|
Indium
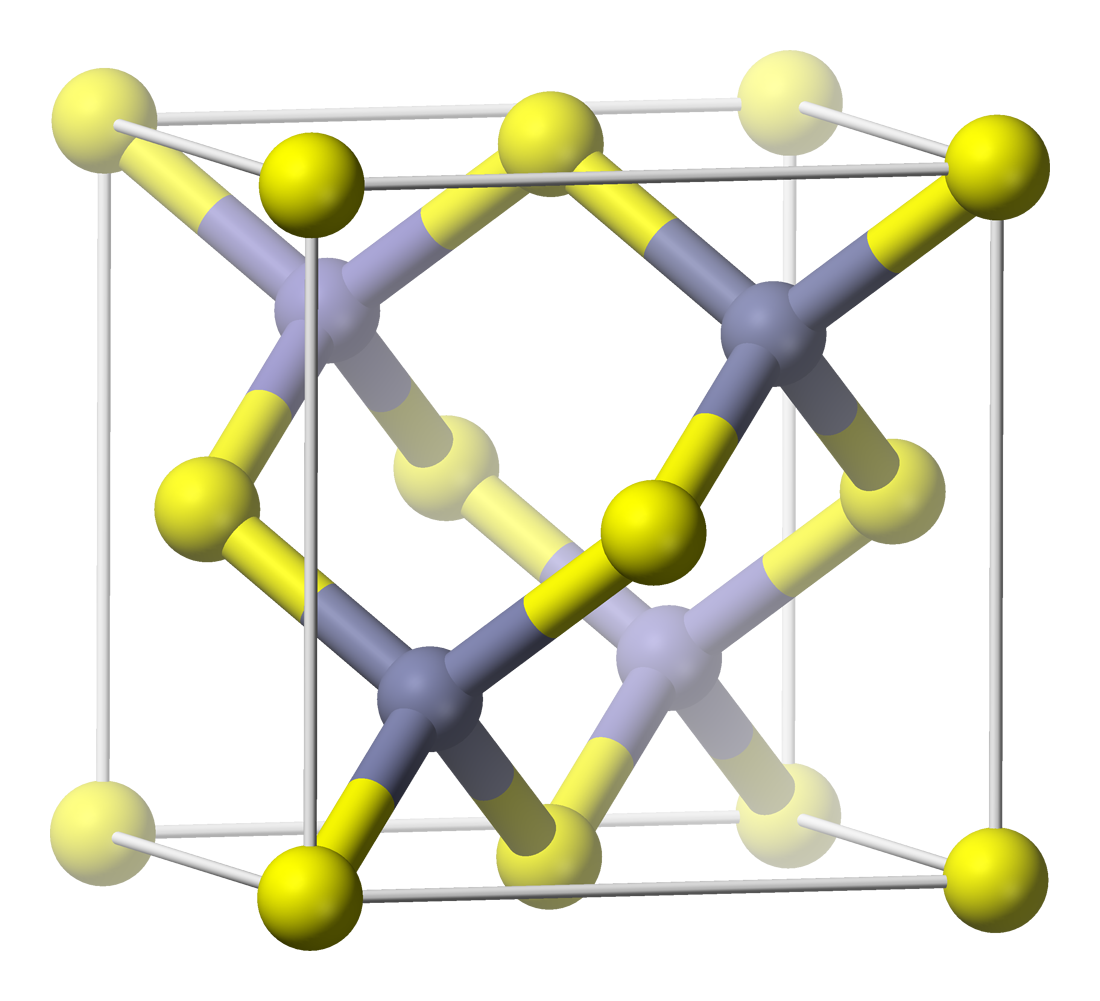
Indium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol In and atomic number 49. It is a silvery-white post-transition metal and one of the softest elements. Chemically, indium is similar to gallium and thallium, and its properties are largely intermediate between the two. It was discovered in 1863 by Ferdinand Reich and Hieronymous Theodor Richter by spectroscope, spectroscopic methods and named for the indigo blue line in its spectrum. Indium is used primarily in the production of flat-panel displays as indium tin oxide (ITO), a transparent and conductive coating applied to glass. It is also used in the semiconductor industry, in low-melting-point metal alloys such as Solder#Alloying element roles, solders and soft-metal high-vacuum seals. It is produced exclusively as a by-product during the processing of the ores of other metals, chiefly from sphalerite and other zinc Sulfide mineral, sulfide ores. Indium has no biological role and its compounds are toxic when inhaled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indium Wetting Glass
Indium is a chemical element; it has symbol In and atomic number 49. It is a silvery-white post-transition metal and one of the softest elements. Chemically, indium is similar to gallium and thallium, and its properties are largely intermediate between the two. It was discovered in 1863 by Ferdinand Reich and Hieronymous Theodor Richter by spectroscopic methods and named for the indigo blue line in its spectrum. Indium is used primarily in the production of flat-panel displays as indium tin oxide (ITO), a transparent and conductive coating applied to glass. It is also used in the semiconductor industry, in low-melting-point metal alloys such as solders and soft-metal high-vacuum seals. It is produced exclusively as a by-product during the processing of the ores of other metals, chiefly from sphalerite and other zinc sulfide ores. Indium has no biological role and its compounds are toxic when inhaled or injected into the bloodstream, although they are poorly absorbed foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indium Tin Oxide
Indium tin oxide (ITO) is a ternary composition of indium, tin and oxygen in varying proportions. Depending on the oxygen content, it can be described as either a ceramic or an alloy. Indium tin oxide is typically encountered as an oxygen-saturated composition with a formulation of 74% In, 8% Sn, and 18% O by weight. Oxygen-saturated compositions are so typical that unsaturated compositions are termed ''oxygen-deficient ITO''. It is transparent and colorless in thin layers, while in bulk form it is yellowish to gray. In the infrared region of the spectrum it acts as a metal-like mirror. Indium tin oxide is one of the most widely used transparent conducting oxides, not just for its electrical conductivity and optical transparency, but also for the ease with which it can be deposited as a thin film, as well as its chemical resistance to moisture. As with all transparent conducting films, a compromise must be made between conductivity and transparency, since increasing the thickness a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
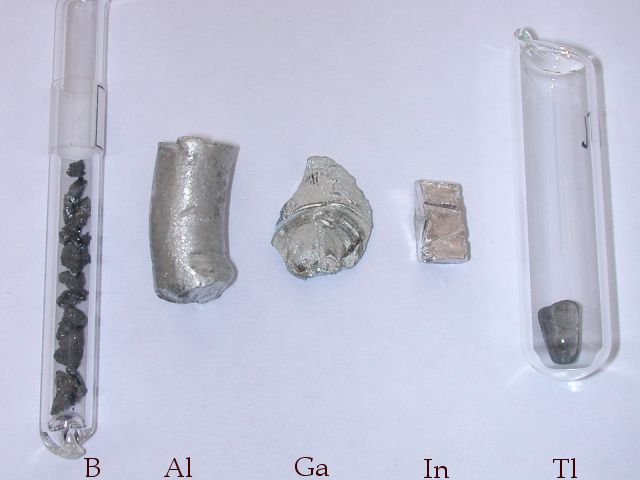
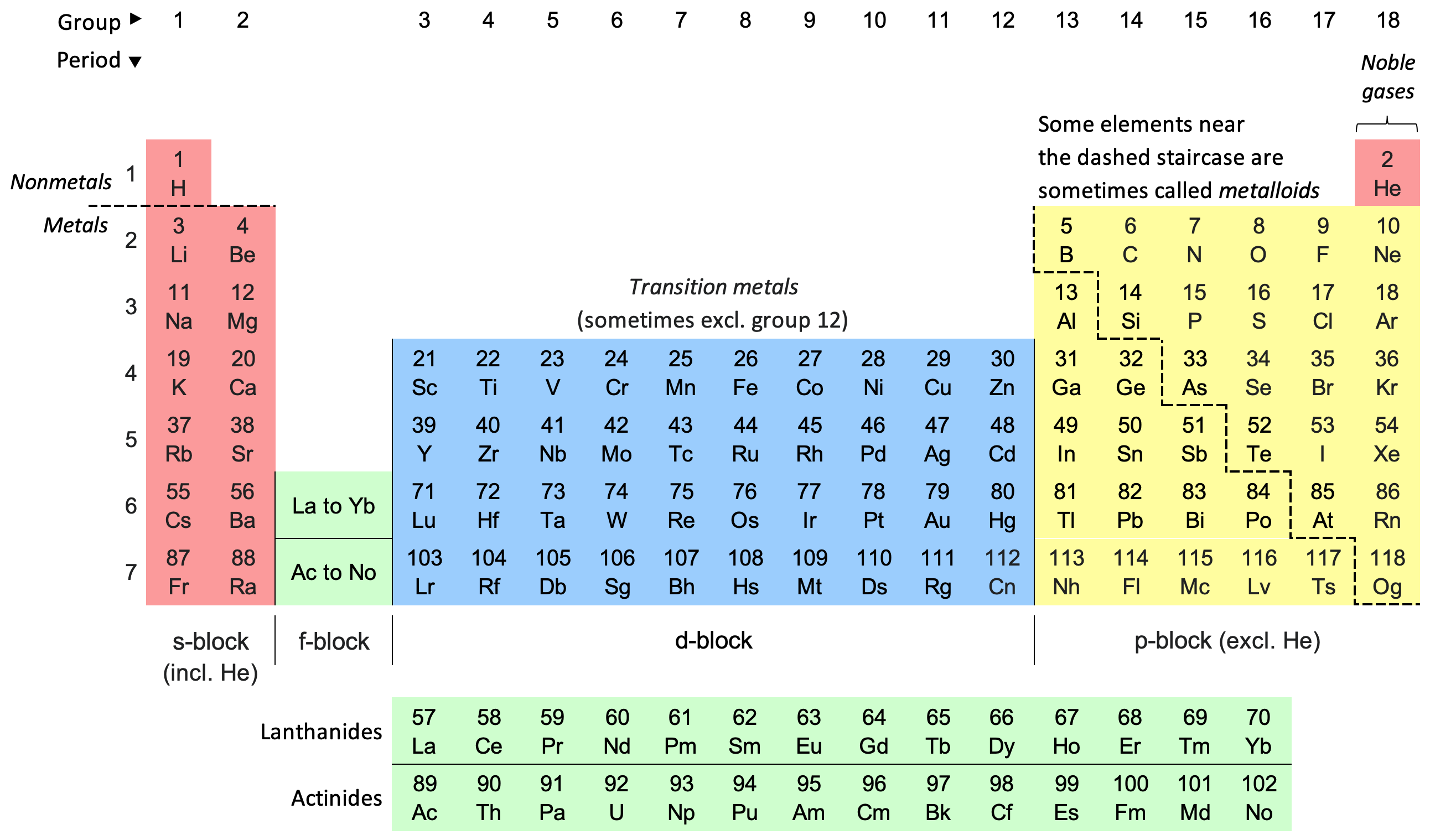
Boron Group
The boron group are the chemical elements in periodic table group, group 13 of the periodic table, consisting of boron (B), aluminium (Al), gallium (Ga), indium (In), thallium (Tl) and nihonium (Nh). This group lies in the p-block of the periodic table. The elements in the boron group are characterized by having three valence electrons. These elements have also been referred to as the triels. Several group 13 elements have biological roles in the ecosystem. Boron is a trace element in humans and is essential for some plants. Lack of boron can lead to stunted plant growth, while an excess can also cause harm by inhibiting growth. Aluminium has neither a biological role nor significant toxicity and is considered safe. Indium and gallium can stimulate metabolism; gallium is credited with the ability to bind itself to iron proteins. Thallium is highly toxic, interfering with the function of numerous vital enzymes, and has seen use as a pesticide. Characteristics Like other groups, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium
Gallium is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Discovered by the French chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1875, elemental gallium is a soft, silvery metal at standard temperature and pressure. In its liquid state, it becomes silvery white. If enough force is applied, solid gallium may fracture conchoidal fracture, conchoidally. Since its discovery in 1875, gallium has widely been used to make alloys with low melting points. It is also used in semiconductors, as a dopant in semiconductor substrates. The melting point of gallium, , is used as a temperature reference point. Gallium alloys are used in thermometers as a non-toxic and environmentally friendly alternative to Mercury (element), mercury, and can withstand higher temperatures than mercury. A melting point of , well below the freezing point of water, is claimed for the alloy galinstan (62–95% gallium, 5–22% indium, and 0–16% tin by weight), but that may be t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-transition Metal
The metallic elements in the periodic table located between the transition metals to their left and the chemically weak nonmetallic metalloids to their right have received many names in the literature, such as post-transition metals, poor metals, other metals, p-block metals, basic metals, and chemically weak metals. The most common name, ''post-transition metals'', is generally used in this article. Physically, these metals are soft (or brittle), have poor mechanical strength, and usually have melting points lower than those of the transition metals. Being close to the metal-nonmetal border, their crystalline structures tend to show covalent or directional bonding effects, having generally greater complexity or fewer nearest neighbours than other metallic elements. Chemically, they are characterised—to varying degrees—by covalent bonding tendencies, acid-base amphoterism and the formation of anionic species such as aluminates, stannates, and bismuthates (in the cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
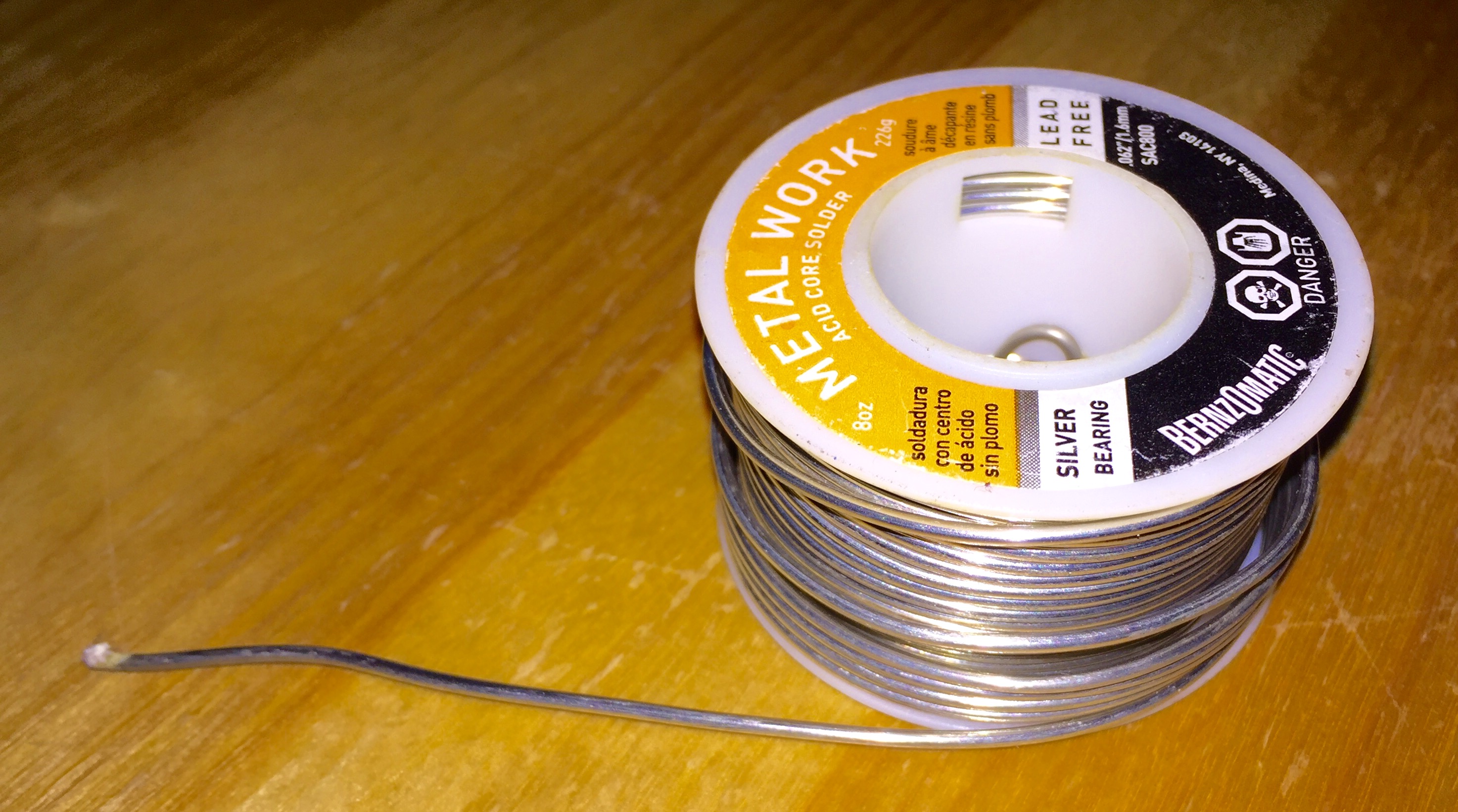
Solder
Solder (; North American English, NA: ) is a fusible alloy, fusible metal alloy used to create a permanent bond between metal workpieces. Solder is melted in order to wet the parts of the joint, where it adheres to and connects the pieces after cooling. Metals or alloys suitable for use as solder should have a lower melting point than the pieces to be joined. The solder should also be resistant to oxidative and corrosive effects that would degrade the joint over time. Solder used in making electrical connections also needs to have favorable electrical characteristics. Soft solder typically has a melting point range of , and is commonly used in electronics, plumbing, and sheet metal work. Alloys that melt between are the most commonly used. Soldering performed using alloys with a melting point above is called "hard soldering", "silver soldering", or brazing. In specific proportions, some alloys are eutectic — that is, the alloy's melting point is the lowest possible for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphalerite
Sphalerite is a sulfide mineral with the chemical formula . It is the most important ore of zinc. Sphalerite is found in a variety of deposit types, but it is primarily in Sedimentary exhalative deposits, sedimentary exhalative, Carbonate-hosted lead-zinc ore deposits, Mississippi-Valley type, and Volcanogenic massive sulfide ore deposit, volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. It is found in association with galena, chalcopyrite, pyrite (and other sulfide mineral, sulfides), calcite, dolomite (mineral), dolomite, quartz, rhodochrosite, and fluorite. German geologist Ernst Friedrich Glocker discovered sphalerite in 1847, naming it based on the Greek word ''sphaleros'', meaning "deceiving", due to the difficulty of identifying the mineral. In addition to zinc, sphalerite is an ore of cadmium, gallium, germanium, and indium. Miners have been known to refer to sphalerite as ''zinc blende'', ''black-jack'', and ''ruby blende''. Marmatite is an opaque black variety with a high iron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodic Table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows (" periods") and columns (" groups"). It is an icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other sciences. It is a depiction of the periodic law, which states that when the elements are arranged in order of their atomic numbers an approximate recurrence of their properties is evident. The table is divided into four roughly rectangular areas called blocks. Elements in the same group tend to show similar chemical characteristics. Vertical, horizontal and diagonal trends characterize the periodic table. Metallic character increases going down a group and from right to left across a period. Nonmetallic character increases going from the bottom left of the periodic table to the top right. The first periodic table to become generally accepted was that of the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869; he formulated the periodic law as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thallium
Thallium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Tl and atomic number 81. It is a silvery-white post-transition metal that is not found free in nature. When isolated, thallium resembles tin, but discolors when exposed to air. Chemists William Crookes and Claude-Auguste Lamy discovered thallium independently, in 1861, in residues of sulfuric acid production. Both used the newly developed method of flame spectroscopy, in which thallium produces a notable green spectral line. Thallium, from Greek language, Greek , , meaning "green shoot" or "twig", was named by Crookes. It was isolated by both Lamy and Crookes in 1862, Lamy by electrolysis and Crookes by precipitation and melting of the resultant powder. Crookes exhibited it as a powder precipitated by zinc at the 1862 International Exhibition, International Exhibition, which opened on 1 May that year. Thallium tends to form the +3 and +1 oxidation states. The +3 state resembles that of the other elements in Boron Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hieronymous Theodor Richter
Hieronymus Theodor Richter (21 November 1824 – 25 September 1898) was a German chemist. In 1863, while working at the Freiberg University of Mining and Technology, he co-discovered indium with Ferdinand Reich. Life From 1843 to 1847, he studied at the Bergakademie Freiberg (with Carl Friedrich Plattner, among others) and became a member of the Corps Saxo-Borussia Freiberg. He then worked for the Freiberg Hüttenwerken, since 1853 as a metallurgist chemist. From 1875 to 1896, Theodor Richter worked as director of the Mining Academy and was the last of the Freiberg directors elected for lifetime. In 1890 he was elected a member of the Leopoldina. He died September 25, 1898, in Freiberg, Saxony Freiberg () is a college town, university and former mining town in Saxony, Germany, with around 41,000 inhabitants. The city lies in the foreland of the Ore Mountains, in the Saxon urbanization axis, which runs along the northern edge of the ..., at the age of 73. Honours In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Reich
Ferdinand Reich (19 February 1799 – 27 April 1882) was a German chemist who co-discovered indium in 1863 with Hieronymous Theodor Richter. Reich was born in Bernburg, Anhalt-Bernburg, Holy Roman Empire and died in Freiberg, Saxony, Freiberg. He was color blindness, color blind, or could only see in whites and blacks, and that is why Theodor Richter became his science partner. Richter would examine the colors produced in reactions that they studied. Reich and Richter ended up isolating the indium, creating a small supply, although it was later found in more regions. They isolated the indium at the Technische Universität Bergakademie Freiberg, Freiberg University of Mining and Technology in Germany. In 1803, Laplace and Gauss both derived that, if a heavy object is dropped from a height h at latitude \Phi, and the earth rotates from west to east with angular velocity \Omega, then the object would be deflected to the east by a distance of d=2 / 3 \Omega \cos (\Phi) \sqrt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tin Cry
Tin cry is the characteristic sound heard when a bar made of tin is bent. Variously described as a "screaming" or "crackling" sound, the effect is caused by the crystal twinning in the metal. The sound is not particularly loud, despite terms like "crying" and "screaming". It is very noticeable when a hot-dip tin-coated sheet metal is bent at high speed over rollers during processing. Tin cry is often demonstrated using a simple science experiment. A bar of tin will "cry" repeatedly when bent until it breaks. The experiment can then be recycled by melting and recrystallizing the metal. The low melting point of tin, , makes re-casting easy. Tin anneals at reasonably low temperature as well, normalizing tin's microstructure of crystallites/grains. Although the cry is most typical of tin, a similar effect occurs in other metals, such as niobium, indium, zinc, cadmium, gallium Gallium is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Discovered b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |