|
ICAD (software)
ICAD (Corporate history: ICAD, Inc., Concentra (name change at IPO in 1995), KTI (name change in 1998), Dassault Systèmes (purchase in 2001) () is a knowledge-based engineering (KBE) system that enables users to encode design knowledge using a semantic representation that can be evaluated for Parasolid output. ICAD has an open architecture that can utilize all the power and flexibility of the underlying language. KBE, as implemented via ICAD, received a lot of attention due to the remarkable results that appeared to take little effort. ICAD allowed one example of end-user computing that in a sense is unparalleled. Most ICAD developers were degreed engineers. Systems developed by ICAD users were non-trivial and consisted of highly complicated code. In the sense of end-user computing, ICAD was the first to allow the power of a domain tool to be in the hands of the user, at the same time being open to allow extensions as identified and defined by the domain expert or subject-matter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corporate History
A corporate history is a historical account of a business or other co-operative organization. Usually it is produced in written format but it can also be published as audio or audiovisually. Thousands of companies across the industrialized world have recorded their histories, albeit in their own unique ways – from relatively benign, albeit colorful chronicles, usually written for the private archives of founding families, to titles with well-defined corporate applications. Corporate histories in the United States have been particularly prolific, those in the UK less so. History In the late 19th century, corporate histories were initially written by Victorian era businessmen, either the founder of a company himself, members of the surviving family owners or long-serving employees. Rather than being sequential histories, as is now done, many of them were diary-type personal recollections or short, superficial public relations exercises. One of the earliest corporate histories, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the latter half of the 19th century after the commercialization of the electric telegraph, the telephone, and electrical power generation, distribution, and use. Electrical engineering is divided into a wide range of different fields, including computer engineering, systems engineering, power engineering, telecommunications, radio-frequency engineering, signal processing, instrumentation, photovoltaic cells, electronics, and optics and photonics. Many of these disciplines overlap with other engineering branches, spanning a huge number of specializations including hardware engineering, power electronics, Electromagnetism, electromagnetics and waves, microwave engineering, nanotechnology, electrochemistry, renewable energies, mechatronics/control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer-aided Design Software
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, mainly by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machines. Automation has been achieved by various means including mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, electrical, electronic devices, and computers, usually in combination. Complicated systems, such as modern factories, airplanes, and ships typically use combinations of all of these techniques. The benefit of automation includes labor savings, reducing waste, savings in electricity costs, savings in material costs, and improvements to quality, accuracy, and precision. Automation includes the use of various equipment and control systems such as machinery, processes in factories, boilers, and heat-treating ovens, switching on telephone networks, steering, stabilization of ships, aircraft and other applications and vehicles with reduced huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faculty Of Aerospace Engineering, Delft University Of Technology
The Faculty of Aerospace Engineering at the Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands is the merger of two interrelated disciplines, aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering. Aeronautical engineering works specifically with aircraft or aeronautics. Astronautical engineering works specifically with spacecraft or astronautics. At the Faculty of Aerospace Engineering, both of the fields are directly addressed along with expansion into fields such as wind energy. Description The Faculty is one of the largest of the eight faculties at TU Delft and one of the largest faculties devoted entirely to aerospace engineering in northern Europe. It is the only institute carrying out research and education directly related to aerospace engineering in the Netherlands. Through the years, the Faculty has responded to the increasing demands of the aerospace industry by further expanding its facilities and laboratories. Today the Faculty has a student body of approximately 2300 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphaned Technology
Orphaned technology refers to computer technologies that have been abandoned by their original developers. As opposed to deprecation, which tends to be a gradual shift away from an older technology to newer technology, orphaned technology is usually abandoned immediately or with no direct replacement. Unlike abandonware, orphaned technology refers to both software and hardware and the practices around them. Users of orphaned technologies must often make a choice continuing to use the technology, which may become harder to maintain over time, or switch to other supported technologies, possibly losing capabilities unique to the orphaned technology. Reasoning While technology can be abandoned due to an unfavourable design or poor implementation, abandoning a technology can happen for a variety of reasons. There are instances where products are phased out of the market because they are no longer viable as business ventures, such as certain medical technologies. Some orphaned tech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knowledge-based Systems
A knowledge-based system (KBS) is a computer program that reasons and uses a knowledge base to solve complex problems. Knowledge-based systems were the focus of early artificial intelligence researchers in the 1980s. The term can refer to a broad range of systems. However, all knowledge-based systems have two defining components: an attempt to represent knowledge explicitly, called a knowledge base, and a reasoning system that allows them to derive new knowledge, known as an inference engine. Components The knowledge base contains domain-specific facts and rules about a problem domain (rather than knowledge implicitly embedded in procedural code, as in a conventional computer program). In addition, the knowledge may be structured by means of a subsumption ontology, frames, conceptual graph, or logical assertions. The inference engine uses general-purpose reasoning methods to infer new knowledge and to solve problems in the problem domain. Most commonly, it employs forw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Programming
In computer science, functional programming is a programming paradigm where programs are constructed by Function application, applying and Function composition (computer science), composing Function (computer science), functions. It is a declarative programming paradigm in which function definitions are Tree (data structure), trees of Expression (computer science), expressions that map Value (computer science), values to other values, rather than a sequence of Imperative programming, imperative Statement (computer science), statements which update the State (computer science), running state of the program. In functional programming, functions are treated as first-class citizens, meaning that they can be bound to names (including local Identifier (computer languages), identifiers), passed as Parameter (computer programming), arguments, and Return value, returned from other functions, just as any other data type can. This allows programs to be written in a Declarative programming, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haskell (programming Language)
Haskell () is a General-purpose programming language, general-purpose, static typing, statically typed, purely functional programming, purely functional programming language with type inference and lazy evaluation. Designed for teaching, research, and industrial applications, Haskell pioneered several programming language #Features, features such as type classes, which enable type safety, type-safe operator overloading, and Monad (functional programming), monadic input/output (IO). It is named after logician Haskell Curry. Haskell's main implementation is the Glasgow Haskell Compiler (GHC). Haskell's Semantics (computer science), semantics are historically based on those of the Miranda (programming language), Miranda programming language, which served to focus the efforts of the initial Haskell working group. The last formal specification of the language was made in July 2010, while the development of GHC continues to expand Haskell via language extensions. Haskell is used in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Programming
In computer science, functional programming is a programming paradigm where programs are constructed by Function application, applying and Function composition (computer science), composing Function (computer science), functions. It is a declarative programming paradigm in which function definitions are Tree (data structure), trees of Expression (computer science), expressions that map Value (computer science), values to other values, rather than a sequence of Imperative programming, imperative Statement (computer science), statements which update the State (computer science), running state of the program. In functional programming, functions are treated as first-class citizens, meaning that they can be bound to names (including local Identifier (computer languages), identifiers), passed as Parameter (computer programming), arguments, and Return value, returned from other functions, just as any other data type can. This allows programs to be written in a Declarative programming, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lisp (programming Language)
Lisp (historically LISP, an abbreviation of "list processing") is a family of programming languages with a long history and a distinctive, fully parenthesized prefix notation. Originally specified in the late 1950s, it is the second-oldest high-level programming language still in common use, after Fortran. Lisp has changed since its early days, and many dialects have existed over its history. Today, the best-known general-purpose Lisp dialects are Common Lisp, Scheme, Racket, and Clojure. Lisp was originally created as a practical mathematical notation for computer programs, influenced by (though not originally derived from) the notation of Alonzo Church's lambda calculus. It quickly became a favored programming language for artificial intelligence (AI) research. As one of the earliest programming languages, Lisp pioneered many ideas in computer science, including tree data structures, automatic storage management, dynamic typing, conditionals, higher-order function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
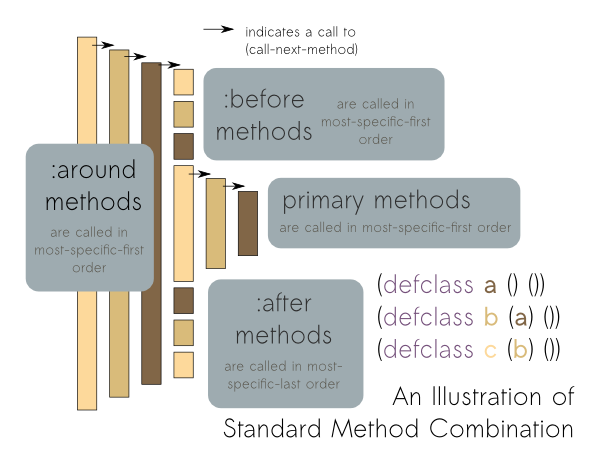
Common Lisp Object System
The Common Lisp Object System (CLOS) is the facility for object-oriented programming in American National Standards Institute, ANSI Common Lisp. CLOS is a powerful dynamic programming language, dynamic object system which differs radically from the OOP facilities found in more static languages such as C++ or Java (programming language), Java. CLOS was inspired by earlier Lisp object systems such as Flavors (computer science), MIT Flavors and CommonLoops, although it is more general than either. Originally proposed as an add-on, CLOS was adopted as part of the ANSI standard for Common Lisp and has been adapted into other Lisp dialects such as EuLisp or Emacs Lisp. Features The basic building blocks of CLOS are method (computer programming), methods, Class (computer programming), classes, instances of those classes, and generic functions. CLOS provides macros to define those: defclass, defmethod, and defgeneric. Instances are created with the method make-instance. Classes can hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavors (programming Language)
Flavors is an early object-oriented extension to Lisp developed by Howard Cannon at the MIT Artificial Intelligence Laboratory for the Lisp machine and its programming language Lisp Machine Lisp. It is notable as the first programming language to include mixins. Symbolics used it for its Lisp machines, and eventually developed it into New Flavors; both the original and new Flavors were message-passing OO models. It was hugely influential in the development of the Common Lisp Object System (CLOS). Implementations of Flavors are also available for Common Lisp Common Lisp (CL) is a dialect of the Lisp programming language, published in American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standard document ''ANSI INCITS 226-1994 (S2018)'' (formerly ''X3.226-1994 (R1999)''). The Common Lisp HyperSpec, a hyperli .... New Flavors replaced message sending with calling generic functions. Flavors offers and daemons with the default method combination (called ). Flavors and CLOS feat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |