|
Isotone
Two nuclides are isotones if they have the same neutron number ''N'', but different proton number ''Z''. For example, boron-12 and carbon-13 nuclei both contain 7 neutrons, and so are isotones. Similarly, 36S, 37Cl, 38Ar, 39K, and 40Ca nuclei are all isotones of 20 because they all contain 20 neutrons. Despite its similarity to the Greek for "same stretching", the term was formed by the German physicist K. Guggenheimer by changing the "p" in "isotope" from "p" for "proton" to "n" for "neutron". The largest numbers of observationally stable nuclides exist for isotones 50 (five: 86Kr, 88Sr, 89Y, 90Zr, 92Mo – noting also the primordial radionuclide 87Rb) and 82 (six: 138Ba, 139La, 140Ce, 141Pr, 142Nd, 144Sm – noting also the primordial radionuclide 136Xe). Neutron numbers for which there are no stable isotones are 19, 21, 35, 39, 45, 61, 89, 115, 123, and 127 or more (though 21, 142, 143, 146, and perhaps 150 have primordial radionuclides). In contrast, the proton numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclide
Nuclides (or nucleides, from nucleus, also known as nuclear species) are a class of atoms characterized by their number of protons, ''Z'', their number of neutrons, ''N'', and their nuclear energy state. The word ''nuclide'' was coined by the American nuclear physicist Truman P. Kohman in 1947. Kohman defined ''nuclide'' as a "species of atom characterized by the constitution of its nucleus" containing a certain number of neutrons and protons. The term thus originally focused on the nucleus. Nuclide vs. isotope A nuclide is an atom with a specific number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus, for example carbon-13 with 6 protons and 7 neutrons. The term was coined deliberately is distinction from isotope in order to consider the nuclear properties independently of the chemical properties, though ''isotope' is still used for that purpose especially where ''nuclide'' might be unfamiliar as in nuclear technology and nuclear medicine. For nuclear propeties, the number of neutrons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isobar (nuclide)
Isobars are atoms (nuclides) of different chemical elements that have the same number of nucleons. Correspondingly, isobars differ in atomic number (or number of protons) but have the same mass number. An example of a series of isobars is 40S, 40Cl, 40Ar, 40K, and 40Ca. While the nuclei of these nuclides all contain 40 nucleons, they contain varying numbers of protons and neutrons. The term "isobars" (originally "isobares") for nuclides was suggested by British chemist Alfred Walter Stewart in 1918. It is derived . Mass The same mass number implies neither the same mass of nuclei, nor equal atomic masses of corresponding nuclides. From the Weizsäcker formula for the mass of a nucleus: : m(A,Z) = Z m_p + N m_n - a_ A + a_ A^ + a_ \frac + a_ \frac - \delta(A,Z) where mass number equals to the sum of atomic number and number of neutrons , and , , , , , are constants, one can see that the mass depends on and non-linearly, even for a constant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes And Half-life
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), but different nucleon numbers (mass numbers) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have similar chemical properties, they have different atomic masses and physical properties. The term isotope is derived from the Greek roots isos (wikt:ἴσος, ἴσος "equal") and topos (wikt:τόπος, τόπος "place"), meaning "the same place"; thus, the meaning behind the name is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. It was coined by Scottish doctor and writer Margaret Todd (doctor), Margaret Todd in a 1913 suggestion to the British chemist Frederick Soddy, who popularized the term. The number of protons within the atomic nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Number
The mass number (symbol ''A'', from the German word: ''Atomgewicht'', "atomic weight"), also called atomic mass number or nucleon number, is the total number of protons and neutrons (together known as nucleons) in an atomic nucleus. It is approximately equal to the ''atomic'' (also known as ''isotopic'') mass of the atom expressed in daltons. Since protons and neutrons are both baryons, the mass number ''A'' is identical with the baryon number ''B'' of the nucleus (and also of the whole atom or ion). The mass number is different for each isotope of a given chemical element, and the difference between the mass number and the atomic number ''Z'' gives the number of neutrons (''N'') in the nucleus: . The mass number is written either after the element name or as a superscript to the left of an element's symbol. For example, the most common isotope of carbon is carbon-12, or , which has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. The full isotope symbol would also have the atomic number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protons
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' ( elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an electron (the proton-to-electron mass ratio). Protons and neutrons, each with a mass of approximately one dalton, are jointly referred to as '' nucleons'' (particles present in atomic nuclei). One or more protons are present in the nucleus of every atom. They provide the attractive electrostatic central force which binds the atomic electrons. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as the atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z''). Since each element is identified by the number of protons in its nucleus, each element has its own atomic number, which determines the number of atomic electrons and consequently the chemical characteristics of the element. The word ''proton'' is Greek for "first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotope
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), but different nucleon numbers (mass numbers) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have similar chemical properties, they have different atomic masses and physical properties. The term isotope is derived from the Greek roots isos (wikt:ἴσος, ἴσος "equal") and topos (wikt:τόπος, τόπος "place"), meaning "the same place"; thus, the meaning behind the name is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. It was coined by Scottish doctor and writer Margaret Todd (doctor), Margaret Todd in a 1913 suggestion to the British chemist Frederick Soddy, who popularized the term. The number of protons within the atomic nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mononuclidic Element
A mononuclidic element or monotopic element is one of the 21 chemical elements that is found naturally on Earth essentially as a single nuclide (which may, or may not, be a stable nuclide). This single nuclide will have a characteristic atomic mass. Thus, the element's natural isotopic abundance is dominated by one isotope that is either stable or very long-lived. There are 19 elements in the first category (which are both monoisotopic and mononuclidic), and 2 ( bismuth and protactinium) in the second category (mononuclidic but not monoisotopic, since they have zero, not one, stable nuclides). A list of the 21 mononuclidic elements is given at the end of this article. Of the 26 '' monoisotopic elements'' that, by definition, have only one stable isotope, seven are ''not'' considered mononuclidic, due to the presence of a significant fraction of a very long-lived ( primordial) radioisotope. These elements are vanadium, rubidium, indium, lanthanum, europium, lutetium, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoisotopic Element
A monoisotopic element is an element which has only a single stable isotope (nuclide). There are 26 such elements, as listed. Stability is experimentally defined for chemical elements, as there are a number of stable nuclides with atomic numbers over ~40 which are theoretically unstable, but apparently have half-lives so long that they have not been observed either directly or indirectly (from measurement of products) to decay. Monoisotopic elements are characterized, except in one case, by odd numbers of protons (odd ''Z''), and even numbers of neutrons. Because of the energy gain from nuclear pairing, the odd number of protons imparts instability to isotopes of an odd ''Z'', which in heavier elements requires a completely paired set of neutrons to offset this tendency into stability. (The five stable nuclides with odd ''Z'' and odd neutron numbers are hydrogen-2, lithium-6, boron-10, nitrogen-14, and tantalum-180m1.) The single monoisotopic exception to the odd ''Z'' rule is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stable Nuclide
Stable nuclides are isotopes of a chemical element whose nucleons are in a configuration that does not permit them the surplus energy required to produce a radioactive emission. The nuclei of such isotopes are not radioactive and unlike radionuclides do not spontaneously undergo radioactive decay. When these nuclides are referred to in relation to specific elements they are usually called that element's stable isotopes. The 80 elements with one or more stable isotopes comprise a total of 251 nuclides that have not been shown to decay using current equipment. Of these 80 elements, 26 have only one stable isotope and are called monoisotopic. The other 56 have more than one stable isotope. Tin has ten stable isotopes, the largest number of any element. Definition of stability, and naturally occurring nuclides Most naturally occurring nuclides are stable (about 251; see list at the end of this article), and about 35 more (total of 286) are known to be radioactive with long eno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Shell Model
In nuclear physics, atomic physics, and nuclear chemistry, the nuclear shell model utilizes the Pauli exclusion principle to model the structure of atomic nuclei in terms of energy levels. The first shell model was proposed by Dmitri Ivanenko (together with E. Gapon) in 1932. The model was developed in 1949 following independent work by several physicists, most notably Maria Goeppert Mayer and J. Hans D. Jensen, who received the 1963 Nobel Prize in Physics for their contributions to this model, and Eugene Wigner, who received the Nobel Prize alongside them for his earlier groundlaying work on the atomic nuclei. The nuclear shell model is partly analogous to the atomic shell model, which describes the arrangement of electrons in an atom, in that a filled shell results in better stability. When adding nucleons (protons and neutrons) to a nucleus, there are certain points where the binding energy of the next nucleon is significantly less than the last one. This observation th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleon
In physics and chemistry, a nucleon is either a proton or a neutron, considered in its role as a component of an atomic nucleus. The number of nucleons in a nucleus defines the atom's mass number. Until the 1960s, nucleons were thought to be elementary particles, not made up of smaller parts. Now they are understood as composite particles, made of three quarks bound together by the strong interaction. The interaction between two or more nucleons is called internucleon interaction or nuclear force, which is also ultimately caused by the strong interaction. (Before the discovery of quarks, the term "strong interaction" referred to just internucleon interactions.) Nucleons sit at the boundary where particle physics and nuclear physics overlap. Particle physics, particularly quantum chromodynamics, provides the fundamental equations that describe the properties of quarks and of the strong interaction. These equations describe quantitatively how quarks can bind together into protons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
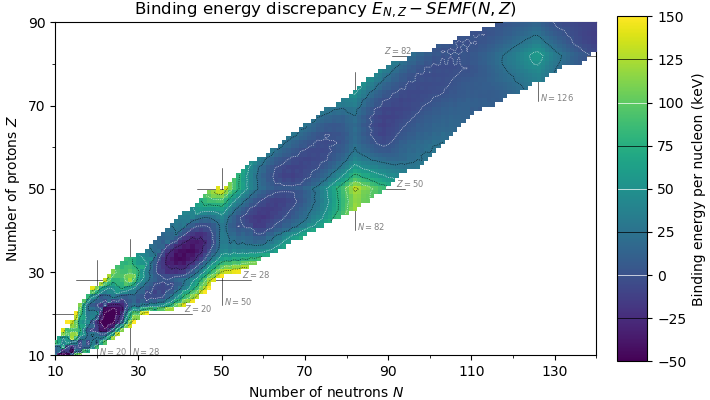
Magic Number (physics)
In nuclear physics, a magic number is a number of nucleons (either protons or neutrons, separately) such that they are arranged into complete shells within the atomic nucleus. As a result, atomic nuclei with a "magic" number of protons or neutrons are much more stable than other nuclei. The seven most widely recognized magic numbers as of 2019 are 2, 8, 20, 28, 50, 82, and 126. For protons, this corresponds to the elements helium, oxygen, calcium, nickel, tin, lead, and the hypothetical unbihexium, although 126 is so far only known to be a magic number for neutrons. Atomic nuclei consisting of such a magic number of nucleons have a higher average binding energy per nucleon than one would expect based upon predictions such as the semi-empirical mass formula and are hence more stable against nuclear decay. The unusual stability of isotopes having magic numbers means that transuranium elements could theoretically be created with extremely large nuclei and yet not be subject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |