|
Isogram
A heterogram (from ''hetero-'', meaning 'different', + ''-gram'', meaning 'written') is a word, phrase, or sentence in which no Letter (alphabet), letter of the alphabet occurs more than once. The terms isogram and nonpattern word have also been used to mean the same thing. It is not clear who coined or popularized the term "heterogram". The concept appears in Dmitri Borgmann's 1965 book ''Language on Vacation: An Olio of Orthographical Oddities'' but he uses the term ''isogram''. In a 1985 article, Borgmann claims to have "launched" the term ''isogram'' then. He also suggests an alternative term, asogram, to avoid confusion with lines of constant value such as contour lines, but uses ''isogram'' in the article itself. ''Isogram'' has also been used to mean a string where each letter present is used the same number of times. Multiple terms have been used to describe words where each letter used appears a certain number of times. For example, a word where every featured letter app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letter (alphabet)
In a writing system, a letter is a grapheme that generally corresponds to a phoneme—the smallest functional unit of speech—though there is rarely total one-to-one correspondence between the two. An alphabet is a writing system that uses letters. Definition and usage A letter is a type of grapheme, the smallest functional unit within a writing system. Letters are graphemes that broadly correspond to phonemes, the smallest functional units of sound in speech. Similarly to how phonemes are combined to form spoken words, letters may be combined to form written words. A single phoneme may also be represented by multiple letters in sequence, collectively called a ''multigraph (orthography), multigraph''. Multigraphs include ''digraphs'' of two letters (e.g. English ''ch'', ''sh'', ''th''), and ''trigraphs'' of three letters (e.g. English ''tch''). The same letterform may be used in different alphabets while representing different phonemic categories. The Latin H, Greek eta , an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dmitri Borgmann
Dmitri Alfred Borgmann (October 22, 1927 – December 7, 1985) was a German-American author best known for his work in recreational linguistics. Early life Borgmann was born on October 22, 1927, in Berlin, Germany, to Hans and Lisa Borgmann. Fearing that the Nazi government would discover Lisa's Jewish ancestry, the family fled to the United States in 1936, and settled in Chicago. Borgmann graduated from the University of Chicago in 1946 and found work as an actuary. In 1964 he quit his job to focus on his writing. In 1971, he started his own research and manuscript writing business, INTELLEX, which employed up to 15 writers at a time to ghost-write and edit short stories, academic books, and TV and movie scripts. Borgmann eventually relocated the company and his family to Dayton, Washington. Writing career Borgmann first attracted media attention for his skill with words in 1958, when over the course of eight weeks he defeated 22 challengers in a row on WGN-TV's ''It's In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contour Line
A contour line (also isoline, isopleth, isoquant or isarithm) of a Function of several real variables, function of two variables is a curve along which the function has a constant value, so that the curve joins points of equal value. It is a cross-section (geometry)#Definition, plane section of the graph of a function of two variables, three-dimensional graph of the function f(x,y) parallel to the (x,y)-plane. More generally, a contour line for a function of two variables is a curve connecting points where the function has the same particular value. In cartography, a contour line (often just called a "contour") joins points of equal elevation (height) above a given level, such as mean sea level. A contour map is a map illustrated with contour lines, for example a topographic map, which thus shows valleys and hills, and the steepness or gentleness of slopes. The contour interval of a contour map is the difference in elevation between successive contour lines. The gradient of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangram
A pangram or holoalphabetic sentence is a sentence using every letter of a given alphabet at least once. Pangrams have been used to display typefaces, test equipment, and develop skills in handwriting, calligraphy, and typing. Origins The best-known English pangram is "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog". It has been used since at least the late 19th century and was used by Western Union to test Telex/ TWX data communication equipment for accuracy and reliability. Pangrams like this are now used by a number of computer programs to display computer typefaces. Short pangrams Short pangrams in English are more difficult to devise and tend to use uncommon words and unnatural sentences. Longer pangrams afford more opportunity for humor, cleverness, or thoughtfulness. The following are examples of pangrams that are shorter than "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog" (which has 35 letters) and use standard written English without abbreviations or proper nouns: *"Quick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
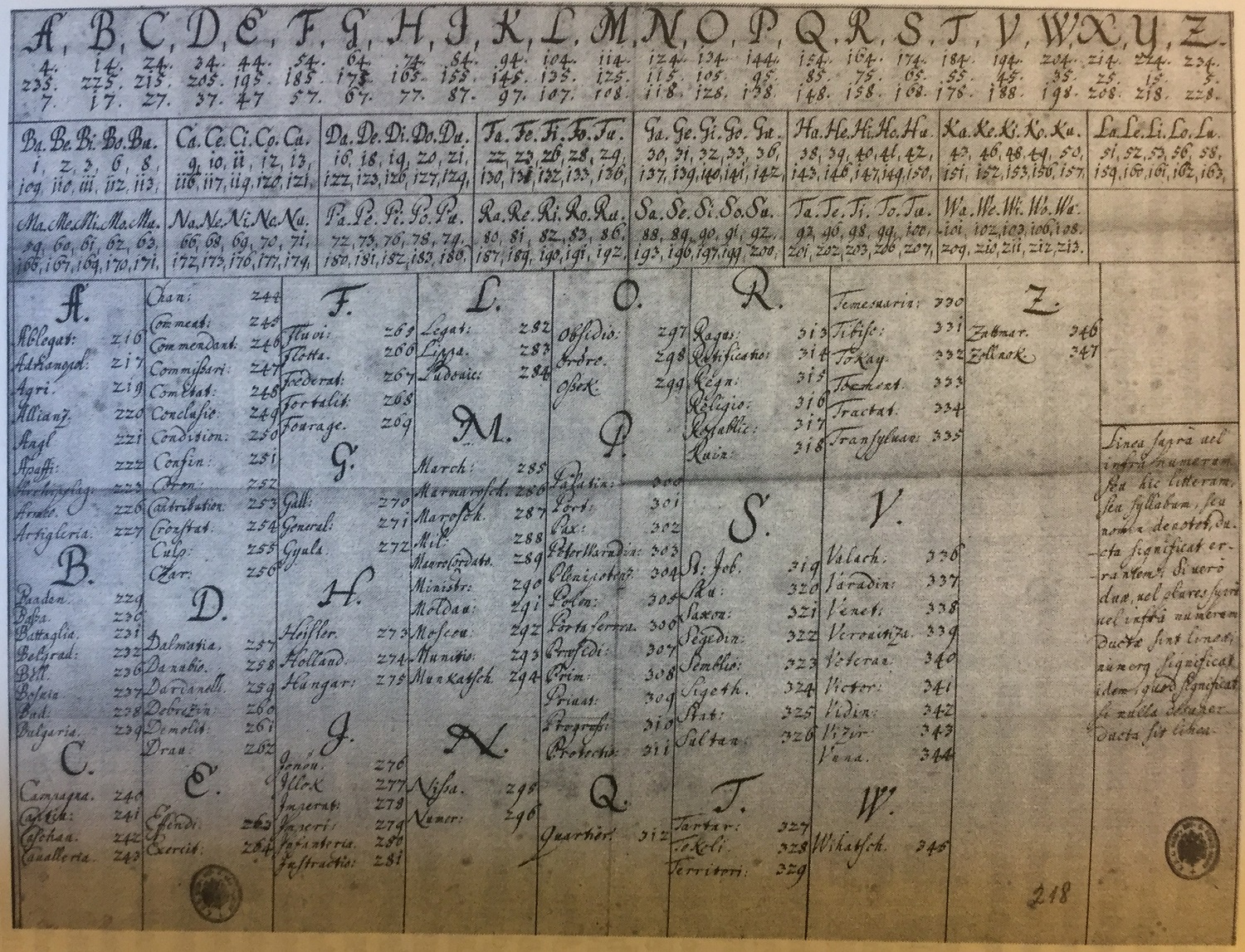
Substitution Cipher
In cryptography, a substitution cipher is a method of encrypting in which units of plaintext are replaced with the ciphertext, in a defined manner, with the help of a key; the "units" may be single letters (the most common), pairs of letters, triplets of letters, mixtures of the above, and so forth. The receiver deciphers the text by performing the inverse substitution process to extract the original message. Substitution ciphers can be compared with transposition ciphers. In a transposition cipher, the units of the plaintext are rearranged in a different and usually quite complex order, but the units themselves are left unchanged. By contrast, in a substitution cipher, the units of the plaintext are retained in the same sequence in the ciphertext, but the units themselves are altered. There are a number of different types of substitution cipher. If the cipher operates on single letters, it is termed a simple substitution cipher; a cipher that operates on larger groups of lett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatoglyphics
Dermatoglyphics (from Ancient Greek ''derma'', "skin", and ''glyph'', "carving") is the scientific study of fingerprints, lines, mounts and shapes of hands, as distinct from the superficially similar pseudoscience of palmistry. Dermatoglyphics also refers to the making of naturally occurring ridges on certain body parts, namely palms, fingers, soles, and toes. These are areas where hair usually does not grow, and these ridges allow for increased leverage when picking up objects or walking barefoot. In a 2009 report, the scientific basis underlying dermatoglyphics was questioned by the National Academy of Sciences, for the discipline's reliance on subjective comparisons instead of conclusions drawn from the scientific method. History 1823 marks the beginning of the scientific study of Dermis#Dermal papillae, papillary ridges of the hands and feet, with the work of Jan Evangelista Purkyně. By 1858, Sir William Herschel, 2nd Baronet, while in India, became the first European to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thumbscrew (other) , a nut with two large metal wings on, intended to be tightened and loosened by hand
{{disambig ...
Thumbscrew can mean: *Thumbscrew (torture), a screwed device formerly used for torture *Thumbscrew (fastener), a type of screw with a tall head and ridged or knurled sides, or a flat vertical head, intended to be tightened and loosened by hand See also *Computer case screws *Wingnut (hardware) A wingnut, wing nut or butterfly nut is a type of nut with two large metal "wings", one on each side, so it can be easily tightened and loosened by hand without tools. A similar fastener with a male thread is known as a wing screw or a wing bol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moral Sense Theory
Moral sense theory (also known as moral sentimentalism) is a theory in moral epistemology and meta-ethics concerning the discovery of moral truths. Moral sense theory typically holds that distinctions between morality and immorality are discovered by emotional responses to experience. Some take it to be primarily a view about the nature of moral facts or moral beliefs (a primarily metaphysical view)—this form of the view more often goes by the name "sentimentalism". Others take the view to be primarily about the nature of justifying moral beliefs (a primarily epistemological view)—this form of the view more often goes by the name "moral sense theory". However, some theorists take the view to be one which claims that both moral facts and how one comes to be justified in believing them are necessarily bound up with human emotions. Popular historical advocates of some version of the moral sense theory or sentimentalism include the 3rd Earl of Shaftesbury (1671–1713), Francis H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fjord
In physical geography, a fjord (also spelled fiord in New Zealand English; ) is a long, narrow sea inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created by a glacier. Fjords exist on the coasts of Antarctica, the Arctic, and surrounding landmasses of the northern and southern hemispheres. Norway's coastline is estimated to be long with its nearly 1,200 fjords, but only long excluding the fjords. Formation A true fjord is formed when a glacier cuts a U-shaped valley by ice segregation and abrasion of the surrounding bedrock. According to the standard model, glaciers formed in pre-glacial valleys with a gently sloping valley floor. The work of the glacier then left an overdeepened U-shaped valley that ends abruptly at a valley or trough end. Such valleys are fjords when flooded by the ocean. Thresholds above sea level create freshwater lakes. Glacial melting is accompanied by the rebounding of Earth's crust as the ice load and eroded sediment is removed (also called isostasy or gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alton, Illinois
Alton ( ) is a city on the Mississippi River in Madison County, Illinois, United States, about north of St. Louis, Missouri. The population was 25,676 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. It is a part of the River Bend (Illinois), River Bend area in the Metro-East region of the Greater St. Louis metropolitan area. It is well known for its limestone bluffs along the river north of the city. It's the former location of an historical state penitentiary, and played a significant role preceding and during the American Civil War. It was the site of the last Abraham Lincoln and Stephen Douglas debate in October 1858. The former state penitentiary in Alton was used during the Civil War to hold up to 12,000 Confederate prisoners of war. History Although Alton once was growing faster than the nearby city of St. Louis, a coalition of St. Louis businessmen planned to build a competing town to stop Alton's expansion and bring business to St. Louis. The resulting town was Grafton, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Alphabet
The modern German alphabet consists of the twenty-six letters of the ISO basic Latin alphabet: German uses letter-diacritic combinations (Ä, Ä/ä, Ö, Ö/ö, Ü, Ü/ü) using the Umlaut (diacritic), umlaut and one ligature (ß, ẞ/ß (called ''eszett'' (sz) or ''scharfes S'', sharp s)), but they do not constitute distinct letters in the alphabet. Before 1940 German employed Fraktur, a blackletter typeface (see also Antiqua–Fraktur dispute), and Kurrent, various cursives that include the 20-century Sütterlin. Grundschrift describes several current handwritting systems. Key characteristics Umlaut diacritic usage Although the diacritic letters represent distinct sounds in German phonology, they are almost universally not considered to be part of the alphabet. Almost all German speakers consider the alphabet to have the 26 cardinal letters above and will name only those when asked to say the alphabet. The diacritic letters ''ä, ö'' and ''ü'' are used to indicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |