|
Inverclyde Line
The Inverclyde Line is a railway line running from Glasgow Central station through Paisley (Gilmour Street) and a series of stations to the south of the River Clyde and the Firth of Clyde, terminating at Gourock and Wemyss Bay, where it connects to Caledonian MacBrayne ferry services. The line has been in operation since the 1840s between Glasgow and Greenock and was the first passenger service to follow the River Clyde to the coast. The line was electrified in 1967. History The line was opened by the Glasgow, Paisley and Greenock Railway on 31 March 1841, and initially ran from Bridge Street railway station in Glasgow to a terminus at Cathcart Street, Greenock (later renamed Greenock Central railway station), with the section between Glasgow, and Paisley Gilmour Street being run by the Glasgow and Paisley Joint Railway. For the first time a railway took passengers right down the River Clyde, taking about one hour whereas Clyde steamers took around twice as long. The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 314
The British Rail Class 314 was a class of alternating current electric multiple unit (EMU) trains built by British Rail Engineering Limited's Holgate Road carriage works in 1979. They were a class of units derived from British Rail's British Rail Classes 445 and 446, 1971 prototype suburban EMU design which, as the BREL 1972 family, eventually encompassed 755 vehicles over five production classes (British Rail Class 313, 313, 314, British Rail Class 315, 315, British Rail Class 507, 507 and British Rail Class 508, 508). The Class 314 fleet was used to operate inner-suburban services on the Strathclyde Partnership for Transport, Strathclyde Passenger Transport rail network in and around Glasgow, most typically on the Argyle Line, Argyle, North Clyde Line, North Clyde, Cathcart Circle Lines, Cathcart Circle, Paisley Canal Line, Paisley Canal and Inverclyde Line, Inverclyde lines. The units, formed of three cars each, worked either independently or in six-car pairs. Although the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gourock
Gourock ( ; ) is a town in the Inverclyde council areas of Scotland, council area and formerly a burgh of the County of Renfrew in the west of Scotland. It was a resort town, seaside resort on the East shore of the upper Firth of Clyde. Its main function today is as a residential area, extending contiguously from Greenock, with a railway terminus and ferry services across the Clyde. History The name Gourock comes from a Gaelic word for "pimple", in reference to the hill above the town. As far back as 1494 it is recorded that James IV of Scotland, James IV sailed from the shore at Gourock to quell the rebellious Highland clans. Two hundred years later William III of England, William and Mary granted a Charter in favour of Stewart of Castlemilk which raised Gourock to a Burgh of Barony. In 1784 the lands of Gourock were purchased by Duncan Darroch, a former merchant in Jamaica. He built Gourock House near the site of the castle in what the family eventually gifted to the town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London, Midland And Scottish Railway
The London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMSIt has been argued that the initials LMSR should be used to be consistent with London and North Eastern Railway, LNER, Great Western Railway, GWR and Southern Railway (UK), SR. The London, Midland and Scottish Railway's corporate image used LMS, and this is what is generally used in historical circles. The LMS occasionally also used the initials LM&SR. For consistency, this article uses the initials LMS.) was a British railway company. It was formed on 1 January 1923 under the Railways Act 1921, which required the grouping of over 120 separate railways into four. The companies merged into the LMS included the London and North Western Railway, the Midland Railway, the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (which had previously merged with the London and North Western Railway on 1 January 1922), several Scottish railway companies (including the Caledonian Railway), and numerous other, smaller ventures. Besides being the world's largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow And South Western Railway
The Glasgow and South Western Railway (G&SWR) was the third biggest of the five major Scottish railway companies prior to the 1923 Grouping. It served a triangular area of south-west Scotland between Glasgow, Stranraer and Carlisle, Cumbria, Carlisle. It was formed on 28 October 1850 by the merger of two earlier railways, the Glasgow, Paisley, Kilmarnock and Ayr Railway and the Glasgow, Dumfries and Carlisle Railway. Already established in Ayrshire, it consolidated its position there and extended southwards, eventually reaching Stranraer. Its main business was mineral traffic, especially coal, and passengers, but its more southerly territory was very thinly populated and local traffic, passenger and goods, was limited, while operationally parts of its network were difficult. It later formed an alliance with the English Midland Railway and ran express passenger trains from Glasgow to London with that company, in competition with the Caledonian Railway and its English partner, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
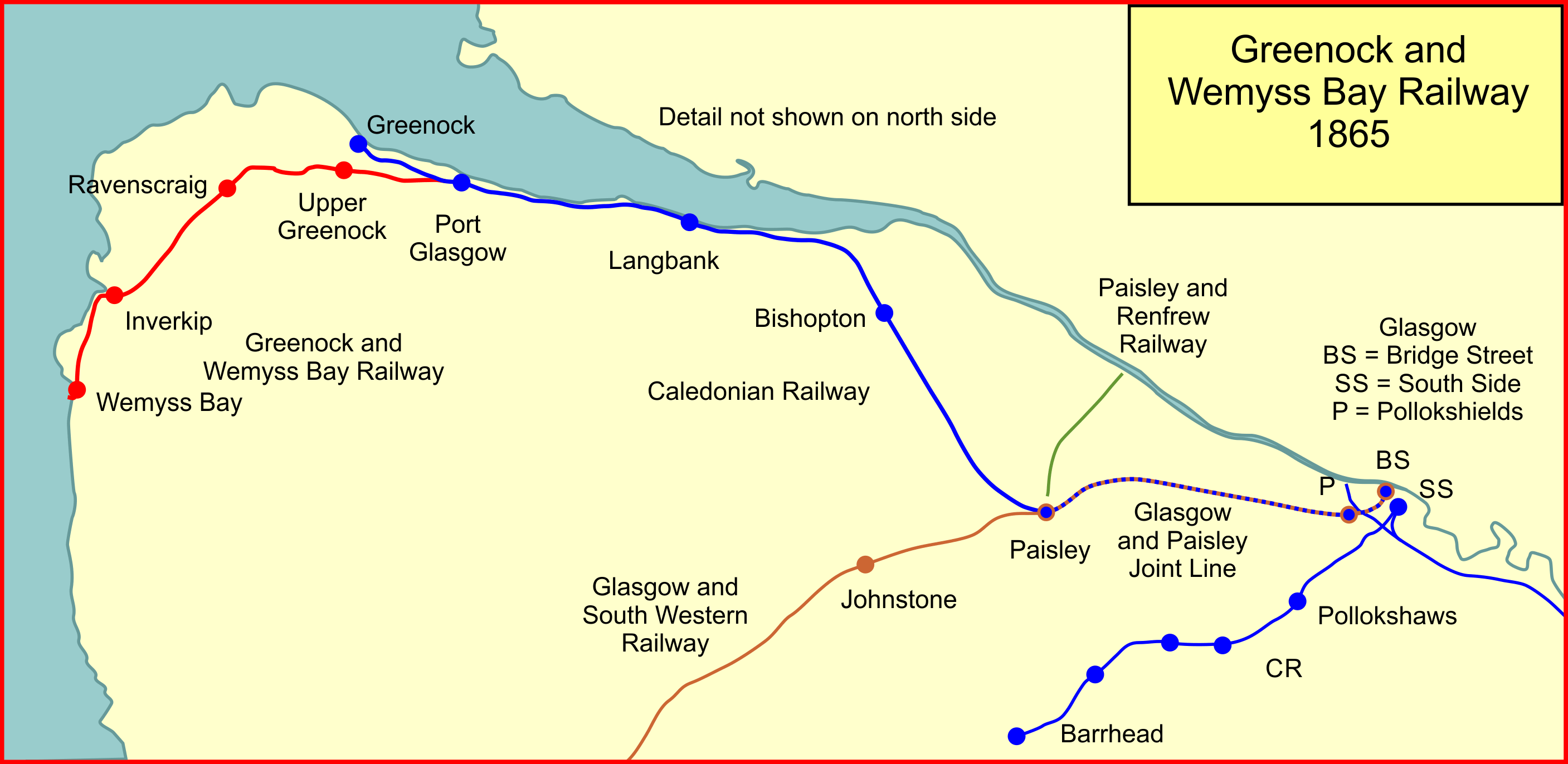
Greenock And Wemyss Bay Railway
The Greenock and Wemyss Bay Railway was a railway owned by the Caledonian Railway, providing services between Greenock and Wemyss Bay. History The Glasgow, Paisley and Greenock Railway In 1841 the Glasgow, Paisley and Greenock Railway opened its line. At the time the River Clyde was heavily used by Clyde steamers, but it was impassable for larger sea-going vessels, which anchored at the Tail of the Bank for transshipment at Greenock, and transfer of passengers. The company's promoters anticipated the carriage of goods from the industries of Greenock, and as well as competing for the transshipment traffic. However their terminal station at Greenock Central railway station, Greenock Cathcart Street, around 300 yards (280 m) from Custom House Quay, and was not directly connected to any shipping berth. Nonetheless substantial traffic built up, and in particular passenger traffic grew considerably. The traffic to resort locations on the Firth of Clyde and other coastal places, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
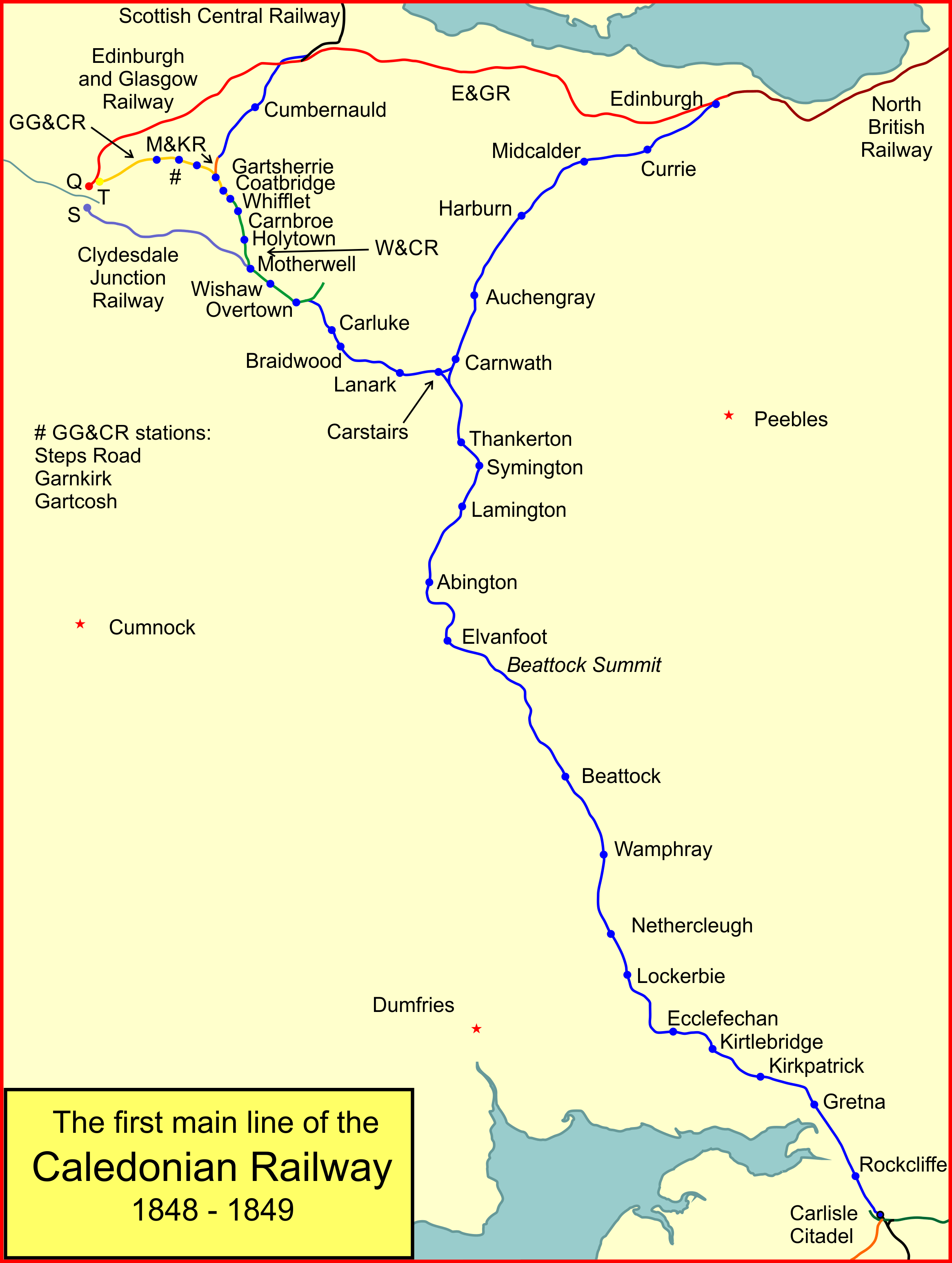
Caledonian Railway
The Caledonian Railway (CR) was one of the two biggest of the five major Scottish railway companies prior to the 1923 Grouping. It was formed in 1845 with the objective of forming a link between English railways and Glasgow. It progressively extended its network and reached Edinburgh and Aberdeen, with a dense network of branch lines in the area surrounding Glasgow. It was absorbed into the London, Midland and Scottish Railway in 1923. Many of its principal routes are still used, and the original main line between Carlisle, Cumbria, Carlisle and Glasgow is in use as part of the West Coast Main Line railway (with a modified entry into Glasgow itself). Introduction In the mid-1830s, railways in England evolved from local concerns to longer routes that connected cities, and then became networks. In Scotland it was clear that this was the way forward, and there was a desire to connect the Central Belt to the incipient English network. There was controversy over the route that such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firth
Firth is a word in the English and Scots languages used to denote various coastal waters in the United Kingdom, predominantly within Scotland. In the Northern Isles, it more often refers to a smaller inlet. It is linguistically cognate to Scandinavian ''fjord'' and ''fjard'' (all from Proto-Germanic *''ferþuz''), with the original meaning of "sailable waterway". The word has a more constrained sense in English. Bodies of water named "firths" tend to be more common on the Scottish east coast, or in the southwest of the country, although the Firth of Clyde is an exception to this. The Highland coast contains numerous estuaries, straits, and inlets of a similar kind, but not called "firth" (e.g. the Minch and Loch Torridon); instead, these are often called sea lochs. Before about 1850, the spelling "Frith" was more common. A firth is generally the result of ice age glaciation and is very often associated with a large river, where erosion caused by the tidal effects of incoming s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clyde Steamer
The Clyde steamer is the collective term for several passenger services that existed on the River Clyde in Scotland, running from Glasgow downstream to Rothesay and other towns, a journey known as going ''doon the watter''. The era of the Clyde steamer began in August 1812 with the very first successful commercial steamboat service in Europe, when Henry Bell's began a passenger service on the River Clyde between Glasgow and Greenock. The ''Comet'' undertook her official trial run on 6 August 1812. Henry Bell himself was on board, along with John Robertson, maker of ''Comet''s engine, and William McKenzie, formerly a schoolmaster in Helensburgh, acting as skipper. According to the ''Glasgow Courier'' newspaper two days later, the journey was completed in three-and-a-half hours. After this success, other operators sprang up in competition, and the Firth of Clyde became immensely popular with holidaymakers. By 1900 there were over three hundred Clyde steamers operating, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow And Paisley Joint Railway
The Glasgow and Paisley Joint Railway was the section of railway line between Glasgow Bridge Street railway station and Paisley, Renfrewshire, Paisley, in the west of Scotland. It was constructed and operated jointly by two competing railway companies as the stem of their lines to Greenock and Ayr respectively, and it opened in 1840. The Joint Committee, which controlled the line, built a branch to Govan and later to Cessnock, Glasgow, Cessnock Dock, and then Prince's Dock. With the passing of the Railways Act 1921 (Grouping Act) the line, together with the Caledonian Railway and the Glasgow and South Western Railway, became part of the London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS). The line is still in heavy use today as the eastern end of the Inverclyde Line and the Ayrshire Coast Line. Formation In the 1830s promoters in the west of Scotland considered the potential for railway construction, and in the 1837 parliamentary session, supporters of two schemes presented bills. One ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow Bridge Street Railway Station
Bridge Street railway station, now disused, was the original Glasgow terminus of the Glasgow and Paisley Joint Railway; jointly owned by the Glasgow, Paisley and Greenock Railway (GP&G), which later merged with the Caledonian Railway, and the Glasgow, Paisley, Kilmarnock and Ayr Railway (GPK&A), which became part of the Glasgow & South Western Railway.Paton, John (2006). ''Design Worthy of the City''. Chapter 4, In: Cameron (2006). The station opened for traffic on the GPK&A in August 1840; and for traffic on the GP&G in March 1841. It was sited in Laurieston on the south side of the River Clyde, but was close to the centre of Glasgow. Clyde services terminus station The railway line between Paisley and Glasgow was built by the Glasgow and Paisley Joint Railway, with Joseph Locke and John Errington as joint engineers. The station layout was designed by James Miller. The line, together with Bridge Street station, was under the control of the Glasgow and Paisley Joint Rai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow, Paisley And Greenock Railway
The Glasgow, Paisley and Greenock Railway (GP&GR) was an early Scotland, Scottish railway, opened in 1841, providing train services between Greenock and Glasgow. At the time the River Clyde was not accessible to sea-going ships, and the intention was to compete with riverboats that brought goods to and from the city. In fact, passenger traffic proved surprisingly buoyant, and connecting steamer services to island resorts in the Firth of Clyde provided a very great source of business. The GP&GR merged with the larger Caledonian Railway in 1851. The Greenock station was not alongside the steamer berths and as the trade developed, this became a significant disadvantage. The independent Greenock and Wemyss Bay Railway built a branch line to a pier at Wemyss Bay, giving much closer access to Rothesay, Bute, Rothesay, and in 1889 the Greenock line itself was extended to Gourock. The work involved building Newton Street Tunnel, the longest railway tunnel in Scotland. The line between G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Electrification In Great Britain
Railway electrification in Great Britain began in the late 19th century. A range of voltages has been used, employing both overhead lines and conductor rails. The two most common systems are using overhead lines, and the third rail system used in Southeast England and on Merseyrail. As of October 2023, (38%) of the British rail network was electrified. According to Network Rail, as at 2003, 64% of the electrified network used the 25kVAC overhead system, and 36% used the 660/750VDC third-rail system.Network Rail, 2003 Technical Plan, Chapter 11 "Network Capability", page 7 "Electrification". "Approximately 40% of the rail network is currently equipped with electrification." From page 1, total network is 30764 km, 7587 km of 25 kV AC, 4285 km of 650/750 V DC and 28 km of 1500 V DC. Excludes CTRL, LUL, Old Danby test track, bulk of Tyne and Wear Metro, etc. NB it does not state what method of counting length of network is used - i.e. sidings, loops, double track etc. produce di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |