|
Image Derivatives
Image derivatives can be computed by using small convolution filters of size 2 × 2 or 3 × 3, such as the Laplacian, Sobel, Roberts and Prewitt operators. However, a larger mask will generally give a better approximation of the derivative and examples of such filters are Gaussian derivatives and Gabor filters. Sometimes high frequency noise needs to be removed and this can be incorporated in the filter so that the Gaussian kernel will act as a band pass filter. The use of Gabor filters in image processing has been motivated by some of its similarities to the perception in the human visual system. The pixel value is computed as a convolution : p'_u=\mathbf \ast G where \mathbf is the derivative kernel and G is the pixel values in a region of the image and \ast is the operator that performs the convolution. Sobel derivatives The derivative kernels, known as the Sobel operator are defined as follows, for the u and v directions respectively: : p'_u = \begi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrete Laplace Operator
In mathematics, the discrete Laplace operator is an analog of the continuous Laplace operator, defined so that it has meaning on a Graph (discrete mathematics), graph or a lattice (group), discrete grid. For the case of a finite-dimensional graph (having a finite number of edges and vertices), the discrete Laplace operator is more commonly called the Laplacian matrix. The discrete Laplace operator occurs in physics problems such as the Ising model and loop quantum gravity, as well as in the study of discrete dynamical systems. It is also used in numerical analysis as a stand-in for the continuous Laplace operator. Common applications include image processing, where it is known as the Laplace filter, and in machine learning for cluster analysis, clustering and semi-supervised learning on neighborhood graphs. Definitions Graph Laplacians There are various definitions of the ''discrete Laplacian'' for Graph (discrete mathematics), graphs, differing by sign and scale factor (sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
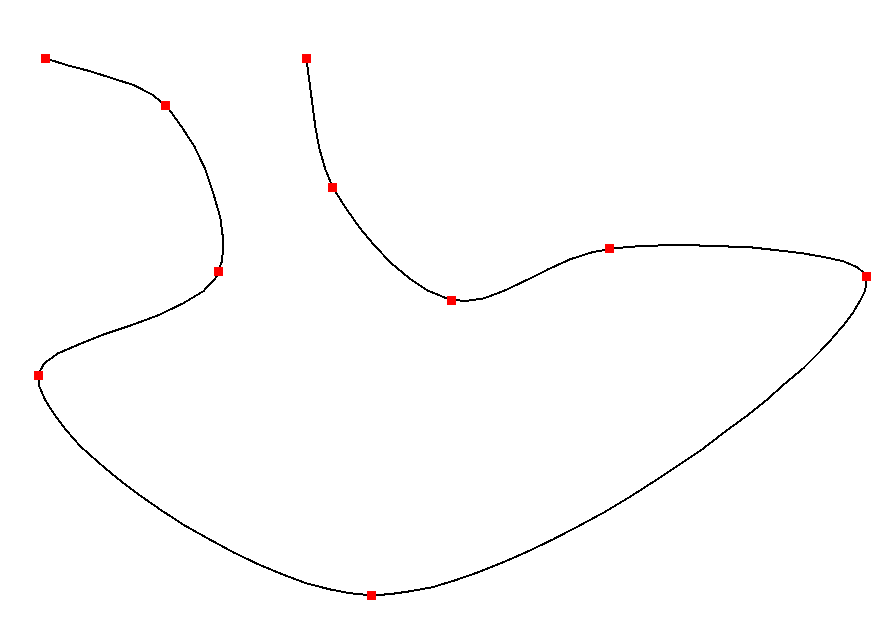
Bézier Curve
A Bézier curve ( , ) is a parametric equation, parametric curve used in computer graphics and related fields. A set of discrete "control points" defines a smooth, continuous curve by means of a formula. Usually the curve is intended to approximate a real-world shape that otherwise has no mathematical representation or whose representation is unknown or too complicated. The Bézier curve is named after France, French engineer Pierre Bézier (1910–1999), who used it in the 1960s for designing curves for the bodywork of Renault cars. Other uses include the design of computer fonts and animation. Bézier curves can be combined to form a Composite Bézier curve, Bézier spline, or generalized to higher dimensions to form Bézier surfaces. The Bézier triangle is a special case of the latter. In vector graphics, Bézier curves are used to model smooth curves that can be scaled indefinitely. "Paths", as they are commonly referred to in image manipulation programs, are combinations of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articles With Example MATLAB/Octave Code
Article often refers to: * Article (grammar), a grammatical element used to indicate definiteness or indefiniteness * Article (publishing), a piece of nonfictional prose that is an independent part of a publication Article(s) may also refer to: Government and law * Elements of treaties of the European Union * Articles of association, the regulations governing a company, used in India, the UK and other countries; called articles of incorporation in the US * Articles of clerkship, the contract accepted to become an articled clerk * Articles of Confederation, the predecessor to the current United States Constitution * Article of impeachment, a formal document and charge used for impeachment in the United States * Article of manufacture, in the United States patent law, a category of things that may be patented * Articles of organization, for limited liability organizations, a US equivalent of articles of association Other uses * Article element , in HTML * "Articles", a song on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Gradient
An image gradient is a directional change in the intensity or color in an image. The gradient of the image is one of the fundamental building blocks in image processing. For example, the Canny edge detector uses image gradient for edge detection. In graphics software for digital image editing, the term gradient or color gradient is also used for a gradual blend of color which can be considered as an even wiktionary:gradation, gradation from low to high values, and seen from black to white in the images to the right. Another name for this is ''color progression''. Mathematically, the gradient of a two-variable function (here the image intensity function) at each image point is a 2D vector (geometric), vector with the components given by the derivatives in the horizontal and vertical directions. At each image point, the gradient vector points in the direction of largest possible intensity increase, and the length of the gradient vector corresponds to the rate of change in that direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savitzky–Golay Filter
A Savitzky–Golay filter is a digital filter that can be applied to a set of digital data points for the purpose of smoothing the data, that is, to increase the precision of the data without distorting the signal tendency. This is achieved, in a process known as convolution, by fitting successive sub-sets of adjacent data points with a low-degree polynomial by the method of linear least squares. When the data points are equally spaced, an analytical solution to the least-squares equations can be found, in the form of a single set of "convolution coefficients" that can be applied to all data sub-sets, to give estimates of the smoothed signal, (or derivatives of the smoothed signal) at the central point of each sub-set. The method, based on established mathematical procedures,. "Graduation Formulae obtained by fitting a Polynomial." was popularized by Abraham Savitzky and Marcel J. E. Golay, who published tables of convolution coefficients for various polynomials and sub-set sizes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steerable Filter
In applied mathematics, a steerable filter is an orientation-selective convolution kernel used for image enhancement and feature extraction that can be expressed via a linear combination of a small set of rotated versions of itself. As an example, the oriented first derivative of a 2D Gaussian is a steerable filter. The oriented first order derivative can be obtained by taking the dot product of a unit vector oriented in a specific direction with the gradient. The basis filters are the partial derivatives of a 2D Gaussian with respect to x and y. The process by which the oriented filter is synthesized at any given angle is known as ''steering'', which is used in similar sense as in beam steering for antenna arrays. Applications of steerable filters include edge detection Edge or EDGE may refer to: Technology Computing * Edge computing, a network load-balancing system * Edge device, an entry point to a computer network * Adobe Edge, a graphical development application * M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catmull-Rom Spline
In numerical analysis, a cubic Hermite spline or cubic Hermite interpolator is a spline where each piece is a third-degree polynomial specified in Hermite form, that is, by its values and first derivatives at the end points of the corresponding domain interval. Cubic Hermite splines are typically used for interpolation of numeric data specified at given argument values x_1,x_2,\ldots,x_n, to obtain a continuous function. The data should consist of the desired function value and derivative at each x_k. (If only the values are provided, the derivatives must be estimated from them.) The Hermite formula is applied to each interval (x_k, x_) separately. The resulting spline will be continuous and will have continuous first derivative. Cubic polynomial splines can be specified in other ways, the Bezier cubic being the most common. However, these two methods provide the same set of splines, and data can be easily converted between the Bézier and Hermite forms; so the names are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-spline
In numerical analysis, a B-spline (short for basis spline) is a type of Spline (mathematics), spline function designed to have minimal Support (mathematics), support (overlap) for a given Degree of a polynomial, degree, smoothness, and set of breakpoints (Knot (mathematics), knots that partition its Domain of a function, domain), making it a fundamental building block for all spline functions of that degree. A B-spline is defined as a piecewise polynomial of Order (mathematics), order n, meaning a degree of n - 1. It’s built from sections that meet at these knots, where the continuity of the function and its Derivative, derivatives depends on how often each knot repeats (its multiplicity). Any spline function of a specific degree can be uniquely expressed as a linear combination of B-splines of that degree over the same knots, a property that makes them versatile in mathematical modeling. A special subtype, cardinal B-splines, uses equidistant knots. The concept of B-splines tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Hermite Spline
In numerical analysis, a cubic Hermite spline or cubic Hermite interpolator is a spline where each piece is a third-degree polynomial specified in Hermite form, that is, by its values and first derivatives at the end points of the corresponding domain interval. Cubic Hermite splines are typically used for interpolation of numeric data specified at given argument values x_1,x_2,\ldots,x_n, to obtain a continuous function. The data should consist of the desired function value and derivative at each x_k. (If only the values are provided, the derivatives must be estimated from them.) The Hermite formula is applied to each interval (x_k, x_) separately. The resulting spline will be continuous and will have continuous first derivative. Cubic polynomial splines can be specified in other ways, the Bezier cubic being the most common. However, these two methods provide the same set of splines, and data can be easily converted between the Bézier and Hermite forms; so the names are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bézier Surface
Bézier surfaces are a type of mathematical spline used in computer graphics, computer-aided design, and finite element modeling. As with Bézier curves, a Bézier surface is defined by a set of control points. Similar to interpolation in many respects, a key difference is that the surface does not, in general, pass through the central control points; rather, it is "stretched" toward them as though each were an attractive force. They are visually intuitive and, for many applications, mathematically convenient. History Bézier surfaces were first described in 1962 by the French engineer Pierre Bézier who used them to design automobile bodies. Bézier surfaces can be of any degree, but bicubic Bézier surfaces generally provide enough degrees of freedom for most applications. Equation A given Bézier surface of degree (''n'', ''m'') is defined by a set of (''n'' + 1)(''m'' + 1) control points k''i'',''j'' where ''i'' = 0, ..., ''n'' and ''j'' = 0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sobel Operator
The Sobel operator, sometimes called the Sobel–Feldman operator or Sobel filter, is used in image processing and computer vision, particularly within edge detection algorithms where it creates an image emphasising edges. It is named after Irwin Sobel and Gary M. Feldman, colleagues at the Stanford Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (SAIL). Sobel and Feldman presented the idea of an "Isotropic 3 × 3 Image Gradient Operator" at a talk at SAIL in 1968.Irwin Sobel, 2014''History and Definition of the Sobel Operator''/ref> Technically, it is a discrete differentiation operator, computing an approximation of the gradient of the image intensity function. At each point in the image, the result of the Sobel–Feldman operator is either the corresponding gradient vector or the norm of this vector. The Sobel–Feldman operator is based on convolving the image with a small, separable, and integer-valued filter in the horizontal and vertical directions and is therefore relativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spline Interpolation
In the mathematical field of numerical analysis, spline interpolation is a form of interpolation where the interpolant is a special type of piecewise polynomial called a spline. That is, instead of fitting a single, high-degree polynomial to all of the values at once, spline interpolation fits low-degree polynomials to small subsets of the values, for example, fitting nine cubic polynomials between each of the pairs of ten points, instead of fitting a single degree-nine polynomial to all of them. Spline interpolation is often preferred over polynomial interpolation because the interpolation error can be made small even when using low-degree polynomials for the spline. Spline interpolation also avoids the problem of Runge's phenomenon, in which oscillation can occur between points when interpolating using high-degree polynomials. Introduction Originally, '' spline'' was a term for elastic rulers that were bent to pass through a number of predefined points, or ''knots''. These we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |