|
Isolated Brain
An isolated brain is a brain kept alive in vitro, either by perfusion or by a blood substitute, often an oxygenated solution of various salts, or by submerging the brain in oxygenated artificial cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). It is the biological counterpart of brain in a vat. A related concept, attaching the brain or head to the circulatory system of another organism, is called a brain transplant or a head transplant. An isolated brain, however, is more typically attached to an artificial perfusion device rather than a biological body. The brains of many different organisms have been kept alive in vitro for hours, or in some cases days. The central nervous system of invertebrate animals is often easily maintained as they need less oxygen and to a larger extent get their oxygen from CSF; for this reason their brains are more easily maintained without perfusion. Mammalian brains, on the other hand, have a much lesser degree of survival without perfusion and an artificial blood perfu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Lobes
The lobes of the brain are the four major identifiable regions of the human cerebral cortex, and they comprise the surface of each hemisphere of the cerebrum. The two hemispheres are roughly symmetrical in structure, and are connected by the corpus callosum. Some sources include the insula and limbic lobe but the limbic lobe incorporates parts of the other lobes. The lobes are large areas that are anatomically distinguishable, and are also functionally distinct. Each lobe of the brain has numerous ridges, or gyri, and furrows, sulci that constitute further subzones of the cortex. The expression "lobes of the brain" usually refers only to those of the cerebrum, not to the distinct areas of the cerebellum. Frontal lobe The frontal lobe is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere and positioned in front of the parietal lobe and above and in front of the temporal lobe. It is separated from the parietal lobe by a space between tissues called the central sulcus, and from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles-Édouard Brown-Séquard
Charles-Édouard Brown-Séquard FRS (8 April 1817 – 2 April 1894) was a Mauritian physiologist and neurologist who, in 1850, became the first to describe what is now called Brown-Séquard syndrome. Early life Brown-Séquard was born at Port Louis, Mauritius, to an American father and a French mother. He attended the Royal College in Mauritius, and graduated in medicine at Paris in 1846. He then returned to Mauritius with the intention of practising there, but in 1852 he went to the United States. There he was appointed to the faculty of the Medical College of Virginia where he conducted experiments in the basement of the Egyptian Building. He was elected as a member of the American Philosophical Society in 1854. Later life He returned to Paris, and in 1859 he migrated to London, becoming physician to the National Hospital for the Paralysed and Epileptic. There he stayed for about five years, expounding his views on the pathology of the nervous system in numerous lecture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thought Experiment
A thought experiment is an imaginary scenario that is meant to elucidate or test an argument or theory. It is often an experiment that would be hard, impossible, or unethical to actually perform. It can also be an abstract hypothetical that is meant to test our intuitions about morality or other fundamental philosophical questions. History The ancient Greek , "was the most ancient pattern of mathematical proof", and existed before Euclidean geometry, Euclidean mathematics, where the emphasis was on the conceptual, rather than on the experimental part of a thought experiment. Johann Witt-Hansen established that Hans Christian Ørsted was the first to use the equivalent German term . Ørsted was also the first to use the equivalent term in 1820. By 1883, Ernst Mach used in a different sense, to denote exclusively the conduct of a experiment that would be subsequently performed as a by his students. Physical and mental experimentation could then be contrasted: Mach asked hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophy
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational and critical inquiry that reflects on its methods and assumptions. Historically, many of the individual sciences, such as physics and psychology, formed part of philosophy. However, they are considered separate academic disciplines in the modern sense of the term. Influential traditions in the history of philosophy include Western philosophy, Western, Islamic philosophy, Arabic–Persian, Indian philosophy, Indian, and Chinese philosophy. Western philosophy originated in Ancient Greece and covers a wide area of philosophical subfields. A central topic in Arabic–Persian philosophy is the relation between reason and revelation. Indian philosophy combines the Spirituality, spiritual problem of how to reach Enlightenment in Buddhism, enlighten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in a brachial artery, where it is most commonly measured. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure (maximum pressure during one Cardiac cycle, heartbeat) over diastolic pressure (minimum pressure between two heartbeats) in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in Millimetre of mercury, millimetres of mercury (mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure, or in Pascal (unit), kilopascals (kPa). The difference between the systolic and diastolic pressures is known as pulse pressure, while the average pressure during a cardiac cycle is known as mean arterial pressure. Blood pressure is one of the vital signs—together with respiratory rate, heart rate, Oxygen saturation (me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemodynamics
Hemodynamics or haemodynamics are the dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. The hemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment. Hemodynamics explains the physical laws that govern the flow of blood in the blood vessels. Blood flow ensures the transportation of nutrients, hormones, metabolic waste products, oxygen, and carbon dioxide throughout the body to maintain cell-level metabolism, the regulation of the pH, osmotic pressure and temperature of the whole body, and the protection from microbial and mechanical harm. Blood is a non-Newtonian fluid, and is most efficiently studied using rheology rather than hydrodynamics. Because blood vessels are not rigid tubes, classic hydrodynamics and fluids mechanics based on the use of classical viscometers are not capable of explaining haemodynamics. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Texas Southwestern Medical Center
The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center (UT Southwestern or UTSW) is a public academic health science center in Dallas, Texas. With approximately 23,000 employees, more than 3,000 full-time faculty, and nearly 4 million outpatient visits per year, UT Southwestern is the largest medical school in the University of Texas System and the State of Texas. UT Southwestern's operating budget in 2021 was more than , and is the largest medical institution in the Dallas–Fort Worth Metroplex (and therefore North Texas region), annually training about 3,800 medical, graduate, and health professions students, residents, and postdoctoral fellows. UT Southwestern Research Programs amounted to in 2022. UT Southwestern's faculty also provide services at Scottish Rite for Children, VA North Texas Health Care System, and other affiliated hospitals and community clinics in the North Texas region. Faculty and residents provide care in more than 80 specialties to more than 100,000 ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and plants, as opposed to a tissue extract or dead organism. Examples of investigations ''in vivo'' include: the pathogenesis of disease by comparing the effects of bacterial infection with the effects of purified bacterial toxins; the development of non-antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and new drugs generally; and new surgical procedures. Consequently, animal testing and clinical trials are major elements of ''in vivo'' research. ''In vivo'' testing is often employed over ''in vitro'' because it is better suited for observing the overall effects of an experiment on a living subject. In drug discovery, for example, verification of efficacy ''in vivo'' is crucial, because ''in vitro'' assays can sometimes yield misleading results with drug c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodolfo Llinás
Rodolfo Llinás Riascos (born 16 December 1934) is a Colombian neuroscientist. He is currently the Thomas and Suzanne Murphy Professor of Neuroscience and Chairman Emeritus of the Department of Physiology & Neuroscience at the NYU School of Medicine. Llinás has published over 800 scientific articles. Early life Llinás was born in Bogotá, Colombia. He is the son of Jorge Enrique Llinás (a surgeon of Spanish descent, whose family arrived in Colombia at the end of the 19th century) and Bertha Riascos. He was motivated to study the brain by watching his grandfather Pablo Llinás Olarte working as a neuropsychiatrist. Llinás describes himself as a logical positivist. Education and early research Llinás went to the Gimnasio Moderno school in Bogotá and graduated as a medical doctor from the Pontifical Xavierian University in 1959. During his medical studies he had the opportunity to travel to Europe and there he met several researchers in Spain, France and finally Switzerl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert J
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' () "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown, godlike" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin.Reaney & Wilson, 1997. ''Dictionary of English Surnames''. Oxford University Press. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe, the name entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
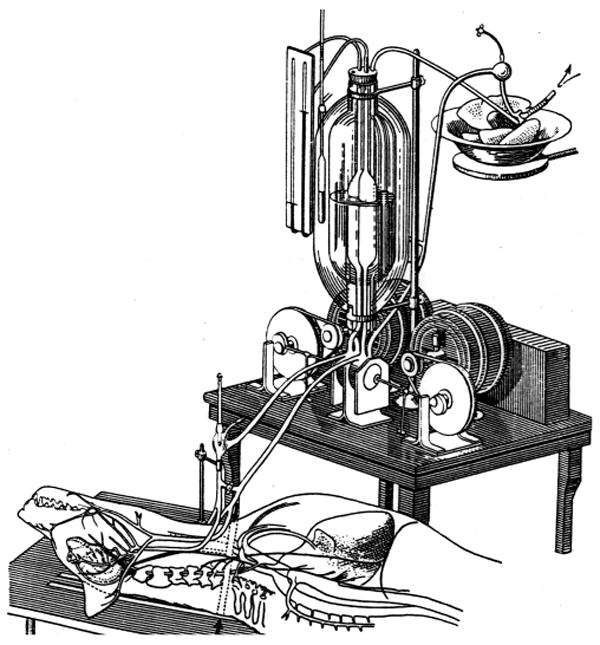
Experiments In The Revival Of Organisms
''Experiments in the Revival of Organisms'' () is a 1940 documentary film directed by that purports to document Soviet research into the resuscitation of clinically dead organisms. The English version of the film begins with British scientist J. B. S. Haldane giving an introduction. The operations in the film, as well as the design of the heart-lung machine demonstrated in it, the autojektor, were done by Sergei Brukhonenko, whose work is said to have led to the first operations on heart valves. While the experiments shown are generally considered to have taken place, the legitimacy of the film itself is controversial. Synopsis The film depicts and discusses a series of medical experiments. The English version of the film begins with British scientist J. B. S. Haldane appearing and discussing how he has personally seen the procedures carried out in the film at an all-Russian physiological congress. The Russian version lacks this explanation. The experiments start with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergey Bryukhonenko
Sergei Sergeevich Brukhonenko (; 30 April 1890 – 20 April 1960) was a Soviet Union, Soviet physician, biomedical scientist and technologist during the Stalinism, Stalinist era. Brukhonenko's research was vital to the development of open-heart procedures in Russia. He was one of the leaders of the Research Institute of Experimental Surgery, where Professor Alexander Alexandrovich Vishnevsky, Alexander Vishnevsky performed the first Soviet open-heart operation in 1957. Brukhonenko is primarily remembered for his development of the autojektor, one of the first Cardiopulmonary bypass, heart and lung machines. The device was used to mixed results in a series of experiments with canines during the year 1939, which can be seen in the film ''Experiments in the Revival of Organisms''. While there is some speculation today that the film is a re-staging of the procedures, the experiments themselves were well documented, and resulted in Brukhonenko being posthumously awarded the prestigiou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |