|
Ioan Căianu
Johannes Caioni (''Ion Căian'' or ''Căianu'' in Romanian language, Romanian or ''Kájoni János'' in Hungarian language, Hungarian; 8 March 1629 – 25 April 1687) was a Transylvanian Franciscan friar and Roman Catholic Church, Roman Catholic priest, musician, folklorist, Humanism, humanist, constructor and repairer of Organ (music), organs of Romanians, Romanian origin (according to his own testimony, "''Natus valachus sum''" - "I was born a Vlachs, Vlach"). Biography Caioni was born in Kiskaján (Căianu Mic), in the Principality of Transylvania (1570–1711), Principality of Transylvania (now in Bistrița-Năsăud County, Romania). He was raised in Kolozsvár (Cluj-Napoca) and Csíksomlyó (Șumuleu Ciuc). He was of a Nobility and royalty of the Kingdom of Hungary, noble family — Caioni's aunt was the wife of a garrison commander in Csíkszereda (Miercurea Ciuc). Through her connections, he was admitted in the Franciscan monastery of Csíksomlyó (Șumuleu Ciuc). Caioni s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Caioni
Johannes Caioni (''Ion Căian'' or ''Căianu'' in Romanian or ''Kájoni János'' in Hungarian; 8 March 1629 – 25 April 1687) was a Transylvanian Franciscan friar and Roman Catholic priest, musician, folklorist, humanist, constructor and repairer of organs of Romanian origin (according to his own testimony, "''Natus valachus sum''" - "I was born a Vlach"). Biography Caioni was born in Kiskaján ( Căianu Mic), in the Principality of Transylvania (now in Bistrița-Năsăud County, Romania). He was raised in Kolozsvár (Cluj-Napoca) and Csíksomlyó (Șumuleu Ciuc). He was of a noble family — Caioni's aunt was the wife of a garrison commander in Csíkszereda ( Miercurea Ciuc). Through her connections, he was admitted in the Franciscan monastery of Csíksomlyó (Șumuleu Ciuc). Caioni studied with the Jesuits in Kolozsvár, and continued his studies in Csíksomlyó. In 1647, he became a friar, and continued his studies in Nagyszombat (Trnava), training in music. He was ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobility And Royalty Of The Kingdom Of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary held a Nobility, noble class of individuals, most of whom owned landed property, from the 11th century until the mid-20th century. Initially, a diverse body of people were described as noblemen, but from the late 12th century only high-ranking royal officials were regarded as noble. Most aristocrats claimed ancestry from chieftains of the period Principality of Hungary, preceding the establishment of the kingdom around 1000; others were descended from western European knights who settled in Hungary. The lower-ranking castle warriors also held landed property and served in the royal army. From the 1170s, most privileged laymen called themselves Royal servant (Kingdom of Hungary), royal servants to emphasize their direct connection to the monarchs. The Golden Bull of 1222 established their liberties, especially tax exemption and the limitation of military obligations. From the 1220s, royal servants were associated with the nobility and the high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Călușari
The Călușari (, ; ; singular: Călușar) are the participants to an old traditional Romanian dance known as the . "Căluș" translates to horse, but in an endearing form. Originally Romanian, the practice later spread to North Bulgaria. From three weeks after Easter until Pentecost, called in Romanian, for around two weeks they have traditionally travelled to all their local communities where they would dance, accompanied by a few fiddlers. History The origins of the Călușari are unknown, although the first written attestations are from the 17th-century musical notations of Ioan Căianu. Romanian historian of religion Mircea Eliade noted that "Although the oath taken is made in the name of God, the mythico-ritual scenario enacted by the calusari has nothing in common with Christianity" and that, in the 19th century at least, there was clerical opposition to the group, with its members being excluded from taking communion for three years in some regions. Etymology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age Of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment (also the Age of Reason and the Enlightenment) was a Europe, European Intellect, intellectual and Philosophy, philosophical movement active from the late 17th to early 19th century. Chiefly valuing knowledge gained through rationalism and empiricism, the Enlightenment was concerned with a wide range of social and Politics, political ideals such as natural law, liberty, and progress, toleration and fraternity (philosophy), fraternity, constitutional government, and the formal separation of church and state. The Enlightenment was preceded by and overlapped the Scientific Revolution, which included the work of Johannes Kepler, Galileo Galilei, Francis Bacon, Pierre Gassendi, Christiaan Huygens and Isaac Newton, among others, as well as the philosophy of Descartes, Hobbes, Spinoza, Leibniz, and John Locke. The dating of the period of the beginning of the Enlightenment can be attributed to the publication of René Descartes' ''Discourse on the Method'' in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and surpass the ideas and achievements of classical antiquity. Associated with great social change in most fields and disciplines, including Renaissance art, art, Renaissance architecture, architecture, politics, Renaissance literature, literature, Renaissance exploration, exploration and Science in the Renaissance, science, the Renaissance was first centered in the Republic of Florence, then spread to the Italian Renaissance, rest of Italy and later throughout Europe. The term ''rinascita'' ("rebirth") first appeared in ''Lives of the Artists'' () by Giorgio Vasari, while the corresponding French word was adopted into English as the term for this period during the 1830s. The Renaissance's intellectual basis was founded in its version of Renaiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
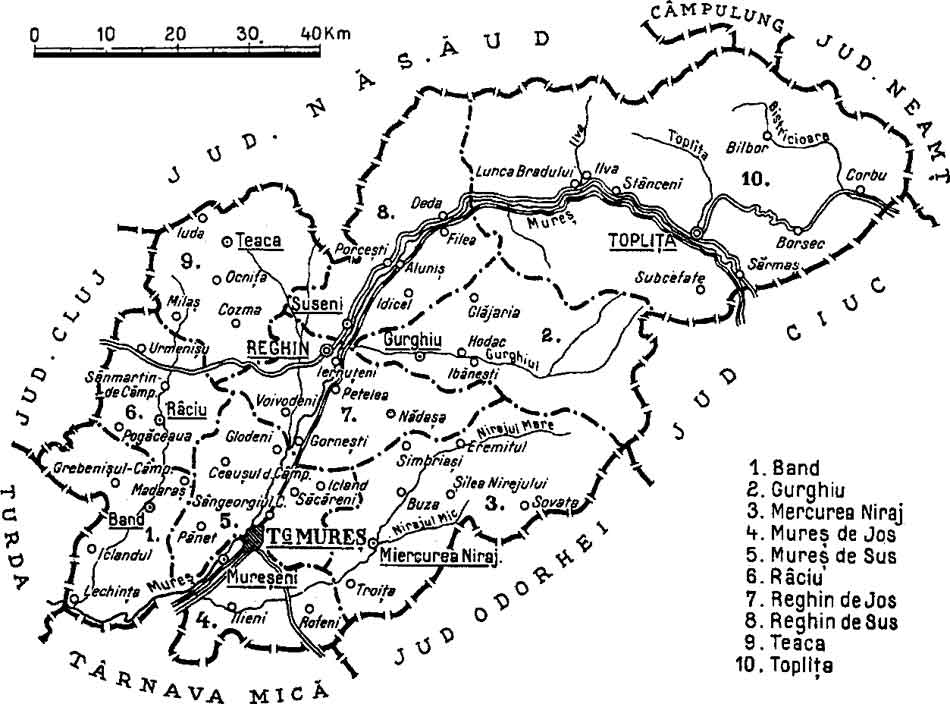
Mureș County
Mureș County (, , ) is a county (''județ'') of Romania, in the Historical regions of Romania, historical region of Transylvania, with the administrative centre in Târgu Mureș. The county was established in 1968, after the administrative reorganization that re-introduced the historical ''județ'' (Counties of Romania, county) system, still used today. This reform eliminated the previous Magyar Autonomous Region, Mureș-Magyar Autonomous Region, which had been created in 1952 within the People's Republic of Romania. Mureș County has a vibrant multicultural fabric that includes Székely Land, Hungarian-speaking Székelys and Transylvanian Saxons, with a rich heritage of Villages with fortified churches in Transylvania, fortified churches and towns. Name In Hungarian language, Hungarian, it is known as ''Maros megye'' (), and in German language, German as ''Kreis Mieresch''. Under Kingdom of Hungary, a county with a similar name (Maros-Torda County, ) was created in 1876. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of Romania
A commune (''comună'' in Romanian language, Romanian) is the lowest level of administrative subdivision in Romania. There are 2,686 communes in Romania. The commune is the rural subdivision of a Counties of Romania, county. Urban areas, such as towns and cities within a county, are given the status of ''Cities in Romania, city'' or ''Municipality in Romania, municipality''. In principle, a commune can contain any size population, but in practice, when a commune becomes relatively urbanised and exceeds approximately 10,000 residents, it is usually granted city status. Although cities are on the same administrative level as communes, their local governments are structured in a way that gives them more power. Some urban or semi-urban areas of fewer than 10,000 inhabitants have also been given city status. Each commune is administered by a mayor (''primar'' in Romanian). A commune is made up of one or more villages which do not themselves have an administrative function. Communes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eremitu
Eremitu (, Hungarian pronunciation: ) is a commune in Mureș County, Transylvania, Romania, composed of five villages: Călugăreni (''Mikháza''), Câmpu Cetății (''Vármező''), Dămieni (''Deményháza''), Eremitu (''Nyárádremete''), and Mătrici (''Nyárádköszvényes''). Călugăreni is the site of the Roman Castra of Călugăreni fort in the Roman province of Dacia, located on the north-western periphery of the village. The route of the Via Transilvanica long-distance trail passes through Eremitu, where the ''Highlands'' section of the trail ends, and the ''Terra Siculorum'' section begins. Demographics At the 2011 census, the commune had a population of 3,893, of which 89% were Hungarians, 4.2% Romanians, and 4% Roma. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lăzarea
Lăzarea ( or colloquially ''Szárhegy'', Hungarian pronunciation: , meaning ''Bald Mountain in Gyergyószék, Gyergyó'') is a commune in Harghita County, Romania. It lies in the Székely Land, an ethno-cultural region in eastern Transylvania, and is composed of two villages, Ghiduț (''Güdüc'') and Lăzarea. The commune is one of the oldest settlements in the area, and is now a tourist and cultural centre. It has various local attractions, including the Lázár Castle (1450). It is located in the central-north part of the county, at the foot of the Căliman-Harghita Mountains, on the banks of the river Lăzarea (river), Lăzarea. History The history of the village is closely interwoven with that of the Lázár family. Its first written mention is from 1482 when a certain Erzsébet Bíró of Kide warned a Székelys, Székely named Lázár of '' Zarhegh'' and Péter Szilvási to beware of disposing of the estate of Kide to which she was entitled under the title of bride price ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordination
Ordination is the process by which individuals are Consecration in Christianity, consecrated, that is, set apart and elevated from the laity class to the clergy, who are thus then authorized (usually by the religious denomination, denominational hierarchy composed of other clergy) to perform various religious rites and ceremonies. The process and ceremonies of ordination vary by religion and denomination. One who is in preparation for, or who is undergoing the process of ordination is sometimes called an ordinand. The liturgy used at an ordination is commonly found in a book known as an Order of Mass, Ordinal which provides the ordo (ritual and rubrics) for celebrations. Christianity Catholic, Orthodox, Lutheran and Anglican churches In Catholicism and Orthodoxy, ordination is one of the seven sacraments, variously called holy orders or ''Christian laying on of hands, cheirotonia'' ("Laying on of Hands"). Apostolic succession is considered an essential and necessary concept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trnava
Trnava (, , ; , also known by other #Names and etymology, alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, to the northeast of Bratislava, on the Trnávka river. It is the capital of the Trnava Region and the Trnava District. It is the seat of a Roman Catholic archbishopric (1541–1820 and then again since 1977). The city has a historic center. Because of the many churches within its city walls, Trnava has often been called "Little Rome" (, ), or more recently, the "Slovak Rome". Names and etymology The name of the city is derived from the name of the creek Trnava. It comes from the Old Slavic/Slovak word ''tŕň'' ("thornbush")Martin Štefánik – Ján Lukačka et al. 2010, Lexikón stredovekých miest na Slovensku, Historický ústav SAV, Bratislava, 2010, p. 523, . http://forumhistoriae.sk/-/lexikon-stredovekych-miest-na-slovensku which characterized the river banks in the region. Many towns in Central and Eastern Europe have a similar etymology including Trnovo, Marti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society Of Jesus
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rome. It was founded in 1540 by Ignatius of Loyola and six companions, with the approval of Pope Paul III. The Society of Jesus is the largest religious order in the Catholic Church and has played significant role in education, charity, humanitarian acts and global policies. The Society of Jesus is engaged in evangelization and apostolic ministry in 112 countries. Jesuits work in education, research, and cultural pursuits. They also conduct retreats, minister in hospitals and parishes, sponsor direct social and humanitarian works, and promote ecumenical dialogue. The Society of Jesus is consecrated under the patronage of Madonna della Strada, a title of the Blessed Virgin Mary, and it is led by a superior general. The headquarters of the society, its general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |