|
Iptables
iptables is a user-space utility program that allows a system administrator to configure the IP packet filter rules of the Linux kernel firewall, implemented as different Netfilter modules. The filters are organized in a set of tables, which contain chains of rules for how to treat network traffic packets. Different kernel modules and programs are currently used for different protocols; ''iptables'' applies to IPv4, ''ip6tables'' to IPv6, ''arptables'' to ARP, and ' to Ethernet frames. iptables requires elevated privileges to operate and must be executed by user root, otherwise it fails to function. On most Linux systems, iptables is installed as and documented in its man pages, which can be opened using man iptables when installed. It may also be found in /sbin/iptables, but since iptables is more like a service rather than an "essential binary", the preferred location remains . The term ''iptables'' is also commonly used to inclusively refer to the kernel-level compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nftables
nftables is a subsystem of the Linux kernel providing filtering and classification of network packets/datagrams/frames. It has been available since Linux kernel 3.13 released on 19 January 2014. nftables replaces the legacy iptables component of Netfilter. Among the advantages of nftables over iptables is less code duplication and easier extension to new protocols. Among the disadvantages of nftables is that Deep_packet_inspection, DPI that was provided by "iptables string match" like Server_Name_Indication, SNI filtering is not supported. nftables is configured via the user-space utility ''nft'', while legacy tools are configured via the utilities ''iptables'', ''ip6tables'', ''arptables'' and ''ebtables'' frameworks. nftables utilizes the building blocks of the Netfilter infrastructure, such as the existing hooks into the networking stack, connection tracking system, userspace queueing component, and logging subsystem. nft Command-line syntax A command to drop any packets wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ipchains
Linux IP Firewalling Chains, normally called ipchains, is free software to control the packet filter or firewall capabilities in the 2.2 series of Linux kernels. It superseded ipfirewall (managed by ipfwadm command), but was replaced by iptables in the 2.4 series. Unlike iptables, ipchains is stateless. History It is a rewrite of Linux's previous IPv4 firewall, ipfirewall. This newer ipchains was required to manage the packet filter in Linux kernels starting with version 2.1.102 (which was a 2.2 development release). Patches are also available to add ipchains to 2.0 and earlier 2.1 series kernels. Improvements include larger maxima for packet counting, filtering for fragmented packets and a wider range of protocols, and the ability to match packets based on the inverse of a rule. The ipchains suite also included some shell scripts for easier maintenance and to emulate the behavior of the old ipfwadm command. The ipchains software was superseded by the iptables system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FireHOL
FireHOL is a shell script designed as a wrapper for iptables written to ease the customization of the Linux kernel's firewall netfilter. FireHOL is free software and open-source, distributed under the terms of the GNU General Public License. FireHOL does not have graphical user interface, but is configured through an easy to understand plain text In computing, plain text is a loose term for data (e.g. file contents) that represent only characters of readable material but not its graphical representation nor other objects ( floating-point numbers, images, etc.). It may also include a lim ... configuration file. FireHOL first parses the configuration file and then sets the appropriate iptables rules to achieve the expected firewall behavior. It is a large, complex BASH script file, depending on the iptables console tools rather than communicating with the kernel directly. Any Linux system with iptables, BASH, and the appropriate tools can run it. Its main drawback is slower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rusty Russell
Rusty Russell is an Australian free software programmer and advocate, known for his work on the Linux kernel's networking subsystem and the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard. Software development Russell wrote the packet filtering systems ipchains and netfilter/iptables in the Linux operating system kernel. Linus Torvalds referred to him as one of his "top deputies" in 2003. In 2002, Russell announced the creation of the Trivial Patch Monkey, an email address for kernel hackers to submit trivial patches such as spelling errors, one-liners, documentation tweaks and other minor amendments to the code base. Adrian Bunk took over the role in 2005. In 2006 Russell started work as the major developer of the "lguest" virtualisation system in the Linux Kernel. In October 2009, he was officially given a SAMBA Team T-shirt welcoming him to the Samba Team. In 2014 he started pettycoin, a cryptocurrency project. Rusty Russell authored the majority part of Bitcoin, Bitcoin's Lightning Netwo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
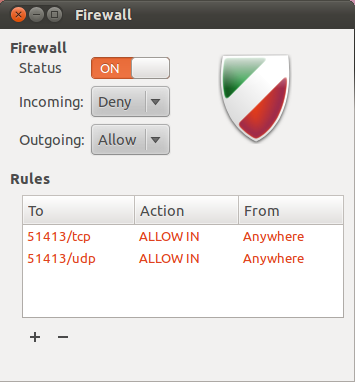
Uncomplicated Firewall
Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) is a program for managing a netfilter Firewall (computing), firewall designed to be easy to use. It uses a command-line interface consisting of a small number of simple commands, and uses iptables for configuration. UFW is available by default in all Ubuntu (operating system), Ubuntu installations since 8.04 LTS. UFW has been available by default in all Debian (operating system), Debian installations since 10. GUIs for Uncomplicated Firewall Gufw is intended to be an easy, intuitive graphical user interface for managing Uncomplicated Firewall. It supports common tasks such as allowing or blocking pre-configured, common Peer-to-peer, P2P, or individual ports. Gufw has been designed for Ubuntu (operating system), Ubuntu, but is also available in Debian-based distributions and in Arch Linux; anywhere Python (programming language), Python, GTK and UFW are available. Features References External links Ubuntu Firewall – Information about ''Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ipfirewall
ipfirewall or ipfw is a FreeBSD IP, stateful firewall, packet filter and traffic accounting facility. Its ruleset logic is similar to many other packet filters except IPFilter. ipfw is authored and maintained by FreeBSD volunteer staff members. Its syntax enables use of sophisticated filtering capabilities and thus enables users to satisfy advanced requirements. It can either be used as a loadable kernel module or incorporated into the kernel; use as a loadable kernel module where possible is highly recommended. ipfw was the built-in firewall of Mac OS X until Mac OS X 10.7 Lion in 2011 when it was replaced with the OpenBSD project's PF. Like FreeBSD, ipfw is open source. It is used in many FreeBSD-based firewall products, including m0n0wall and FreeNAS. A port of an early version of ipfw was used since Linux 1.1 as the first implementation of firewall available for Linux, until it was replaced by ipchains. A modern port of ipfw and the ''dummynet'' traffic shaper is av ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PF (firewall)
PF (Packet Filter, also written pf) is a BSD licensed stateful packet filter, a central piece of software for firewalling. It is comparable to netfilter (iptables), ipfw, and ipfilter. PF was developed for OpenBSD, but has been ported to many other operating systems. History PF was originally designed as replacement for Darren Reed's IPFilter, from which it derives much of its rule syntax. IPFilter was removed from OpenBSD's CVS tree on 30 May 2001 due to OpenBSD developers' concerns with its license. The initial version of PF was written by Daniel Hartmeier. It appeared in OpenBSD 3.0, which was released on 1 December 2001. It was later extensively redesigned by Henning Brauer and Ryan McBride with most of the code written by Henning Brauer. Henning Brauer is currently the main developer of PF. Features The filtering syntax is similar to IPFilter, with some modifications to make it clearer. Network address translation (NAT) and quality of service (QoS) have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NPF (firewall)
NPF is a BSD licensed stateful packet filter, a central piece of software for firewalling. It is comparable to iptables, ipfw, ipfilter and PF. NPF is developed on NetBSD. History NPF was primarily written by Mindaugas Rasiukevicius. NPF first appeared in the NetBSD 6.0 release in 2012. Features NPF is designed for high performance on SMP systems and for easy extensibility. It supports various forms of Network Address Translation Network address translation (NAT) is a method of mapping an IP address space into another by modifying network address information in the IP header of packets while they are in transit across a traffic Router (computing), routing device. The te ... (NAT), stateful packet inspection, tree and hash tables for IP sets, bytecode ( BPF or n-code) for custom filter rules and other features. NPF has extension framework for supporting custom modules. Features such as packet logging, traffic normalization, random blocking are provided as NPF exten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shorewall
Shorewall is an open source firewall tool for Linux that builds upon the Netfilter (iptables/ipchains) system built into the Linux kernel, making it easier to manage more complex configuration schemes by providing a higher level of abstraction for describing rules using text files. Its documentation is hosted on shorewall.org, while the latest code is hosted at https://gitlab.com/shorewall/code. Configuration It is not a daemon since it does not run continuously, but rather configures rules in the kernel allowing and disallowing traffic through the system. Shorewall is configured through a group of plain-text configuration files and does not have a graphical user interface, though a Webmin module is available separately. A monitoring utility packaged with Shorewall can be used to watch the status of the system as it operates and to assist in testing. Use Shorewall is mainly used in network installations (as opposed to a personal computer firewall), since most of its stre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NuFW
NuFW is a software package that extends Netfilter, the Linux kernel-internal packet filtering firewall module. NuFW adds authentication to filtering rules. NuFW is also provided as a hardware firewall, in the EdenWall firewalling appliance. NuFW has been restarted by the FFI and renamed into UFWI. Introduction NuFW / UFWI is an extension of Netfilter which brings the notion of user to IP filtering. NuFW / UFWI can : * Authenticate any connection that goes through your gateway or only from/to a chosen subset or a specific protocol (iptables is used to select the connections to authenticate). * Perform accounting, routing and Quality of service (QOS) based on users and not simply on IPs. * Filter packets with criteria such as application and OS used by distant users. * Be the key of a secure and simple Single Sign On system. Principles NuFW / UFWI refuses the idea of ''IP user'' as an IP address An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label such as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OSI Model
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model is a reference model developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that "provides a common basis for the coordination of standards development for the purpose of systems interconnection." In the OSI reference model, the components of a communication system are distinguished in seven abstraction layers: Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, and Application. The model describes communications from the physical implementation of transmitting bits across a transmission medium to the highest-level representation of data of a distributed application. Each layer has well-defined functions and semantics and serves a class of functionality to the layer above it and is served by the layer below it. Established, well-known communication protocols are decomposed in software development into the model's hierarchy of function calls. The Internet protocol suite as defined in and is a model of net ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Command-line Software
A command-line interface (CLI) is a means of interacting with software via commands each formatted as a line of text. Command-line interfaces emerged in the mid-1960s, on computer terminals, as an interactive and more user-friendly alternative to the non-interactive mode available with punched cards. For a long time, a CLI was the most common interface for software, but today a graphical user interface (GUI) is more common. Nonetheless, many programs such as operating system and software development utilities still provide CLI. A CLI enables automating programs since commands can be stored in a script file that can be used repeatedly. A script allows its contained commands to be executed as group; as a program; as a command. A CLI is made possible by command-line interpreters or command-line processors, which are programs that execute input commands. Alternatives to a CLI include a GUI (including the desktop metaphor such as Windows), text-based menuing (including DOS S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |