|
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L), symptoms associated with hypoglycemia, and resolution of symptoms when blood sugar returns to normal. Hypoglycemia may result in headache, tiredness, clumsiness, trouble talking, confusion, fast heart rate, sweating, shakiness, nervousness, hunger, loss of consciousness, seizures, or death. Symptoms typically come on quickly. The most common cause of hypoglycemia is medications used to treat diabetes such as insulin, sulfonylureas, and biguanides. Risk is greater in diabetics who have eaten less than usual, recently exercised, or consumed alcohol. Other causes of hypoglycemia include severe illness, sepsis, kidney failure, liver disease, hormone deficiency, tumors such as insulinomas or non-B cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
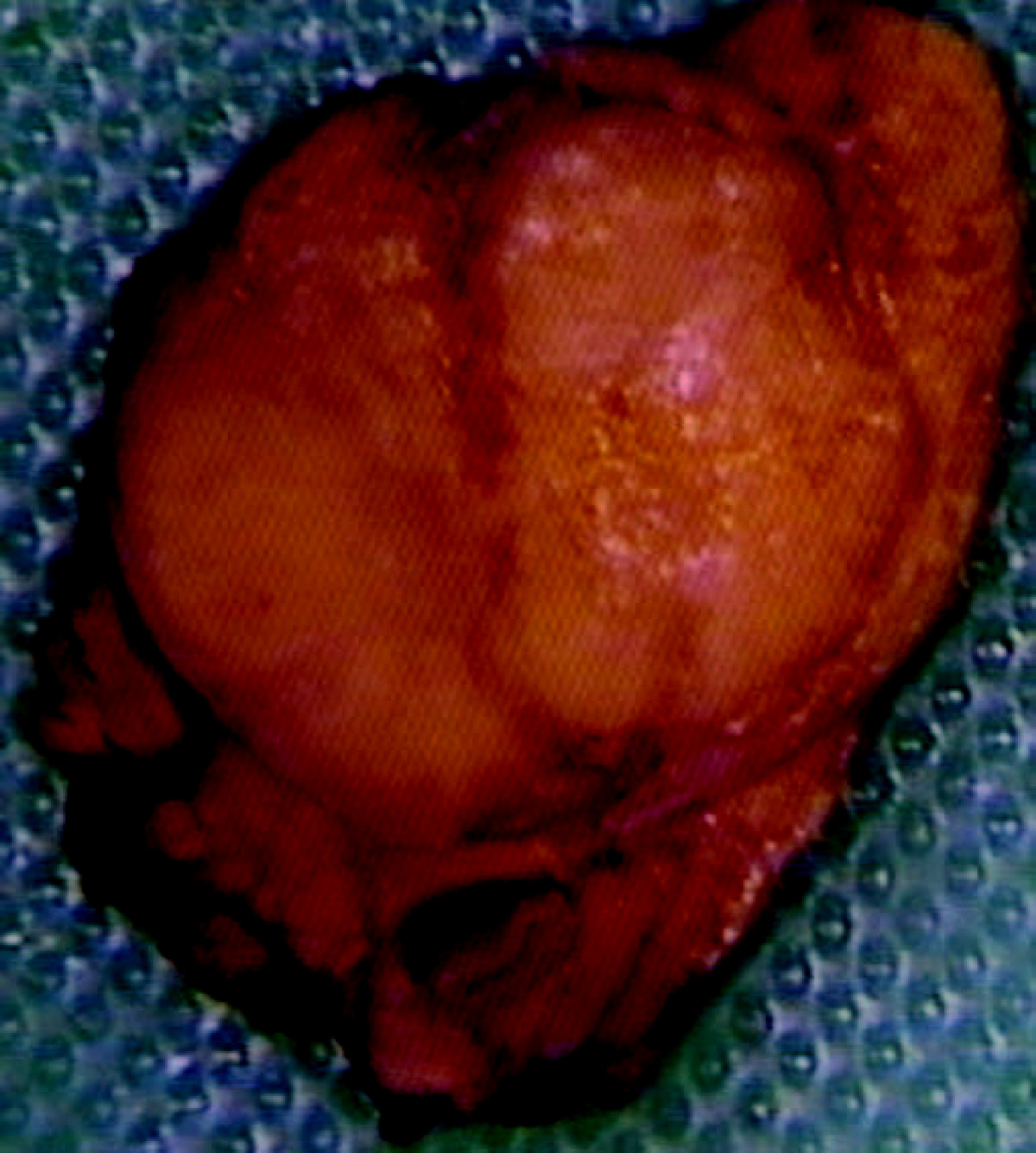
Insulinoma
An insulinoma is a tumour of the pancreas that is derived from beta cells and secretes insulin. It is a rare form of a neuroendocrine tumour. Most insulinomas are benign in that they grow exclusively at their origin within the pancreas, but a minority metastasize. Insulinomas are one of the functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumour (PNET) group ("functional" because it increases production of insulin). In the Medical Subject Headings classification, insulinoma is the only subtype of "islet cell adenoma". Beta cells secrete insulin in response to increases in blood glucose. The resulting increase in insulin acts to lower blood glucose back to normal levels, at which point further secretion of insulin is stopped. In contrast, the secretion of insulin by insulinomas is not properly regulated by glucose, and the tumours continue to secrete insulin causing glucose levels to fall further than normal. As a result, patients present symptoms of low blood glucose (hypoglycemia), which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-diabetic Medication
Drugs used in diabetes treat diabetes mellitus by altering the glucose level in the blood. With the exceptions of insulin, most GLP receptor agonists ( liraglutide, exenatide, and others), and pramlintide, all are administered orally and are thus also called oral hypoglycemic agents or oral antihyperglycemic agents. There are different classes of anti-diabetic drugs, and their selection depends on the nature of the diabetes, age and situation of the person, as well as other factors. Diabetes mellitus type 1 is a disease caused by the lack of insulin. Insulin must be used in type 1, which must be injected. Diabetes mellitus type 2 is a disease of insulin resistance by cells. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is the most common type of diabetes. Treatments include agents that (1) increase the amount of insulin secreted by the pancreas, (2) increase the sensitivity of target organs to insulin, (3) decrease the rate at which glucose is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, and (4) inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose Meter
A glucose meter, also referred to as a "glucometer", is a medical device for determining the approximate concentration of glucose in the blood. It can also be a strip of glucose paper dipped into a substance and measured to the glucose chart. It is a key element of glucose testing including home blood glucose monitoring (HBGM) by people with diabetes mellitus or hypoglycemia. A small drop of blood, obtained by pricking the skin with a lancet, is placed on a disposable test strip that the meter reads and uses to calculate the blood glucose level. The meter then displays the level in units of mg/dL or mmol/L. Since approximately 1980, a primary goal of the management of type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus has been achieving closer-to-normal levels of glucose in the blood for as much of the time as possible, guided by HBGM several times a day. The benefits include a reduction in the occurrence rate and severity of long-term complications from hyperglycemia as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucagon (medication)
Glucagon, sold under the brand name Baqsimi among others, is a medication and hormone. As a medication it is used to treat low blood sugar, beta blocker overdose, calcium channel blocker overdose, and those with anaphylaxis who do not improve with epinephrine. It is given by injection into a vein, muscle, or under the skin. A version given in the nose is also available. Common side effects include vomiting. Other side effects include low blood potassium and low blood pressure. It is not recommended in people who have a pheochromocytoma or insulinoma. Use in pregnancy has not be found to be harmful to the baby. Glucagon is in the glycogenolytic family of medications. It works by causing the liver to break down glycogen into glucose. Glucagon was approved for medical use in the United States in 1960. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is a manufactured form of the glucagon hormone. A generic version became available in the Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into liver, fat and skeletal muscle cells. In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen via glycogenesis or fats (triglycerides) via lipogenesis, or, in the case of the liver, into both. Glucose production and secretion by the liver is strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is therefore an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large molecules inside the cells. Low insulin levels in the blood have the opposite effect by promoting widespread catabolism, especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
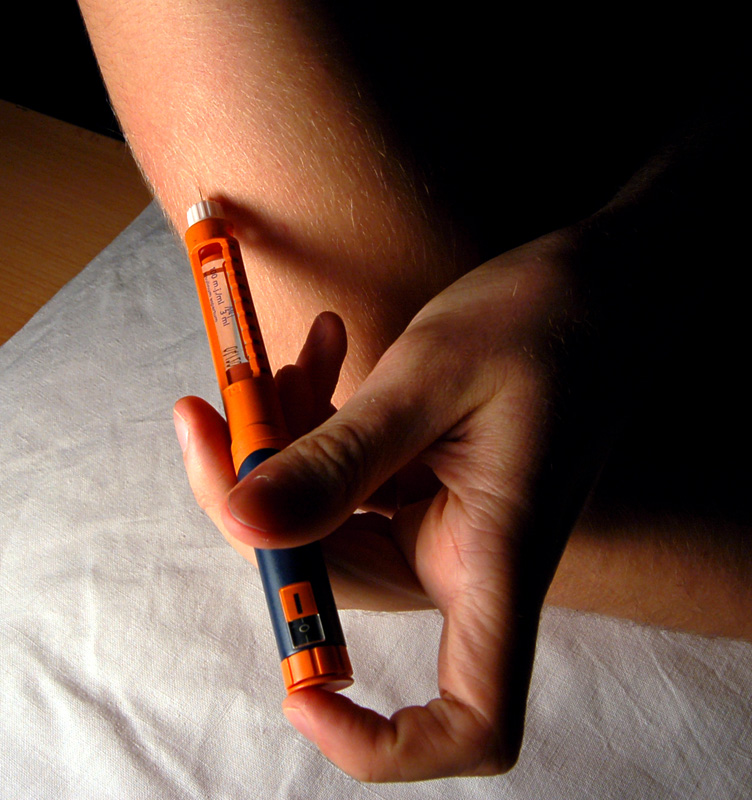
Insulin (medication)
As a medication, insulin is any pharmaceutical preparation of the protein hormone insulin that is used to treat high blood glucose. Such conditions include type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and complications of diabetes such as diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic states. Insulin is also used along with glucose to treat hyperkalemia (high blood potassium levels). Typically it is given by injection under the skin, but some forms may also be used by injection into a vein or muscle. There are various types of insulin, suitable for various time spans. The types are often all called ''insulin'' in the broad sense, although in a more precise sense, insulin is identical to the naturally occurring molecule whereas insulin analogues have slightly different molecules that allow for modified time of action. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2020, regular human insulin was the 307th most commonly prescribed med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfonylurea
Sulfonylureas (UK: sulphonylurea) are a class of organic compounds used in medicine and agriculture, for example as antidiabetic drugs widely used in the management of diabetes mellitus type 2. They act by increasing insulin release from the beta cells in the pancreas. A number of sulfonylureas are also used as herbicides, because they can interfere with plant biosynthesis of certain amino acids. Sulfonylureas are also used experimentally to inhibit interleukin 1 beta release from the NALP3 (or NLRP3) inflammasome. Drugs * First-generation drugs include acetohexamide, carbutamide, chlorpropamide, glycyclamide (tolcyclamide), metahexamide, tolazamide and tolbutamide. * Second-generation drugs include glibenclamide (glyburide), glibornuride, gliclazide, glipizide, gliquidone, glisoxepide and glyclopyramide. * Third-generation drugs include glimepiride, although it is sometimes considered a second-generation agent. Medical uses Sulfonylureas are used primarily for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Sugar
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blood of a 70 kg (154 lb) human at all times. The body tightly regulates blood glucose levels as a part of metabolic homeostasis. Glucose is stored in skeletal muscle and liver cells in the form of glycogen; in fasting individuals, blood glucose is maintained at a constant level at the expense of glycogen stores in the liver and skeletal muscle. In humans, a blood glucose level of 4 grams, or about a teaspoon, is critical for normal function in a number of tissues, and the human brain consumes approximately 60% of blood glucose in fasting, sedentary individuals. A persistent elevation in blood glucose leads to glucose toxicity, which contributes to cell dysfunction and the pathology grouped together as complications of diabetes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whipple's Triad
Whipple's triad is a collection of three signs (called Whipple's criteria) that suggests that a patient's symptoms result from hypoglycaemia that may indicate insulinoma. The essential conditions are symptoms of hypoglycaemia, low blood plasma glucose concentration, and relief of symptoms when plasma glucose concentration is increased. It was first described by the pancreatic surgeon Allen Whipple, who aimed to establish criteria for exploratory pancreatic surgery to look for insulinoma. Definition Whipple's triad is stated in various versions. The essential conditions are: # Symptoms known or likely to be caused by hypoglycaemia, especially after fasting or intense exercise. # A low blood plasma glucose concentration measured at the time of the symptoms. This may be measured as a blood plasma glucose concentration of less than 550 milligrams per litre. # Relief of symptoms when glucose level is increased. The use and significance of the criteria have evolved over the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenaline
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands and by a small number of neurons in the medulla oblongata. It plays an essential role in the fight-or-flight response by increasing blood flow to muscles, heart output by acting on the SA node, pupil dilation response, and blood sugar level. It does this by binding to alpha and beta receptors. It is found in many animals, including humans, and some single-celled organisms. It has also been isolated from the plant ''Scoparia dulcis'' found in Northern Vietnam. Medical uses As a medication, it is used to treat several conditions, including allergic reaction anaphylaxis, cardiac arrest, and superficial bleeding. Inhaled adrenaline may be used to improve the symptoms of croup. It may also be used for asthma when other treatments are not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose circulates in the blood plasma. This is generally a blood sugar level higher than 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL), but symptoms may not start to become noticeable until even higher values such as 13.9–16.7 mmol/L (~250–300 mg/dL). A subject with a consistent range between ~5.6 and ~7 mmol/L (100–126 mg/dL) ( American Diabetes Association guidelines) is considered slightly hyperglycemic, and above 7 mmol/L (126 mg/dL) is generally held to have diabetes. For diabetics, glucose levels that are considered to be too hyperglycemic can vary from person to person, mainly due to the person's renal threshold of glucose and overall glucose tolerance. On average, however, chronic levels above 10–12 mmol/L (180–216 mg/dL) can produce noticeable organ damage over time. Signs and symptoms The degree of hyperglycemia can change over time depending on the metabolic cause, for example, impaired ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glinide
Meglitinides or glinides are a class of drugs used to treat type 2 diabetes. Drugs Repaglinide (trade name Prandin) gained US Food and Drug Administration approval in 1997. Other drugs in this class include nateglinide (Starlix) and mitiglinide (Glufast). Side effects Side effects include weight gain and hypoglycemia. While the potential for hypoglycemia is less than for those on sulfonylureas, it is still a serious potential side effect that can be life-threatening. Patients on this medication should know the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia and appropriate management. Repaglinide caused an increased incidence in male rats of benign adenomas (tumors) of the thyroid and liver.Prandin (repaglinide) prescribing information fda.gov No such effect was seen with anot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |