|
I2P
The Invisible Internet Project (I2P) is an anonymous network layer (implemented as a mix network) that allows for censorship-resistant, peer-to-peer communication. Anonymous connections are achieved by encrypting the user's traffic (by using end-to-end encryption), and sending it through a volunteer-run network of roughly 55,000 computers distributed around the world. Given the high number of possible paths the traffic can transit, a third party watching a full connection is unlikely. The software that implements this layer is called an "I2P router", and a computer running I2P is called an "I2P node". I2P is free and open source, and is published under multiple licenses. Technical design I2P started in 2003 as a fork of Freenet. The network is strictly message-based, like IP, but a library is available to allow reliable streaming communication on top of it (similar to Non-blocking IO-based TCP, although from version 0.6, a new ''Secure Semi-reliable'' UDP transport i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garlic Routing
Garlic routing is a variant of onion routing that encrypts multiple messages together to make it more difficult for attackers to perform traffic analysis while also increasing the speed of data transfer. Michael J. Freedman defined garlic routing as an extension of onion routing, in which multiple messages are bundled together. He called each message a "bulb", whereas I2P calls them "garlic cloves." All messages, each with their own delivery instructions, are exposed at the endpoint. This enables efficient bundling of an onion routing reply block with the original message. Garlic routing is one of the key factors that distinguishes I2P from Tor and other privacy-focused or encryption networks. The name alludes to the garlic plant, whose multi-layered structure this protocol resembles. "Garlic routing" was first coined by Michael J. Freedman in Roger Dingledine's Free Haven Master's thesis Section 8.1.1 (June 2000), as derived from Onion Routing. However, the garlic routing im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
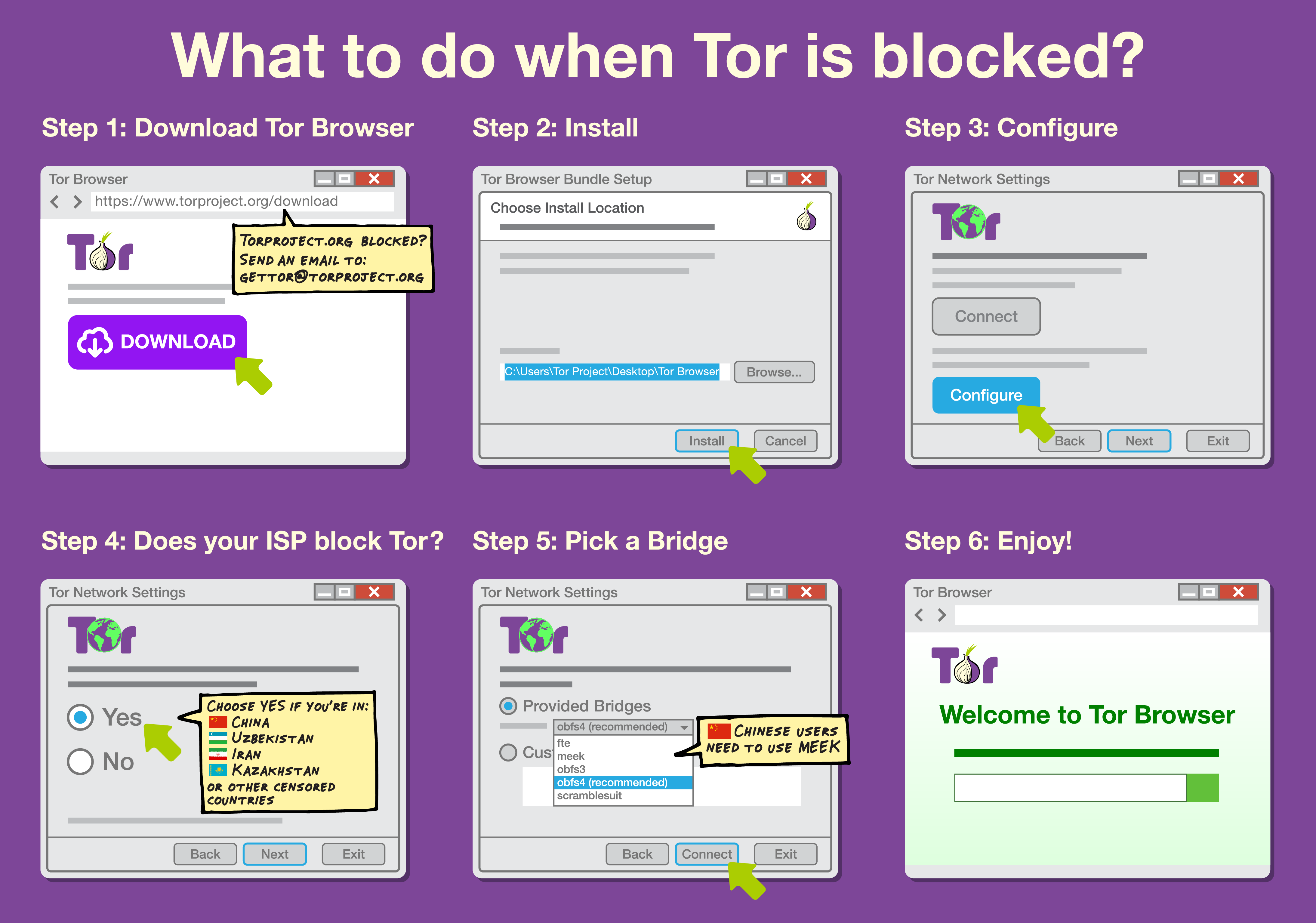
Internet Censorship Circumvention
Internet censorship circumvention is the use of various methods and tools to bypass internet censorship. Commonly used tools include Lantern and Psiphon, which bypass multiple safeguard types. Some methods use alternate DNS servers, false addresses or address lookup systems to evade less sophisticated blocking tools. However, such methods do not work if censors block the IP address of restricted domains in addition to DNS, rendering the bypass ineffective. Other tools tunnel network traffic to proxies in jurisdictions without censorship. Through pluggable transports, traffic obscuration, website mirrors, or archive sites, copies of sites can be accessed in areas under internet censorship. An arms race has developed between censors and developers of circumvention software, resulting in more sophisticated blocking techniques by censors and the development of harder-to-detect tools by tool developers. Estimates of adoption of circumvention tools are disputed, but are widely un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the network, forming a peer-to-peer network of Node (networking), nodes. In addition, a personal area network (PAN) is also in nature a type of Decentralized computing, decentralized peer-to-peer network typically between two devices. Peers make a portion of their resources, such as processing power, disk storage, or network bandwidth, directly available to other network participants, without the need for central coordination by servers or stable hosts. Peers are both suppliers and consumers of resources, in contrast to the traditional client–server model in which the consumption and supply of resources are divided. While P2P systems had previously been used in many application domains, the architecture was popularized by the Internet file sharing system Napster, originally released in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anonymity Application
Anonymity describes situations where the acting person's identity is unknown. Anonymity may be created unintentionally through the loss of identifying information due to the passage of time or a destructive event, or intentionally if a person chooses to withhold their identity. There are various situations in which a person might choose to remain anonymous. Acts of charity have been performed anonymously when benefactors do not wish to be acknowledged. A person who feels threatened might attempt to mitigate that threat through anonymity. A witness to a crime might seek to avoid retribution, for example, by anonymously calling a crime tipline. In many other situations (like conversation between strangers, or buying some product or service in a shop), anonymity is traditionally accepted as natural. Some writers have argued that the term "namelessness", though technically correct, does not capture what is more centrally at stake in contexts of anonymity. The important idea here is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freenet
Hyphanet (until mid-2023: Freenet) is a peer-to-peer platform for censorship-resistant, Anonymity application, anonymous communication. It uses a decentralized distributed data store to keep and deliver information, and has a suite of free software for publishing and communicating on the Web without fear of censorship.What is Freenet? , ''Freenet: The Free network official website''.Taylor, Ian J. ''From P2P to Web Services and Grids: Peers in a Client/Server World''. London: Springer, 2005. Both Freenet and some of its associated tools were originally designed by Ian Clarke (computer scientist), Ian Clarke, who defined Freenet's goal as providing freedom of speech on the Internet with strong anonymity protection. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mix Network
Mix networks are routing protocols that create hard-to-trace communications by using a chain of proxy servers known as ''mixes'' which take in messages from multiple senders, shuffle them, and send them back out in random order to the next destination (possibly another mix node). This breaks the link between the source of the request and the destination, making it harder for eavesdroppers to trace end-to-end communications. Furthermore, mixes only know the node that it immediately received the message from, and the immediate destination to send the shuffled messages to, making the network resistant to malicious mix nodes. Each message is encrypted to each proxy using public key cryptography; the resulting encryption is layered like a Russian doll (except that each "doll" is of the same size) with the message as the innermost layer. Each proxy server strips off its own layer of encryption to reveal where to send the message next. If all but one of the proxy servers are comprom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overlay Network
An overlay network is a logical computer network that is protocol layering, layered on top of a physical network. The concept of overlay networking is distinct from the traditional model of OSI model, OSI layered networks, and almost always assumes that the underlay network is an IP network of some kind. Some examples of overlay networking technologies are, VXLAN, Border Gateway Protocol, BGP VPNs, and IP over IP technologies, such as Generic Routing Encapsulation, GRE, IPSEC tunnels, or SD-WAN. Structure Node (networking), Nodes in an overlay network can be thought of as being connected by virtual or logical links, each of which corresponds to a path, perhaps through many physical links, in the underlying network. For example, distributed systems such as peer-to-peer networks are overlay networks because their nodes form networks over existing network connections. The Internet was originally built as an overlay upon the telephone network, while today (through the advent of V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Protocol
The Internet Protocol (IP) is the network layer communications protocol in the Internet protocol suite for relaying datagrams across network boundaries. Its routing function enables internetworking, and essentially establishes the Internet. IP has the task of delivering Packet (information technology), packets from the source Host (network), host to the destination host solely based on the IP addresses in the packet Header (computing), headers. For this purpose, IP defines packet structures that encapsulation (networking), encapsulate the data to be delivered. It also defines addressing methods that are used to label the datagram with source and destination information. IP was the connectionless datagram service in the original ''Transmission Control Program'' introduced by Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn in 1974, which was complemented by a connection-oriented service that became the basis for the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). The Internet protocol suite is therefore often referre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library (computing)
In computing, a library is a collection of System resource, resources that can be leveraged during software development to implement a computer program. Commonly, a library consists of executable code such as compiled function (computer science), functions and Class (computer programming), classes, or a library can be a collection of source code. A resource library may contain data such as images and Text string, text. A library can be used by multiple, independent consumers (programs and other libraries). This differs from resources defined in a program which can usually only be used by that program. When a consumer uses a library resource, it gains the value of the library without having to implement it itself. Libraries encourage software reuse in a Modular programming, modular fashion. Libraries can use other libraries resulting in a hierarchy of libraries in a program. When writing code that uses a library, a programmer only needs to know how to use it not its internal d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Software
Free software, libre software, libreware sometimes known as freedom-respecting software is computer software distributed open-source license, under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, distribute it and any adapted versions. Free software is a matter of liberty, not price; all users are legally free to do what they want with their copies of a free software (including profiting from them) regardless of how much is paid to obtain the program.Selling Free Software (GNU) Computer programs are deemed "free" if they give end-users (not just the developer) ultimate control over the software and, subsequently, over their devices. The right to study and modify a computer program entails that the source code—the preferred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streaming Algorithm
In computer science, streaming algorithms are algorithms for processing data streams in which the input is presented as a sequence of items and can be examined in only a few passes, typically one-pass algorithm, just one. These algorithms are designed to operate with limited memory, generally L (complexity), logarithmic in the size of the stream and/or in the maximum value in the stream, and may also have limited processing time per item. As a result of these constraints, streaming algorithms often produce approximate answers based on a summary or "sketch" of the data stream. History Though streaming algorithms had already been studied by Munro and Paterson as early as 1978, as well as Philippe Flajolet and G. Nigel Martin in 1982/83, the field of streaming algorithms was first formalized and popularized in a 1996 paper by Noga Alon, Yossi Matias, and Mario Szegedy. For this paper, the authors later won the Gödel Prize in 2005 "for their foundational contribution to streaming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-blocking IO
In computer science, asynchronous I/O (also non-sequential I/O) is a form of input/output processing that permits other processing to continue before the I/O operation has finished. A name used for asynchronous I/O in the Windows API is '' overlapped I/O''. Input and output (I/O) operations on a computer can be extremely slow compared to the processing of data. An I/O device can incorporate mechanical devices that must physically move, such as a hard drive seeking a track to read or write; this is often orders of magnitude slower than the switching of electric current. For example, during a disk operation that takes ten milliseconds to perform, a processor that is clocked at one gigahertz could have performed ten million instruction-processing cycles. A simple approach to I/O would be to start the access and then wait for it to complete. But such an approach, called synchronous I/O or blocking I/O, would block the progress of a program while the communication is in progress, le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |