|
Ipswich Waterfront
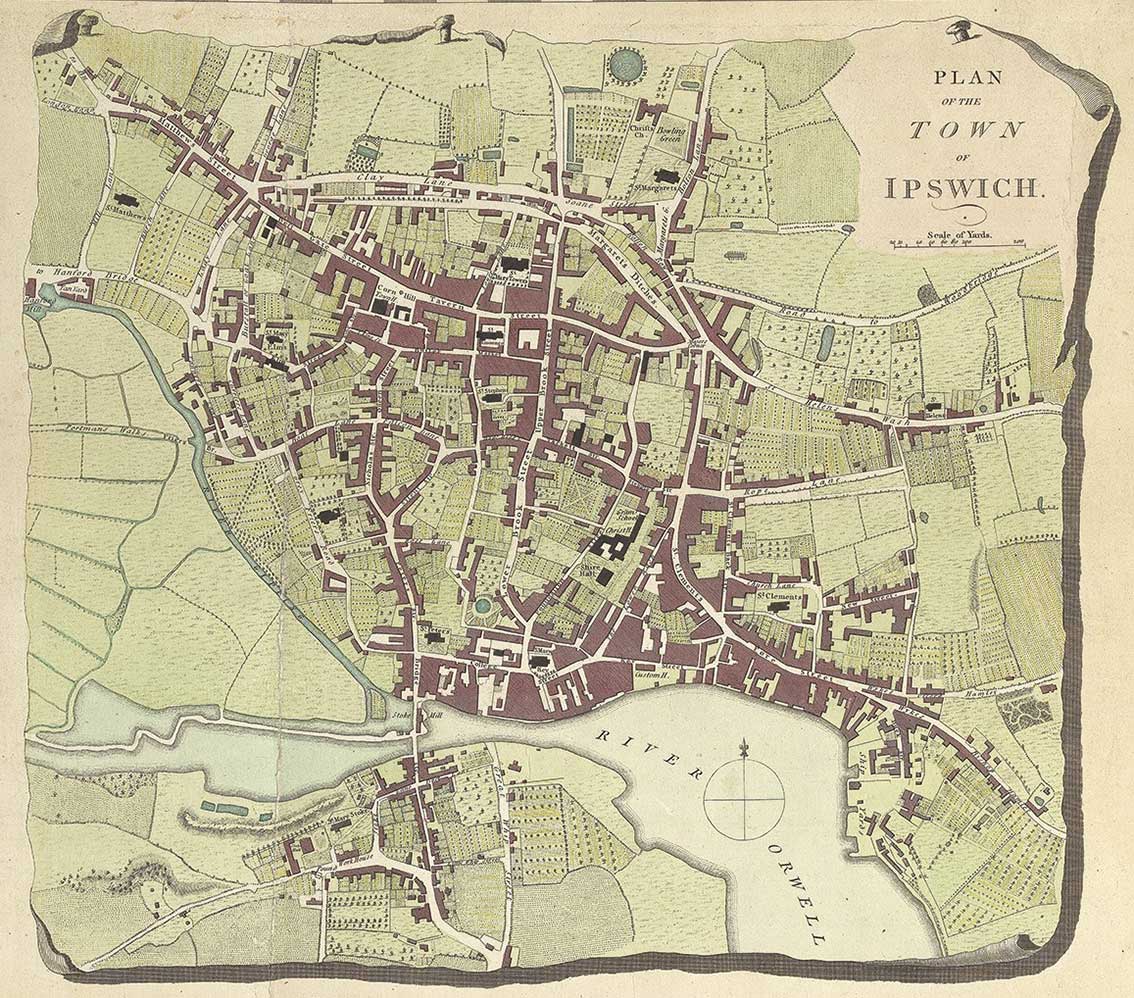
The Ipswich Waterfront is a cultural and historically significant area surrounding the marina in the town of Ipswich, Suffolk, England. The modern dock was constructed in 1842 and the area was a functioning dock up until the 1970s. At the time of completion, the dock was known as 'the biggest and most important enclosed dock in the kingdom'. Although the dock as it stands was constructed in 1842, the area was used for trade as far back as the 7th century. The decline of industry in the town resulted in the area being transformed into a trendy area of Ipswich, the waterfront is now characterised by its marina, known as Neptune Marina, as well as its mix of Classical architecture, classical and Postmodern architecture, postmodern architecture which includes multiple high-rise apartment buildings, restaurants, bars and cafés. The waterfront is also home to the main campus of the region's university, the University of Suffolk. Early period A dock was in operation in Ipswich on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ipswich Dock Original Lock Gates
Ipswich () is a port town and borough in Suffolk, England. It is the county town, and largest in Suffolk, followed by Lowestoft and Bury St Edmunds, and the third-largest population centre in East Anglia, after Peterborough and Norwich. It is northeast of London and in 2011 had a population of 144,957. The Ipswich built-up area is the fourth-largest in the East of England and the 42nd-largest in England and Wales. It includes the towns and villages of Kesgrave, Woodbridge, Bramford and Martlesham Heath. Ipswich was first recorded during the medieval period as ''Gippeswic'', the town has also been recorded as ''Gyppewicus'' and ''Yppswyche''. It has been continuously inhabited since the Saxon period, and is believed to be one of the oldest towns in the United Kingdom.Hills, Catherine"England's Oldest Town" Retrieved 2 August 2015. The settlement was of great economic importance to the Kingdom of England throughout its history, particularly in trade, with the town's historical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ipswich
Ipswich () is a port town and Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough in Suffolk, England. It is the county town, and largest in Suffolk, followed by Lowestoft and Bury St Edmunds, and the third-largest population centre in East Anglia, after Peterborough and Norwich. It is northeast of London and in 2011 had a population of 144,957. The Ipswich built-up area is the fourth-largest in the East of England and the 42nd-largest in England and Wales. It includes the towns and villages of Kesgrave, Woodbridge, Suffolk, Woodbridge, Bramford and Martlesham Heath. Ipswich was first recorded during the medieval period as ''Gippeswic'', the town has also been recorded as ''Gyppewicus'' and ''Yppswyche''. It has been continuously inhabited since the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Saxon period, and is believed to be one of the Oldest town in Britain, oldest towns in the United Kingdom.Hills, Catherine"England's Oldest Town" Retrieved 2 August 2015. The settlement was of great eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ipswich Dock Promenade
Ipswich () is a port town and borough in Suffolk, England. It is the county town, and largest in Suffolk, followed by Lowestoft and Bury St Edmunds, and the third-largest population centre in East Anglia, after Peterborough and Norwich. It is northeast of London and in 2011 had a population of 144,957. The Ipswich built-up area is the fourth-largest in the East of England and the 42nd-largest in England and Wales. It includes the towns and villages of Kesgrave, Woodbridge, Bramford and Martlesham Heath. Ipswich was first recorded during the medieval period as ''Gippeswic'', the town has also been recorded as ''Gyppewicus'' and ''Yppswyche''. It has been continuously inhabited since the Saxon period, and is believed to be one of the oldest towns in the United Kingdom.Hills, Catherine"England's Oldest Town" Retrieved 2 August 2015. The settlement was of great economic importance to the Kingdom of England throughout its history, particularly in trade, with the town's historical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total population of over 84 million in an area of , making it the most populous member state of the European Union. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The Capital of Germany, nation's capital and List of cities in Germany by population, most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Settlement in the territory of modern Germany began in the Lower Paleolithic, with various tribes inhabiting it from the Neolithic onward, chiefly the Celts. Various Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgundii
The Burgundians were an early Germanic tribe or group of tribes. They appeared east in the middle Rhine region in the third century AD, and were later moved west into the Roman Empire, in Gaul. In the first and second centuries AD, they or a people with the same name were mentioned by Roman writers living west of the Vistula river, in the region of Germania, which is now part of Poland. The Burgundians were first mentioned near the Rhine regions together with the Alamanni as early as the 11th panegyric to Emperor Maximian given in Trier in 291 AD, referring to events that must have happened between 248 and 291, and these two peoples apparently remained neighbours for centuries. By 411 AD, Burgundians had established control over Roman cities on the Rhine, between Franks and Alamanni, including Worms, Speyer and Strasbourg. In 436 AD, Aëtius defeated the Burgundians on the Rhine with the help of Hunnish forces, and then in 443, he re-settled the Burgundians within the empire, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thuringii
The Thuringii, or Thuringians were a Germanic people who lived in the kingdom of the Thuringians that appeared during the late Migration Period south of the Harz Mountains of central Germania, a region still known today as Thuringia. The Thuringian kingdom came into conflict with the Merovingian Franks, and it later came under their influence and Frankish control as a stem duchy. The name is still used for one of modern Germany's federal states ('' Bundesländer''). First appearances The Thuringians do not appear in classical Roman texts under that name, but some have suggested that they were the remnants of the Suebic Hermanduri, the last part of whose name (''-duri'') could represent the same sound as (''-thuri'') and the Germanic suffix ''-ing'', suggests a meaning of "descendants of (the ermanuri)". This people were living near the Marcomanni. Tacitus, in his ''Germania'', describes their homeland as being where the Elbe starts, but also having colonies at the Danube, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxon
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like them, speakers of West Germanic dialects, including the inland Franks and Thuringians to the south, and the coastal Frisians and Angles to the north who were among the peoples who were originally referred to as "Saxons" in the context of early raiding and settlements in Roman Britain and Gaul. To their east were Obotrites and other Slavic-speaking peoples. The political history of these continental Saxons is unclear until the 8th century and the conflict between their semi-legendary hero Widukind and the Frankish emperor Charlemagne. They do not appear to have been politically united until the generations leading up to that conflict, and before then they were reportedly ruled by regional "satraps". Previous Frankish rulers of Austrasia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alamanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni were a confederation of Germanic tribes * * * on the Upper Rhine River during the first millennium. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Roman emperor Caracalla of 213 CE, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into present-day Alsace and northern Switzerland, leading to the establishment of the Old High German language in those regions, which by the eighth century were collectively referred to as '' Alamannia''. In 496, the Alemanni were conquered by the Frankish leader Clovis and incorporated into his dominions. Mentioned as still pagan allies of the Christian Franks, the Alemanni were gradually Christianized during the seventh century. The is a record of their customary law during this period. Until the eighth century, Frankish suzerainty over Alemannia was mostly nominal. After an uprising by Theudebald, Duke of Alamannia, however, Carloman executed the Alamannic nobility and installed Frankish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which was the most northerly province of the Roman Empire in continental Europe. These Frankish tribes lived for centuries under varying degrees of Roman hegemony and influence, but after the collapse of Roman institutions in western Europe they took control of a large empire including areas which had been ruled by Rome, and what it meant to be a Frank began to evolve. Once they were deeply established in Gaul, the Franks became a multilingual, Catholic Christian people, who subsequently came to rule over several other post-Roman kingdoms both inside and outside the old empire. In a broader sense much of the population of western Europe could eventually described as Franks in some contexts. The term "Frank" itself first appeared in the third cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frisians
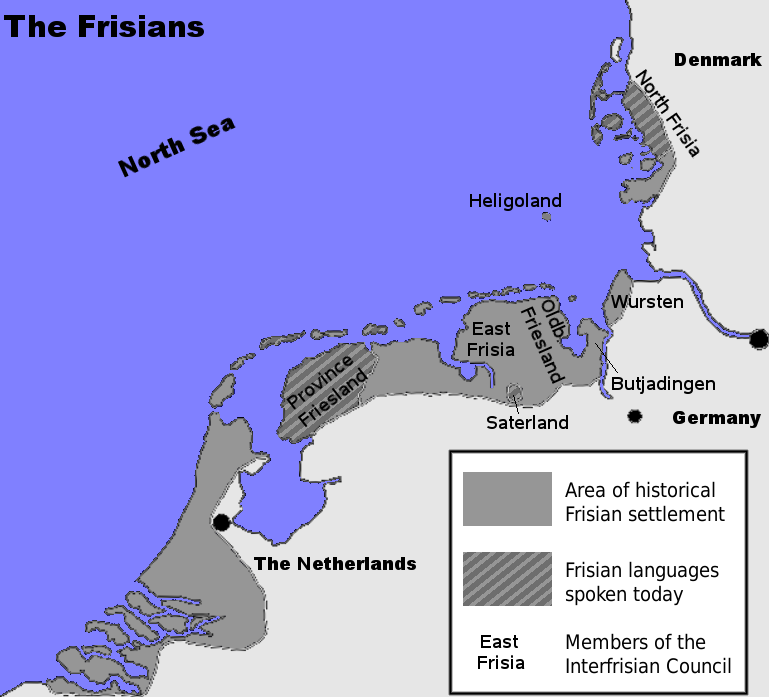
The Frisians () are an ethnic group indigenous to the German Bight, coastal regions of the Netherlands, north-western Germany and southern Denmark. They inhabit an area known as Frisia and are concentrated in the Dutch provinces of Friesland and Groningen (province), Groningen and, in Germany, East Frisia and North Frisia (which was a part of Denmark until 1864). The Frisian languages are spoken by more than 500,000 people; West Frisian language, West Frisian is officially recognised in the Netherlands (in Friesland) while North Frisian language, North Frisian and Saterland Frisian language, Saterland Frisian are recognised as regional languages in Germany. Name There are several theories about the origin of the name of the Frisians, which is derived from ''Frisii'' or ''Fresones'', names used by the Romans to describe a Germanic tribe that inhabited the same region but disappeared during the 5th century before the appearance of the Frisians. Most probably the name is derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxon England
Anglo-Saxon England or early medieval England covers the period from the end of Roman Empire, Roman imperial rule in Roman Britain, Britain in the 5th century until the Norman Conquest in 1066. Compared to modern England, the territory of the Anglo-Saxons stretched north to present day Lothian in southeastern Scotland, whereas it did not initially include western areas of England such as Cornwall, Herefordshire, Shropshire, Cheshire, Lancashire, and Cumbria. The 5th and 6th centuries involved the collapse of economic networks and political structures and also saw a radical change to a new Anglo-Saxon language and culture. This change was driven by movements of peoples as well as changes which were happening in both northern Gaul and the North Sea coast of what is now Germany and the Netherlands. The Anglo-Saxon language, also known as Old English, was a close relative of languages spoken in the latter regions, and genetic studies have confirmed that there was significant migrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andernach
Andernach () is a town in the district of Mayen-Koblenz, in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, of about 30,000 inhabitants. It is situated towards the end of the ''Neuwied basin'' on the left bank of the Rhine between the former tiny fishing village of Fornich in the north and the mouth of the small river Nette in the southeast, just north of Koblenz, with its five external town districts: Kell, Miesenheim, Eich, Namedy, and Bad Tönisstein. A few hundred metres downstream of Andernach the Rhine valley narrows from both sides forming the northern part of the romantic ''Middle Rhine'' stretch. Already in Roman times the place the narrow passage begins was named "Porta Antunnacensis" or ''Andernachian Gate''. It is formed by two hills, the ''Krahnenberg'' (engl. ''Crane hill'') and the ''Engwetter'' (''Narrow weather'') on the right bank near the wine village ''Leutesdorf'' (external town district of Bad Hönningen). The crane hill is named after the old crane beneath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |