|
Intermodulation
Intermodulation (IM) or intermodulation distortion (IMD) is the amplitude modulation of Signal (electrical engineering), signals containing two or more different frequencies, caused by non-linear, nonlinearities or time variance in a system. The intermodulation between frequency components will form additional components at frequencies that are not just at harmonic frequencies (integer multiple (mathematics), multiples) of either, like harmonic distortion, but also at the sum and difference frequencies of the original frequencies and at sums and differences of multiples of those frequencies. Intermodulation is caused by non-linear behaviour of the signal processing (physical equipment or even algorithms) being used. The theoretical outcome of these non-linearities can be calculated by generating a Volterra series of the characteristic, or more approximately by a Taylor series. Practically all audio equipment has some non-linearity, so it will exhibit some amount of IMD, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Chord
A power chord , also called a fifth chord, is a colloquial name for a chord on guitar, especially on electric guitar, that consists of the root note and the fifth, as well as possibly octaves of those notes. Power chords are commonly played with an amp with intentionally added distortion or overdrive effects. Power chords are a key element of many styles of rock, especially heavy metal and punk rock. Analysis When two or more notes are played through a distortion process that non-linearly transforms the audio signal, additional partials are generated at the sums and differences of the frequencies of the harmonics of those notes ( intermodulation distortion). When a typical chord containing such intervals (for example, a major or minor chord) is played through distortion, the number of different frequencies generated, and the complex ratios between them, can make the resulting sound messy and indistinct. This effect is accentuated as most guitars are tuned ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distortion (music)
Distortion and overdrive are forms of audio signal processing used to alter the sound of amplified electric musical instruments, usually by increasing their gain (electronics), gain, producing a "fuzzy", "growling", or "gritty" tone. Distortion is most commonly used with the electric guitar, but may be used with other instruments, such as bass guitar, electric bass, electric piano, synthesizer, and Hammond organ. Guitarists playing Chicago blues, electric blues originally obtained an overdriven sound by turning up their vacuum tube-powered guitar amplifiers to high volumes, which caused the signal to clipping (audio), distort. Other ways to produce distortion have been developed since the 1960s, such as distortion effects unit, effect pedals. The growling tone of a distorted electric guitar is a key part of many genres, including blues and many rock music genres, notably hard rock, punk rock, hardcore punk, acid rock, grunge and heavy metal music, while the use of distorted bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
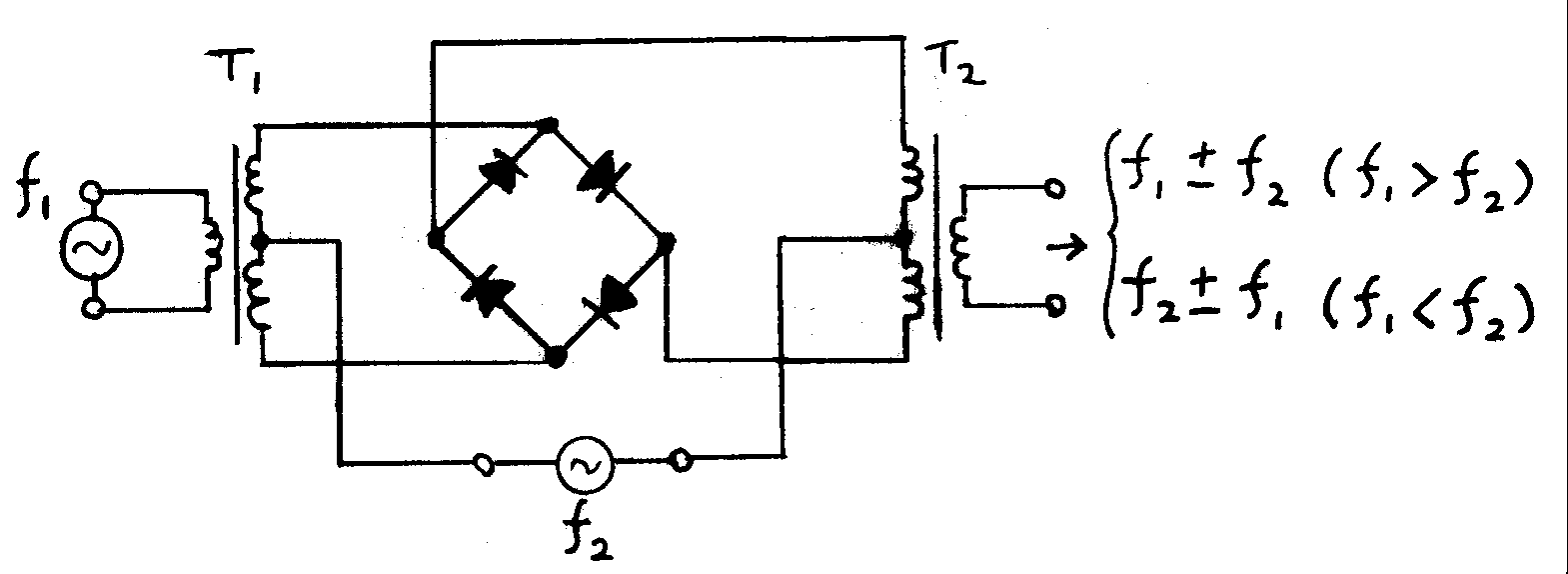
Electronic Mixer
An electronic mixer is a device that combines two or more electrical or electronic signals into one or two composite output signals. There are two basic circuits that both use the term ''mixer'', but they are very different types of circuits: additive mixers and multiplicative mixers. Additive mixers are also known as analog adders to distinguish from the related digital adder circuits. Simple additive mixers use Kirchhoff's circuit laws to add the currents of two or more signals together, and this terminology ("mixer") is only used in the realm of audio electronics where audio mixers are used to add together audio signals such as voice signals, music signals, and sound effects. Multiplicative mixers multiply together two time-varying input signals instantaneously (instant-by-instant). If the two input signals are both sinusoids of specified frequencies f1 and f2, then the output of the mixer will contain two new sinusoids that have the sum f1 + f2 frequency and the diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Harmonic Distortion
The total harmonic distortion (THD or THDi) is a measurement of the harmonic distortion present in a signal and is defined as the ratio of the sum of the powers of all harmonic components to the power of the fundamental frequency. Distortion factor, a closely related term, is sometimes used as a synonym. In audio systems, lower distortion means that the components in a loudspeaker, amplifier or microphone or other equipment produce a more accurate reproduction of an audio recording. In radio communications, devices with lower THD tend to produce less unintentional interference with other electronic devices. Since harmonic distortion can potentially widen the frequency spectrum of the output emissions from a device by adding signals at multiples of the input frequency, devices with high THD are less suitable in applications such as spectrum sharing and spectrum sensing. In power systems, lower THD implies lower peak currents, less heating, lower electromagnetic emissions, and le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spurious Emission
In radio communication, a spurious emission is any component of a radiated radio frequency signal, the complete suppression of which, would not impair the integrity of the modulation type, or the information being transmitted. A radiated signal outside of a transmitter's assigned channel is an example of a spurious emission. Spurious emissions can include harmonic emissions, intermodulation Intermodulation (IM) or intermodulation distortion (IMD) is the amplitude modulation of Signal (electrical engineering), signals containing two or more different frequencies, caused by non-linear, nonlinearities or time variance in a system. ... products and frequency conversion products. See also * Interference (communication) * Radio spectrum pollution References Radio technology {{radio-comm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volterra Series
The Volterra series is a model for non-linear behavior similar to the Taylor series. It differs from the Taylor series in its ability to capture "memory" effects. The Taylor series can be used for approximating the response of a nonlinear system to a given input if the output of the system depends strictly on the input at that particular time. In the Volterra series, the output of the nonlinear system depends on the input to the system at ''all'' other times. This provides the ability to capture the "memory" effect of devices like capacitors and inductors. It has been applied in the fields of medicine (biomedical engineering) and biology, especially neuroscience. It is also used in electrical engineering to model intermodulation distortion in many devices, including power amplifiers and frequency mixers. Its main advantage lies in its generalizability: it can represent a wide range of systems. Thus, it is sometimes considered a non-parametric model. In mathematics, a Volterra se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic Distortion
In signal processing, distortion is the alteration of the original shape (or other characteristic) of a signal. In communications and electronics it means the alteration of the waveform of an information-bearing signal, such as an audio signal representing sound or a video signal representing images, in an electronic device or communication channel. Distortion is usually unwanted, and so engineers strive to eliminate or minimize it. In some situations, however, distortion may be desirable. For example, in noise reduction systems like the Dolby noise-reduction system, Dolby system, an audio signal is deliberately distorted in ways that emphasize aspects of the signal that are subject to electrical noise, then it is symmetrically "undistorted" after passing through a noisy communication channel, reducing the noise in the received signal. Distortion is also used as a Distortion (music), musical effect, particularly with electric guitars. The addition of Electronic noise, noise o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superheterodyne Receiver
A superheterodyne receiver, often shortened to superhet, is a type of radio receiver that uses frequency mixing to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency (IF) which can be more conveniently processed than the original carrier frequency. It was invented by French radio engineer and radio manufacturer Lucien Lévy. Virtually all modern radio receivers use the superheterodyne principle. Precursors Early radio Early Morse code radio broadcasts were produced using an alternator connected to a spark gap. The output signal was at a carrier frequency defined by the physical construction of the gap, modulated by the alternating current signal from the alternator. Since the output frequency of the alternator was generally in the audible range, this produces an audible amplitude modulated (AM) signal. Simple radio detectors filtered out the high-frequency carrier, leaving the modulation, which was passed on to the user's headphones as an audible signal of do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Multiplier
An analog multiplier is an electronic circuit that produces an output level that is the mathematical product of the levels of its two analog signal inputs. Such circuits may be used to implement related functions such as ''squares'' by applying the same signal to both inputs, and ''square roots''. Types Electronic analog multipliers are classified by their function. A single-quadrant multiplier permits only one, typically positive, level on the inputs. A two-quadrant multiplier permits one input signal to swing to positive and negative levels, while the second input remains positive. In a all inputs may swing to positive or negative levels, producing a positive or negative output level. Voltage-controlled amplifier If one input of an analog multiplier is held at a steady voltage, a signal at the second input is scaled in proportion to the level on the fixed input. This may be considered a voltage-controlled amplifier or variable-gain amplifier. Applications are for electroni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diode
A diode is a two-Terminal (electronics), terminal electronic component that conducts electric current primarily in One-way traffic, one direction (asymmetric electrical conductance, conductance). It has low (ideally zero) Electrical resistance and conductance, resistance in one direction and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A semiconductor diode, the most commonly used type today, is a Crystallinity, crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. It has an Exponential function, exponential current–voltage characteristic. Semiconductor diodes were the first Semiconductor device, semiconductor electronic devices. The discovery of asymmetric electrical conduction across the contact between a Crystal, crystalline mineral and a metal was made by German physicist Ferdinand Braun in 1874. Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconducting materials such as gallium arsenide and germanium are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Mixer
In electronics, a mixer, or frequency mixer, is an electrical circuit that creates new frequencies from two signals applied to it. In its most common application, two signals are applied to a mixer, and it produces new signals at the sum and difference of the original frequencies. Other frequency components may also be produced in a practical frequency mixer. Mixers are widely used to shift signals from one frequency range to another, a process known as heterodyning, for convenience in transmission or further signal processing. For example, a key component of a superheterodyne receiver is a mixer used to move received signals to a common intermediate frequency. Frequency mixers are also used to modulation, modulate a carrier signal in Transmitter, radio transmitters. Types The essential characteristic of a mixer is that it produces a component in its output which is the product of the two input signals. Both active and passive circuits can realize mixers. Passive mixers use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semiconductor material, usually with at least three terminal (electronics), terminals for connection to an electronic circuit. A voltage or Electric current, current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Some transistors are packaged individually, but many more in miniature form are found embedded in integrated circuits. Because transistors are the key active components in practically all modern electronics, many people consider them one of the 20th century's greatest inventions. Physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld proposed the concept of a field-effect transisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |