|
Inertial
In classical physics and special relativity, an inertial frame of reference (also called an inertial space or a Galilean reference frame) is a frame of reference in which objects exhibit inertia: they remain at rest or in uniform motion relative to the frame until acted upon by external forces. In such a frame, the laws of nature can be observed without the need to correct for acceleration. All frames of reference with zero acceleration are in a state of constant rectilinear motion (straight-line motion) with respect to one another. In such a frame, an object with zero net force acting on it, is perceived to move with a constant velocity, or, equivalently, Newton's first law of motion holds. Such frames are known as inertial. Some physicists, like Isaac Newton, originally thought that one of these frames was absolute — the one approximated by the fixed stars. However, this is not required for the definition, and it is now known that those stars are in fact moving, relative to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fictitious Force
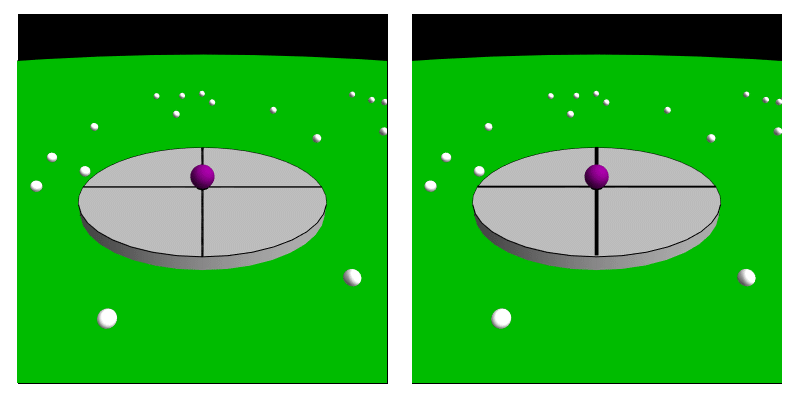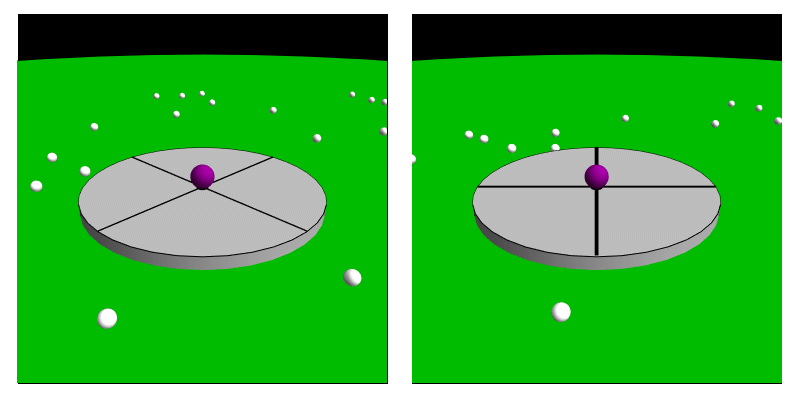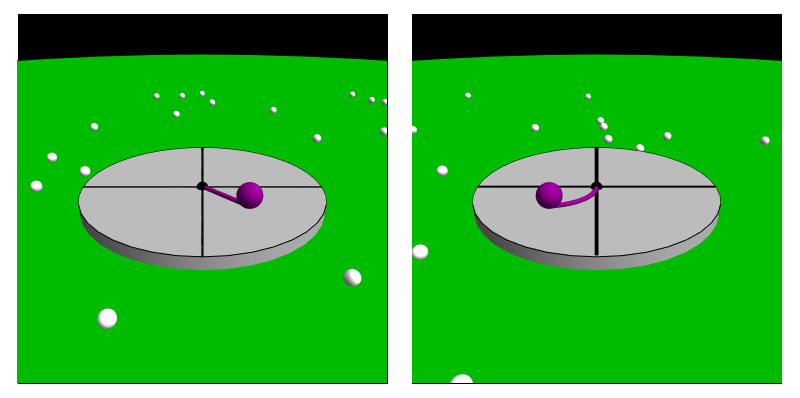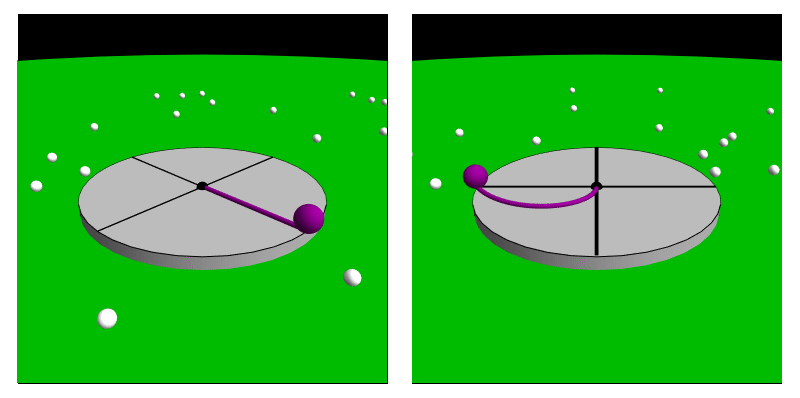
A fictitious force, also known as an inertial force or pseudo-force, is a force that appears to act on an object when its motion is described or experienced from a non-inertial reference frame, non-inertial frame of reference. Unlike real forces, which result from physical interactions between objects, fictitious forces occur due to the acceleration of the observer’s frame of reference rather than any actual force acting on a body. These forces are necessary for describing motion correctly within an accelerating frame, ensuring that Newton's laws of motion#Second, Newton's second law of motion remains applicable. Common examples of fictitious forces include the centrifugal force, which appears to push objects outward in a rotating system; the Coriolis force, which affects moving objects in a rotating frame such as the Earth; and the Euler force, which arises when a rotating system changes its angular velocity. While these forces are not real in the sense of being caused by ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coriolis Effect
In physics, the Coriolis force is a pseudo force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the left of the motion of the object. In one with anticlockwise (or counterclockwise) rotation, the force acts to the right. Deflection of an object due to the Coriolis force is called the Coriolis effect. Though recognized previously by others, the mathematical expression for the Coriolis force appeared in an 1835 paper by French scientist Gaspard-Gustave de Coriolis, in connection with the theory of water wheels. Early in the 20th century, the term ''Coriolis force'' began to be used in connection with meteorology. Newton's laws of motion describe the motion of an object in an inertial (non-accelerating) frame of reference. When Newton's laws are transformed to a rotating frame of reference, the Coriolis and centrifugal accelerations appear. When applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory of the relationship between Spacetime, space and time. In Albert Einstein's 1905 paper, Annus Mirabilis papers#Special relativity, "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies", the theory is presented as being based on just Postulates of special relativity, two postulates: # The laws of physics are Invariant (physics), invariant (identical) in all Inertial frame of reference, inertial frames of reference (that is, Frame of reference, frames of reference with no acceleration). This is known as the principle of relativity. # The speed of light in vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of the motion of light source or observer. This is known as the principle of light constancy, or the principle of light speed invariance. The first postulate was first formulated by Galileo Galilei (see ''Galilean invariance''). Background Special relativity builds upon important physics ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-inertial Reference Frame
A non-inertial reference frame (also known as an accelerated reference frame) is a frame of reference that undergoes acceleration with respect to an inertial frame. An accelerometer at rest in a non-inertial frame will, in general, detect a non-zero acceleration. While the laws of motion are the same in all inertial frames, in non-inertial frames, they vary from frame to frame, depending on the acceleration. In classical mechanics it is often possible to explain the motion of bodies in non-inertial reference frames by introducing additional fictitious forces (also called inertial forces, pseudo-forces, and d'Alembert forces) to Newton's second law. Common examples of this include the Coriolis force and the centrifugal force. In general, the expression for any fictitious force can be derived from the acceleration of the non-inertial frame. As stated by Goodman and Warner, "One might say that F ''m''a holds in any coordinate system provided the term 'force' is redefined to inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrifugal Force
Centrifugal force is a fictitious force in Newtonian mechanics (also called an "inertial" or "pseudo" force) that appears to act on all objects when viewed in a rotating frame of reference. It appears to be directed radially away from the axis of rotation of the frame. The magnitude of the centrifugal force ''F'' on an object of mass ''m'' at the perpendicular distance ''ρ'' from the axis of a rotating frame of reference with angular velocity is F = m\omega^2 \rho. This fictitious force is often applied to rotating devices, such as centrifuges, centrifugal pumps, centrifugal governors, and centrifugal clutches, and in centrifugal railways, planetary orbits and banked curves, when they are analyzed in a non–inertial reference frame such as a rotating coordinate system. The term has sometimes also been used for the '' reactive centrifugal force'', a real frame-independent Newtonian force that exists as a reaction to a centripetal force in some scenarios. History F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principle Of Relativity
In physics, the principle of relativity is the requirement that the equations describing the laws of physics have the same form in all admissible frames of reference. For example, in the framework of special relativity, the Maxwell equations have the same form in all inertial frames of reference. In the framework of general relativity, the Maxwell equations or the Einstein field equations have the same form in arbitrary frames of reference. Several principles of relativity have been successfully applied throughout science, whether implicitly (as in Newtonian mechanics) or explicitly (as in Albert Einstein's special relativity and general relativity). Basic concepts Certain principles of relativity have been widely assumed in most scientific disciplines. One of the most widespread is the belief that any law of nature should be the same at all times; and scientific investigations generally assume that laws of nature are the same regardless of the person measuring them. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorentz Transformation
In physics, the Lorentz transformations are a six-parameter family of Linear transformation, linear coordinate transformation, transformations from a Frame of Reference, coordinate frame in spacetime to another frame that moves at a constant velocity relative to the former. The respective inverse transformation is then parameterized by the negative of this velocity. The transformations are named after the Dutch physicist Hendrik Lorentz. The most common form of the transformation, parametrized by the real constant v, representing a velocity confined to the -direction, is expressed as \begin t' &= \gamma \left( t - \frac \right) \\ x' &= \gamma \left( x - v t \right)\\ y' &= y \\ z' &= z \end where and are the coordinates of an event in two frames with the spatial origins coinciding at , where the primed frame is seen from the unprimed frame as moving with speed along the -axis, where is the speed of light, and \gamma = \frac is the Lorentz factor. When speed is much smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frame Of Reference
In physics and astronomy, a frame of reference (or reference frame) is an abstract coordinate system, whose origin (mathematics), origin, orientation (geometry), orientation, and scale (geometry), scale have been specified in physical space. It is based on a set of reference points, defined as point (geometry), geometric points whose position (geometry), position is identified both mathematically (with numerical coordinate values) and physically (signaled by conventional markers). An important special case is that of ''inertial reference frames'', a stationary or uniformly moving frame. For ''n'' dimensions, reference points are sufficient to fully define a reference frame. Using Cartesian coordinate system, rectangular Cartesian coordinates, a reference frame may be defined with a reference point at the origin and a reference point at one unit distance along each of the ''n'' coordinate Cartesian coordinate system, axes. In Theory of relativity, Einsteinian relativity, referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newton's Laws Of Motion
Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. These laws, which provide the basis for Newtonian mechanics, can be paraphrased as follows: # A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, unless it is acted upon by a force. # At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum is changing with time. # If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but opposite directions. The three laws of motion were first stated by Isaac Newton in his ''Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica'' (''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy''), originally published in 1687. Newton used them to investigate and explain the motion of many physical objects and systems. In the time since Newton, new insights, especially around t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newtonian Physics
Classical mechanics is a physical theory describing the motion of objects such as projectiles, parts of machinery, spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. The development of classical mechanics involved substantial change in the methods and philosophy of physics. The qualifier ''classical'' distinguishes this type of mechanics from physics developed after the revolutions in physics of the early 20th century, all of which revealed limitations in classical mechanics. The earliest formulation of classical mechanics is often referred to as Newtonian mechanics. It consists of the physical concepts based on the 17th century foundational works of Sir Isaac Newton, and the mathematical methods invented by Newton, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Leonhard Euler and others to describe the motion of bodies under the influence of forces. Later, methods based on energy were developed by Euler, Joseph-Louis Lagrange, William Rowan Hamilton and others, leading to the development of analy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Mechanics
Classical mechanics is a Theoretical physics, physical theory describing the motion of objects such as projectiles, parts of Machine (mechanical), machinery, spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. The development of classical mechanics involved Scientific Revolution, substantial change in the methods and philosophy of physics. The qualifier ''classical'' distinguishes this type of mechanics from physics developed after the History of physics#20th century: birth of modern physics, revolutions in physics of the early 20th century, all of which revealed limitations in classical mechanics. The earliest formulation of classical mechanics is often referred to as Newtonian mechanics. It consists of the physical concepts based on the 17th century foundational works of Sir Isaac Newton, and the mathematical methods invented by Newton, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Leonhard Euler and others to describe the motion of Physical body, bodies under the influence of forces. Later, methods bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity, and as Einstein's theory of gravity, is the differential geometry, geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics. General theory of relativity, relativity generalizes special relativity and refines Newton's law of universal gravitation, providing a unified description of gravity as a geometric property of space and time in physics, time, or four-dimensional spacetime. In particular, the ''curvature of spacetime'' is directly related to the energy and momentum of whatever is present, including matter and radiation. The relation is specified by the Einstein field equations, a system of second-order partial differential equations. Newton's law of universal gravitation, which describes gravity in classical mechanics, can be seen as a prediction of general relativity for the almost flat spacetime geometry around stationary mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |