|
Internal Elastic Lamina
The internal elastic lamina or internal elastic lamella is a layer of elastic tissue that forms the outermost part of the tunica intima of blood vessels. It separates tunica intima from tunica media. Histology It is readily visualized with light microscopy in sections of muscular arteries, where it is thick and prominent, and arterioles, where it is slightly less prominent and often incomplete. It is very thin in veins and venules. In elastic arteries such as the aorta, which have very regular elastic laminae between layers of smooth muscle cells in their tunica media, the internal elastic lamina is approximately the same thickness as the other elastic laminae that are normally present. There is small amount of subendothelial connective tissue between basement membrane of endothelial cells and internal elastic lamina. Reduplication of internal elastic lamina can be seen in elderly individuals due to intimal fibroplasia, which is part of the aging process. Associated pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
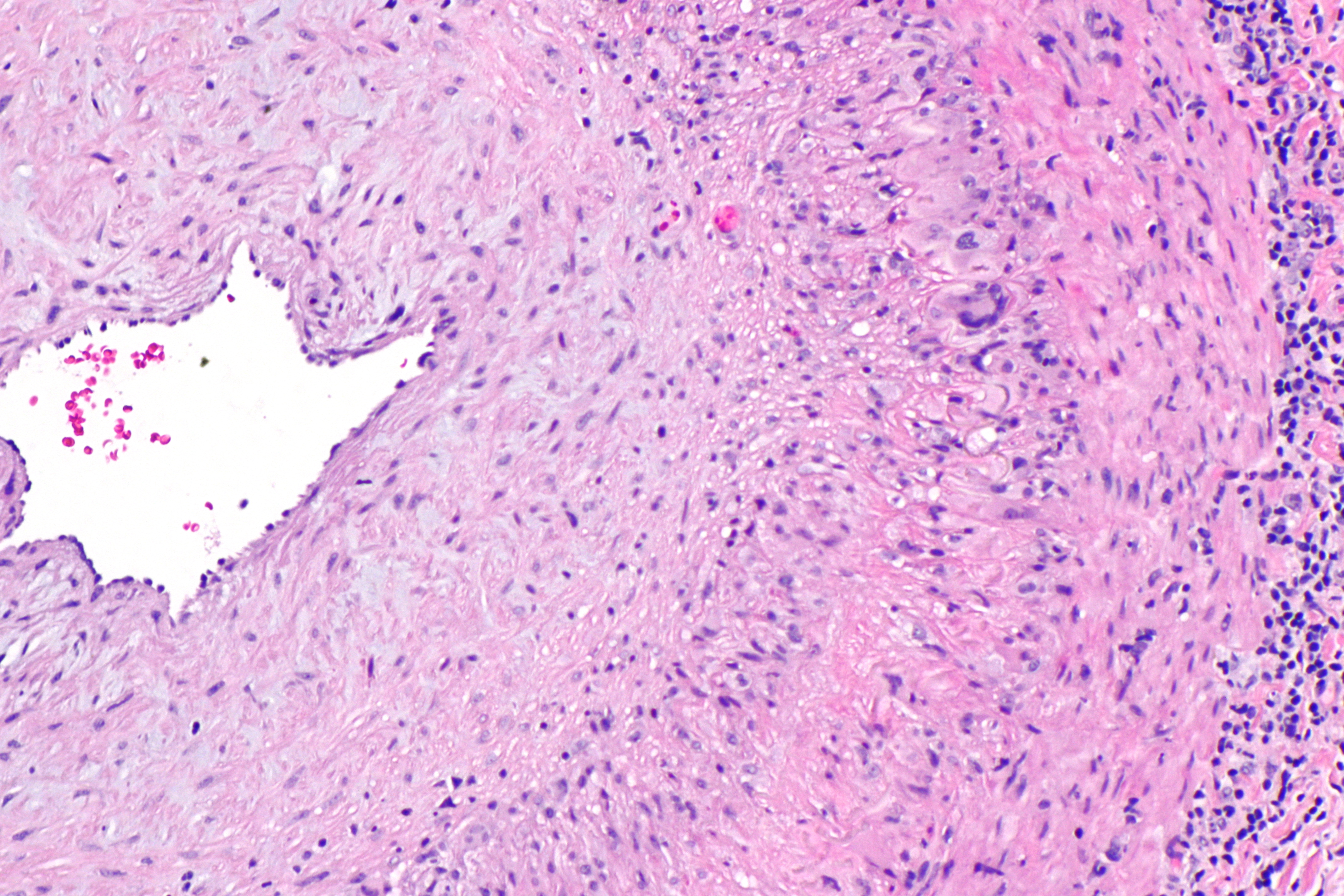
Cholesterol Embolus - Very High Mag
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils. Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all animal Cell (biology)#Eukaryotic cells, cells and is an essential structural and cholesterol signaling, signaling component of animal cell membranes. In vertebrates, hepatocyte, hepatic cells typically produce the greatest amounts. In the brain, astrocytes produce cholesterol and transport it to neurons. It is absent among prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), although there are some exceptions, such as ''Mycoplasma'', which require cholesterol for growth. Cholesterol also serves as a Precursor (chemistry), precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones, bile acid and vitamin D. Elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood, especially when bound to low-density lipoprotein (LDL, often referred to as "bad cholesterol"), may increase the risk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
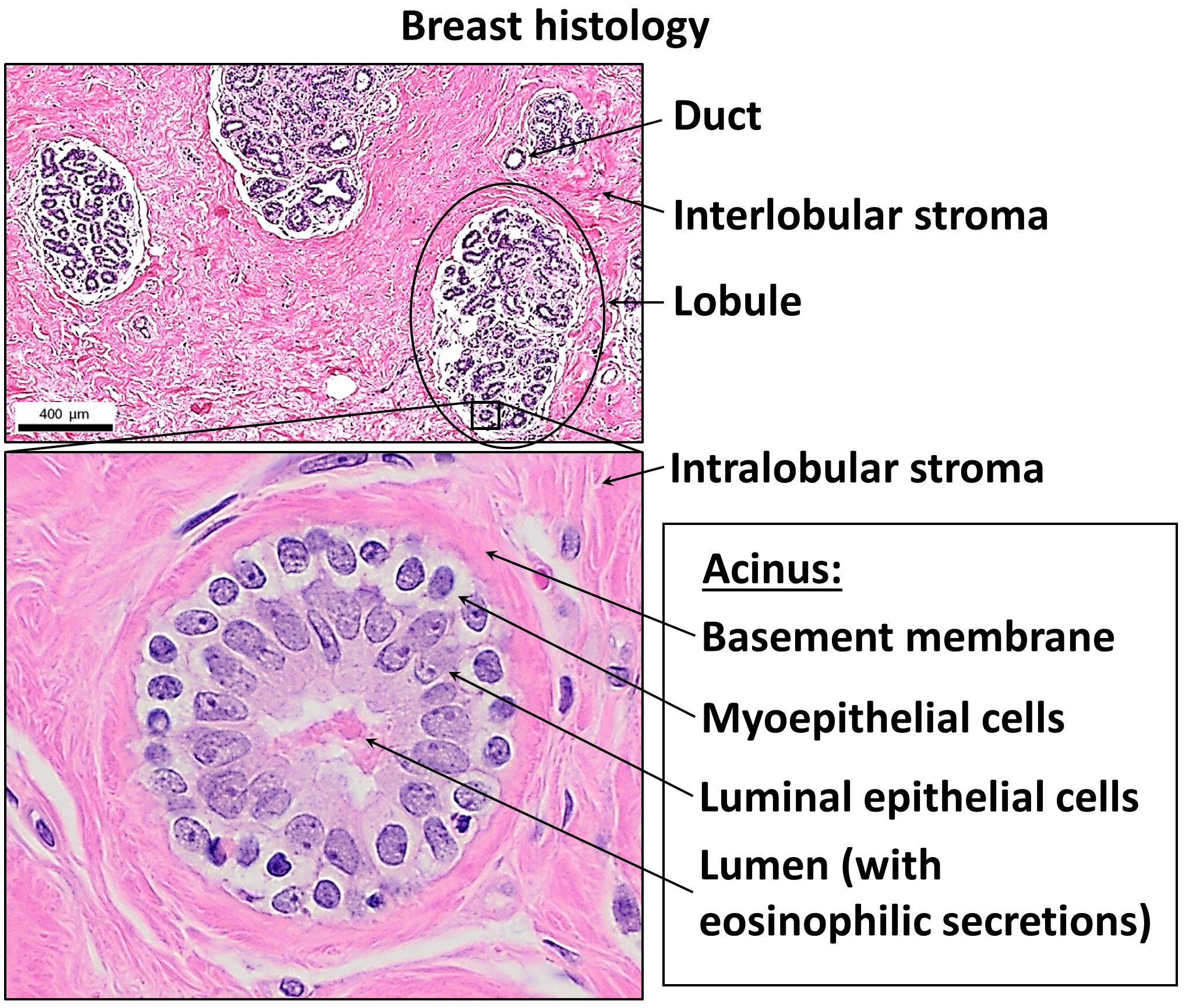
Basement Membrane
The basement membrane, also known as base membrane, is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium and endothelium, and the underlying connective tissue. Structure As seen with the electron microscope, the basement membrane is composed of two layers, the basal lamina and the reticular lamina. The underlying connective tissue attaches to the basal lamina with collagen VII anchoring fibrils and fibrillin microfibrils. The basal lamina layer can further be subdivided into two layers based on their visual appearance in electron microscopy. The lighter-colored layer closer to the epithelium is called the lamina lucida, while the denser-colored layer closer to the connective tissue is called the lamina densa. The electron-dense lamina densa layer is about 30–70 nanometers thick and consists of an und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Allograft Nephropathy
Chronic allograft nephropathy (CAN) is a kidney disorder which is the leading cause of kidney transplant failure, occurring months to years after the transplant. Symptoms and signs CAN is characterized by a gradual decline in kidney function and, typically, accompanied by high blood pressure and hematuria. Pathology The histopathology is characterized by interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy, fibrotic intimal thickening of arteries An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ... and glomerulosclerosis. Diagnosis CAN is diagnosed by examination of tissue, e.g. a kidney biopsy. References {{reflist Organ transplantation Kidney diseases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesoderm, the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord, are composed of connective tissue. Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells. Blood and lymph are classed as specialized fluid connective tissues that do not contain fiber. All are immersed in the body water. The cells of connective tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells and leukocytes. The term "connective tissue" (in German, ) was introduced in 1830 by Johannes Peter Müller. The tissue was already recognized as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contraction, contract. Muscle tissue contains special Muscle contraction, contractile proteins called actin and myosin which interact to cause movement. Among many other muscle proteins, present are two regulatory proteins, troponin and tropomyosin. Muscle is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle tissue is striated consisting of elongated, multinucleate muscle cells called muscle fibers, and is responsible for movements of the body. Other tissues in skeletal muscle include tendons and perimysium. Smooth and cardiac muscle contract involuntarily, without conscious intervention. These muscle types may be activated both through the interaction of the central nervous system as well as by innervation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Gieson
Van Gieson's stain is a histological staining technique used to differentiate between collagen and other tissue elements in microscopic sections. It is a combination of two Acidic dye - picric acid and acid fuchsin, producing distinct coloration that aids in the visualization of connective tissue. When examining histological specimens, it colors collagen fibers bright red while staining muscle and other cytoplasmic elements yellow. It was introduced in the late 19th century to histology by American psychiatrist and neuropathologist Ira Van Gieson. Van Gieson’s solution is commonly used as a counterstain in histology, sharply highlighting collagen against a yellow background. History Van Gieson’s stain was first described by Ira T. Van Gieson in 1889 as a method for examining nervous system tissue. Van Gieson was a pathologist who published ''The Laboratory notes of technical methods for the nervous system'' in 1889, introducing the picric–fuchsin method at that time. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Cell Arteritis
Giant cell arteritis (GCA), also called temporal arteritis, is an inflammatory autoimmune disease of large blood vessels. Symptoms may include headache, pain over the temples, flu-like symptoms, double vision, and difficulty opening the mouth. Complications can include blockage of the artery to the eye with resulting blindness, as well as aortic dissection, and aortic aneurysm. GCA is frequently associated with polymyalgia rheumatica. The cause is unknown. The underlying mechanism involves inflammation of the small blood vessels that supply the walls of larger arteries. This mainly affects arteries around the head and neck, though some in the chest may also be affected. Diagnosis is suspected based on symptoms, blood tests, and medical imaging, and confirmed by biopsy of the temporal artery. However, in about 10% of people the temporal artery is normal. Treatment is typical with high doses of steroids such as prednisone or prednisolone. Once symptoms have resolved, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aging
Ageing (or aging in American English) is the process of becoming Old age, older until death. The term refers mainly to humans, many other animals, and fungi; whereas for example, bacteria, perennial plants and some simple animals are potentially biologically immortal. In a broader sense, ageing can refer to single cells within an organism which have Cellular senescence, ceased dividing, or to the Population ageing, population of a species. In humans, ageing represents the accumulation of changes in a human being over time and can encompass physical, psychological, and social changes. Reaction time, for example, may slow with age, while memories and general knowledge typically increase. Of the roughly 150,000 people who die each day across the globe, about two-thirds die from age-related causes. Current Theory of aging, ageing theories are assigned to the damage concept, whereby the accumulation of damage (such as DNA oxidation) may cause biological systems to fail, or to the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intimal Fibroplasia
The tunica intima (Neo-Latin "inner coat"), or intima for short, is the innermost tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It is made up of one layer of endothelial cells (and macrophages in areas of disturbed blood flow), and is supported by an internal elastic lamina. The endothelial cells are in direct contact with the blood flow. The three layers of a blood vessel are an inner layer (the tunica intima), a middle layer (the tunica media), and an outer layer (the tunica externa). In dissection, the inner coat (tunica intima) can be separated from the middle (tunica media) by a little maceration, or it may be stripped off in small pieces; but, because of its friability, it cannot be separated as a complete membrane. It is a fine, transparent, colorless structure which is highly elastic, and, after death, is commonly corrugated into longitudinal wrinkles. Structure The structure of the tunica intima depends on the blood vessel type. Elastic arteries – A single layer of endoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
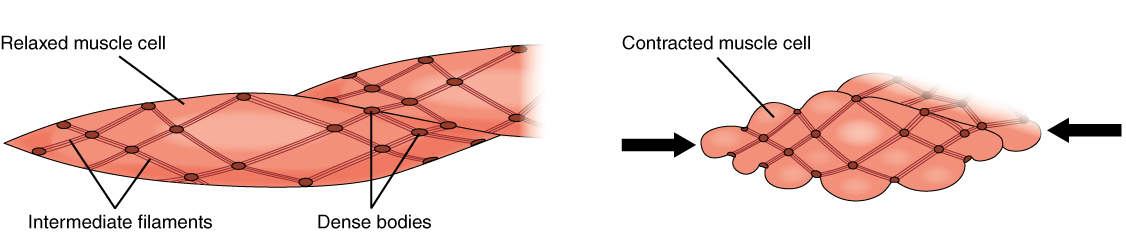
Smooth Muscle Cells
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal muscle, skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non-striated muscle tissue, striated, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It can be divided into two subgroups, ''single-unit'' and ''multi-unit'' smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of #Smooth muscle cells, smooth muscle cells muscle contraction, contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, urinary bladder, bladder and uterus. In the walls of blood vessels, and lymph vessels, (excluding blood and lymph capillaries) it is known as vascular smooth muscle. There is smooth muscle in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive Organ system, systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunica Intima
The tunica intima (Neo-Latin "inner coat"), or intima for short, is the innermost tunica (biology), tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It is made up of one layer of endothelium, endothelial cells (and macrophages in areas of disturbed blood flow), and is supported by an internal elastic lamina. The endothelial cells are in direct contact with the blood flow. The three layers of a blood vessel are an inner layer (the tunica intima), a middle layer (the tunica media), and an outer layer (the tunica externa). In dissection, the inner coat (tunica intima) can be separated from the middle (tunica media) by a little maceration, or it may be stripped off in small pieces; but, because of its friability, it cannot be separated as a complete membrane. It is a fine, transparent, colorless structure which is highly elastic, and, after death, is commonly corrugated into longitudinal wrinkles. Structure The structure of the tunica intima depends on the blood vessel type. Elastic artery, E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |