 476 AD. This empire had been ruled by a succession of weak emperors, with the real political might being increasingly concentrated among military leaders. Internal instability allowed a Visigoth army to reach and ransack Rome in 410. Some recovery took place during the following decades, but the Western Empire received another serious blow when a second foreign group, the Vandals, occupied Carthage, capital of an extremely important province in Africa. Attempts to retake the province were interrupted by the invasion of the Huns under Attila. After Attila's defeat, both Eastern and Western empires joined forces for a final assault on Vandal North Africa, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |