|
Interlobar Arteries
The interlobar arteries are vessels of the renal circulation The renal circulation supplies the blood to the kidneys via the renal artery, renal arteries, left and right, which branch directly from the abdominal aorta. Despite their relatively small size, the kidneys receive approximately 20% of the cardiac ... which supply the renal lobes. The interlobar arteries branch from the lobar arteries which branch from the segmental arteries, from the renal artery. They give rise to arcuate arteries. References External links * - "Renal Vasculature: Efferent Arterioles & Peritubular Capillaries" * - "Urinary System: neonatal kidney, vasculature" Diagram at eku.edu* * Kidney anatomy {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Pyramid
The renal medulla (Latin: ''medulla renis'' 'marrow of the kidney') is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. Blood enters into the kidney via the renal artery, which then splits up to form the segmental arteries which then branch to form interlobar arteries. The interlobar arteries each in turn branch into arcuate arteries, which in turn branch to form interlobular arteries, and these finally reach the glomerulus (kidney), glomeruli. At the glomerulus the blood reaches a highly disfavourable pressure gradient and a large exchange surface area, which forces the serum (blood), serum portion of the blood out of the vessel and into the renal tubules. Flow continues through the renal tubules, including the proximal tubule, the loop of Henle, through the distal tubule and finally leaves the kidney by means of the collecting duct, leading to the renal pelvis, the dilated portion of the ureter. The renal med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Sinus
The renal sinus is a cavity within the kidney which is occupied by the renal pelvis, renal calyces, blood vessels, nerves and fat. The renal hilum extends into a large cavity within the kidney occupied by the renal vessels, minor renal calyces, major renal calyces, renal pelvis and some adipose tissue Adipose tissue (also known as body fat or simply fat) is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, Blood vessel, vascular endothel .... Additional images File:Slide3iii.JPG, Renal sinus File:Slide22iii.JPG, Renal sinus References Kidney anatomy {{genitourinary-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
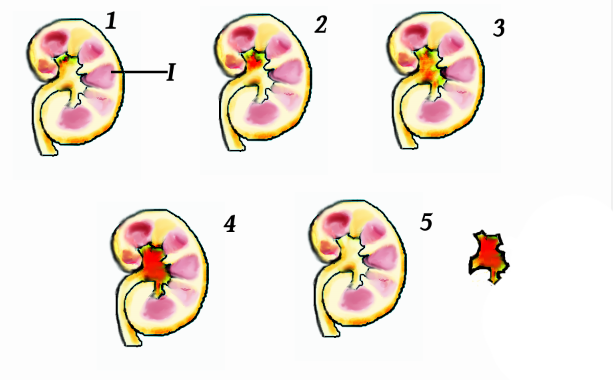
Renal Lobes
The renal lobe is a portion of a kidney consisting of a renal pyramid and the renal cortex above it. In humans, on average there are 7 to 18 renal lobes. It is visible without a microscope, though it is easier to see in humans than in other animals. It is composed of many renal lobules, which are not visible without a microscope. See also * Renal capsule * Renal medulla The renal medulla (Latin: ''medulla renis'' 'marrow of the kidney') is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. Blood enters into the kidney via the renal artery, which ... References External links * Kidney anatomy {{Portal bar, Anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Circulation
The renal circulation supplies the blood to the kidneys via the renal artery, renal arteries, left and right, which branch directly from the abdominal aorta. Despite their relatively small size, the kidneys receive approximately 20% of the cardiac output. Each renal artery branches into segmental arteries, dividing further into interlobar arteries, which penetrate the renal capsule and extend through the renal columns between the renal pyramids. The interlobar arteries then supply blood to the arcuate arteries that run through the boundary of the cortex and the medulla. Each arcuate artery supplies several interlobular arteries that feed into the afferent arterioles that supply the glomerulus (kidney), glomeruli. After filtration occurs, the blood moves through a small network of venules that converge into interlobular veins. As with the arteriole distribution, the veins follow the same pattern: the interlobular provide blood to the arcuate veins then back to the interlobar veins, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interlobar Veins
The interlobar veins are veins of the renal circulation The renal circulation supplies the blood to the kidneys via the renal artery, renal arteries, left and right, which branch directly from the abdominal aorta. Despite their relatively small size, the kidneys receive approximately 20% of the cardiac ... which drain the renal lobes. They collect blood from the arcuate veins. The interlobar veins unite to form a renal vein. Each interlobar vein passes along the edge of the renal pyramids. References External links * - "Renal Vasculature: Efferent Arterioles & Peritubular Capillaries" * - "Urinary System: neonatal kidney, vasculature" Kidney anatomy Thoracic veins {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcuate Arteries
The arcuate arteries of the kidney, also known as arciform arteries, are vessels of the renal circulation. They are located at the border of the renal cortex and renal medulla. They are named after the fact that they are shaped in arcs due to the nature of the shape of the renal medulla. Arcuate arteries arise from renal interlobar arteries The interlobar arteries are vessels of the renal circulation The renal circulation supplies the blood to the kidneys via the renal artery, renal arteries, left and right, which branch directly from the abdominal aorta. Despite their relatively sm .... References External links * - "Urinary System: kidney, PAS stain, arcuate artery and vein, longitudinal" * - "Urinary System: kidney, PAS stain, arcuate artery and vein, transverse" * - "Urinary System: neonatal kidney, vasculature" Kidney anatomy {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segmental Arteries
The renal circulation supplies the blood to the kidneys via the renal arteries, left and right, which branch directly from the abdominal aorta. Despite their relatively small size, the kidneys receive approximately 20% of the cardiac output. Each renal artery branches into segmental arteries, dividing further into interlobar arteries, which penetrate the renal capsule and extend through the renal columns between the renal pyramids. The interlobar arteries then supply blood to the arcuate arteries that run through the boundary of the cortex and the medulla. Each arcuate artery supplies several interlobular arteries that feed into the afferent arterioles that supply the glomeruli. After filtration occurs, the blood moves through a small network of venules that converge into interlobular veins. As with the arteriole distribution, the veins follow the same pattern: the interlobular provide blood to the arcuate veins then back to the interlobar veins, which come to form the renal v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Artery
The renal arteries are paired arteries that supply the kidneys with blood. Each is directed across the crus of the diaphragm, so as to form nearly a right angle. The renal arteries carry a large portion of total blood flow to the kidneys. Up to a third of total cardiac output can pass through the renal arteries to be filtered by the kidneys. Structure The renal arteries normally arise at a 90° angle off of the left interior side of the abdominal aorta, immediately below the superior mesenteric artery. They have a radius of approximately 0.25 cm, 0.26 cm at the root. The measured mean diameter can differ depending on the imaging method used. For example, the diameter was found to be 5.04 ± 0.74 mm using ultrasound but 5.68 ± 1.19 mm using angiography. Due to the anatomical position of the aorta, the inferior vena cava, and the kidneys, the right renal artery is normally longer than the left renal artery. * The right passes behind the inferior vena cava, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Column
The renal columns, Bertin columns, or columns of Bertin, a.k.a. columns of Bertini are extensions of the renal cortex in between the renal pyramids. They allow the cortex to be better anchored. (Cortical extensions into the medullary space.) Each column consists of lines of blood vessels and urinary tubes and a fibrous material. A hypertrophied renal column (or ''renal pseudotumor'') may be differentiated from an actual renal tumor with the help of a DMSA scan. The scan will show the area as one with normal activity if it is a pseudotumor or will show decreased uptake if it is a cystic or solid renal mass. See also * Renal pyramids * Renal papilla * Renal medulla The renal medulla (Latin: ''medulla renis'' 'marrow of the kidney') is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. Blood enters into the kidney via the renal artery, which ... Additional images File:Slide12iii.JPG, Renal column File:Slide1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Papilla
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid-base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Calyx
The renal calyces ( calyx) are conduits in the kidney through which urine passes. The minor calyces form a cup-shaped drain around the apex of the renal pyramids. Urine formed in the kidney passes through a renal papilla at the apex into the minor calyx; four or five minor calyces converge to form a major calyx through which urine passes into the renal pelvis (which in turn drains urine out of the kidney through the ureter). Function Peristalsis of the smooth muscle originating in pace-maker cells originating in the walls of the calyces propels urine through the renal pelvis and ureters to the bladder. The initiation is caused by the increase in volume that stretches the walls of the calyces. This causes them to fire impulses which stimulate rhythmical contraction and relaxation, called peristalsis. Parasympathetic innervation enhances the peristalsis while sympathetic innervation inhibits it. Clinical significance A "staghorn calculus" is a kidney stone that may extend into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |