|
Ijūin Hikokichi
Baron Ijūin Hikokichi (伊集院 彦吉, ''Ijūin Hikokichi''; 22 July 1864 – 26 April 1924) was a Japanese diplomat and politician who served as minister of foreign affairs and Japanese ambassador to the Qing dynasty. Early life Ijūin was born on 22 July 1864, in Kōrai, Kagoshima, Satsuma Domain, the eldest son of samurai Ijūin Kichitsugu. Career Ijūin was appointed consul at Yantai in China in 1893. He served again in China as consul general at Tianjin from 1901 to 1907. He was appointed ambassador to Beijing in 1908. On 4 September 1909, he signed the Japan–China Agreement concerning Kando as the Japanese ambassador to the Qing dynasty in Beijing. During the Chinese Revolution broke out in October 1911, together with then Foreign Minister Uchida Yasuya, he argued for the provision of support to the Qing government. His term as ambassador to China lasted until 1913. Then, Ijūin was appointed the Japanese ambassador to Italy in 1916 and was in office until 1920 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junior Second Rank
The court ranks of Japan, also known in Japanese language, Japanese as ''ikai'' (位階), are indications of an individual's court rank in Japan based on the system of the Nation, state. ''Ikai'' as a system was the indication of the rank of bureaucrats and officials in countries that inherited (class system). Currently, the Japanese court ranks and titles are among the types of honours conferred to those who have held government posts for a long time and to those who have made distinguished achievements. In recent times, most appointments, if not all, are offered posthumously. A notable recipient of such a court rank is the late former Prime Minister of Japan, prime minister Shinzo Abe, who received Junior First Rank (従一位, ''ju ichi-i'') on 8 July 2022. Court ranks The national system for ranking politicians and officials who served the Japanese dynasty began in 603 when Empress Suiko enacted the Twelve Level Cap and Rank System. Each rank was identified by the color of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satsuma Domain
The , briefly known as the , was a Han system, domain (''han'') of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan during the Edo period from 1600 to 1871. The Satsuma Domain was based at Kagoshima Castle in Satsuma Province, the core of the modern city of Kagoshima, located in the south of the island of Kyushu. The Satsuma Domain was ruled for its existence by the ''Tozama daimyō, Tozama'' ''daimyō'' of the Shimazu clan, who had ruled the Kagoshima area since the 1200s, and covered territory in the Provinces of Japan, provinces of Satsuma, Ōsumi Province, Ōsumi and Hyūga Province, Hyūga. The Satsuma Domain was assessed under the ''Kokudaka'' system and its value peaked at 770,000 ''koku'', the second-highest domain in Japan after the Kaga Domain.Conrad Totman, Totman, Conrad. (1993) ''Early Modern Japan'', p. 119 The Satsuma Domain was one of the most powerful and prominent of Japan's domains during the Edo period, conquering the Ryukyu Kingdom as a vassal state after the invasion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makino Nobuaki
Count , was a Japanese politician and imperial court official. As Lord Keeper of the Privy Seal of Japan, Makino served as Emperor Hirohito's chief counselor on the monarch's position in Japanese society and policymaking. After victory in World War I, Makino was appointed to be one of Japan's ambassador plenipotentiaries to the Paris Peace Conference of 1919, headed by the elder statesman, Marquis Saionji. At the conference, he and other members of the delegation put forth a Racial Equality Proposal. It won the majority of votes, but was vetoed by the chairman, President Woodrow Wilson. Even after his retirement in 1935, he remained a close advisor to the throne through the end of World War II in 1945. Early life and education Born to a samurai family in Kagoshima, Satsuma Domain (present day Kagoshima Prefecture), Makino was the second son of Ōkubo Toshimichi, but adopted into the Makino family at a very early age. In 1871, at age 11, he accompanied Ōkubo on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiyoura Keigo
Count was a Japanese politician. He was the Prime Minister of Japan in 1924, during the period which historians have called the "Taishō Democracy". Early life and education Kiyoura was born Ōkubo Fujaku in Kamoto District, Kumamoto, Kamoto, Higo Province (part of present-day Yamaga, Kumamoto), as the fifth son of Ōkubo Ryōshi, the Abbot (Buddhism), abbot of Menshōji Temple. He studied at the private school of Hirose Tanso from 1865 to 1871. During this time, he befriended Governor Nomura Morihide and took up the name "Kiyoura Keigo". Political career Nomura was appointed governor of Saitama Prefecture in 1873 and appointed Kiyoura to a junior-grade civil service position there. In 1876, at the age of twenty-six, Kiyoura joined the Ministry of Justice (Japan), Ministry of Justice, and served as a prosecutor and helping draft Japan's first modern Criminal procedures laws. In 1884 he caught the attention of Yamagata Aritomo who appointed him head of the police forces in Jap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indiana University
Indiana University (IU) is a state university system, system of Public university, public universities in the U.S. state of Indiana. The system has two core campuses, five regional campuses, and two regional centers under the administration of IU Indianapolis. The flagship campus of Indiana University is Indiana University Bloomington. Campuses Core campuses *Indiana University Bloomington (IU Bloomington) is the flagship campus of Indiana University. The Bloomington campus is home to numerous premier Indiana University schools, including the College of Arts and Sciences, the Hutton Honors College, the Jacobs School of Music, an extension of the Indiana University School of Medicine, the Indiana University School of Informatics, Luddy School of Informatics, Computing, and Engineering, which includes the former School of Library and Information Science (now Department of Library and Information Science), School of Optometry, the Indiana University School of Public and Enviro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kwantung Leased Territory
The Kwantung Leased Territory () was a Concessions in China, leased territory of the Empire of Japan in the Liaodong Peninsula from 1905 to 1945. Japan first acquired Kwantung from the Qing dynasty, Qing Empire in perpetuity in 1895 in the Treaty of Shimonoseki after victory in the First Sino-Japanese War. Kwantung was located at the militarily and economically significant southern tip of the Liaodong Peninsula at the entrance of the Bohai Sea, and included the port city of Lüshunkou, Ryojun (Port Arthur/Lüshunkou). Japan lost Kwantung weeks later in the Triple Intervention and the Qing transferred the lease to the Russian Empire in 1898, who governed the territory as Russian Dalian and rapidly developed infrastructure and the city of Dalian, Dairen (Dalniy/Dalian). Japan re-acquired the Kwantung lease from Russia in 1905 in the Treaty of Portsmouth after victory in the Russo-Japanese War, continued to rapidly develop the territory, and obtained extraterritorial rights known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hara Takashi
was a Japanese politician who served as the Prime Minister of Japan from 1918 until his assassination. Hara held several minor ambassadorial roles before rising through the ranks of the Rikken Seiyūkai and being elected to the House of Representatives. Hara served as Home Minister in several cabinets under Saionji Kinmochi and Yamamoto Gonnohyōe between 1906 and 1913. Hara was appointed prime minister following the Rice Riots of 1918 and positioned himself as a moderate, participating in the Paris Peace Conference, founding the League of Nations, and relaxing oppressive policies in Japanese Korea. Hara's premiership oversaw the Siberian intervention and the suppression of the March 1st Movement in Japanese-occupied Korea. Hara was assassinated by Nakaoka Kon'ichi, a far-right nationalist, on 4 November 1921. Hara was the first commoner and first Christian appointed to be Prime Minister of Japan, informally known as Hara Kei, and given the moniker of . Early life Hara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
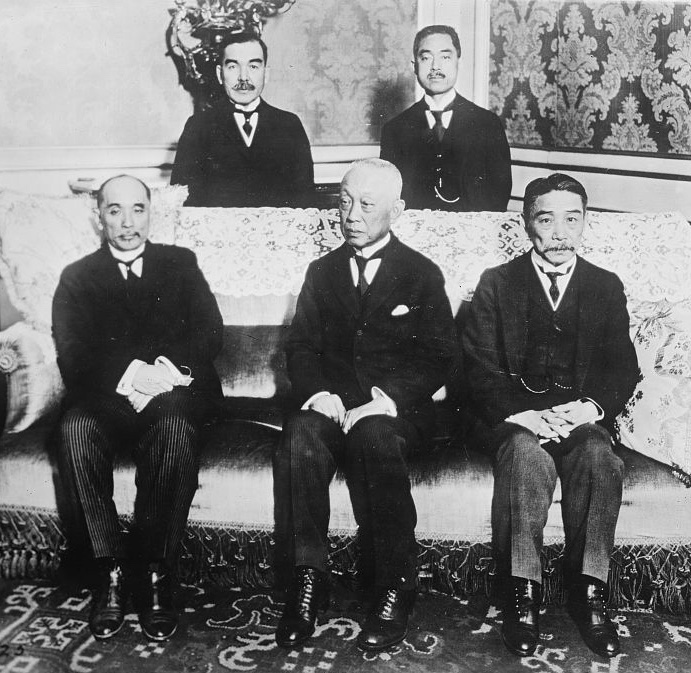
Japanese Peace Delegates In 1919 With Makino Nobuaki
Japanese may refer to: * Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia * Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan * Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture ** Japanese diaspora, Japanese emigrants and their descendants around the world * Japanese citizens, nationals of Japan under Japanese nationality law ** Foreign-born Japanese, naturalized citizens of Japan * Japanese writing system, consisting of kanji and kana * Japanese cuisine, the food and food culture of Japan See also * List of Japanese people * * Japonica (other) * Japanese studies , sometimes known as Japanology in Europe, is a sub-field of area studies or East Asian studies involved in social sciences and humanities research on Japan. It incorporates fields such as the study of Japanese language, history, culture, litera ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris Peace Conference, 1919
Paris () is the capital and largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the fourth-most populous city in the European Union and the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2022. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, culture, fashion, and gastronomy. Because of its leading role in the arts and sciences and its early adoption of extensive street lighting, Paris became known as the City of Light in the 19th century. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an official estimated population of 12,271,794 inhabitants in January 2023, or about 19% of the population of France. The Paris Region had a nominal GDP of €765 billion (US$1.064 trillion when adjusted for PPP) in 2021, the highest in the European Union. According to the Economist Intelligence Unit Worldwide Cost of Liv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uchida Yasuya
Uchida (written: 内田 lit. "within ricefield") is a Japanese surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Aguri Uchida (born 1949), a Japanese watercolour painter * Akiko Uchida (born 1985), a Japanese volleyball player * Asahi Uchida (born 1982), a Japanese actor * Atsuto Uchida, a Japanese football player *Aya Uchida (born 1986), a Japanese voice actress *, Japanese footballer * Hyakken Uchida, (1889–1971), a Japanese author and academic * Irene Uchida (1917–2013), Canadian scientist and researcher * Jun Uchida, a Japanese football player * Uchida Kakichi (1866–1933), a Japanese politician * Kaichi Uchida, a Japanese tennis player * Katherine Uchida (born 1999), a Canadian rhythmic gymnast * Kenji Uchida, a Japanese anime producer * Kenji Uchida (film director), a Japanese film director * Kenta Uchida, a Japanese football player *, Japanese footballer * Uchida Kosai (1865–1936), a Japanese statesman *Uchida Kuichi (1844–1875), a Japanese photographer * Makoto Uchi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Revolution Of 1911
The 1911 Revolution, also known as the Xinhai Revolution or Hsinhai Revolution, ended China's last imperial dynasty, the Qing dynasty, and led to the establishment of the Republic of China (ROC). The revolution was the culmination of a decade of agitation, revolts, and uprisings. Its success marked the collapse of the Chinese monarchy, the end of over two millennia of imperial rule in China and the 200-year reign of the Qing, and the beginning of China's early republican era. The Qing had struggled for a long time to reform the government and resist foreign aggression, but the program of reforms after 1900 was opposed by conservatives in the Qing court as too radical and by reformers as too slow. Several factions, including underground anti-Qing groups, revolutionaries in exile, reformers who wanted to save the monarchy by modernizing it, and activists across the country debated how or whether to overthrow the Qing dynasty. The flash-point came on 10 October 1911, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |