|
Hydration System
A hydration system is an apparatus used in recreation and other sustained outdoor activities. It is intended to help its user carry liquid, to support the physical effort involved in the activity, without the need to use one's hands or take off the pack. Such systems for consumers were first sold to cyclists, and by the 1990s had also found a substantial market among hikers. Familiar commercial models can also be recognized occasionally worn by western military personnel in southwest Asia. In practice, such a system is almost always a commercially manufactured unit that features at least * a flexible bladder of one or a few liters' (quarts') capacity with some means, usually a screwtop, to fill and then reliably seal it, * a light hose to convey the beverage to the user's mouth, and * a bite valve that starts and stops the flow through the hose with minimal effort. Also common are designs that include specific hands-free means to comfortably carry the hydration system. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydration Bladder
A hydration pack or drink bag is a type of hydration system built as a backpack or waistpack containing a reservoir or "bladder" commonly made of rubber or flexible plastic. The reservoir contains a capped mouth for filling with liquid and a hose that allows the wearer to drink hands-free. Most hoses end with a "bite valve" that opens when the user bites down on it; the valve may be protected by a dust cover. Some hydration packs are insulated to keep water from freezing or becoming warm. Uses The volume of the reservoir and the pack carrying it can vary widely depending on the purpose of the hydration pack. Some packs are extremely small and minimalist, designed to add as little weight as possible and remain secure while running or cycling, while others are more suited for backpacking and extended hikes, equipped with much larger bladders. However, as water weighs , it is impractical to carry more than a few liters in most situations; typical reservoirs are between 1-3 L even f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backpack
A backpack—also called knapsack, schoolbag, rucksack, rucksac, pack, sackpack, booksack, bookbag or backsack—is, in its simplest frameless form, a fabric sack carried on one's back and secured with two straps that go over the shoulders, but it can have an external frame, internal frame, and there are bodypacks. Backpacks are commonly used by hiking, hikers and students, and are often preferred to handbags for carrying heavy loads or carrying any sort of equipment, because of the limited capacity to carry heavy weights for long periods of time in the hands. Large backpacks, used to carry loads over , as well as smaller sports backpacks (e.g. running, cycling, hiking and hydration), usually offload the largest part (up to about 90%) of their weight onto padded hip belts, leaving the shoulder straps mainly for stabilising the load. This improves the potential to carry heavy loads, as the hips are stronger than the shoulders, and also increases agility and balance, since t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid Replacement
Fluid replacement or fluid resuscitation is the medical practice of replenishing bodily fluid lost through sweating, bleeding, fluid shifts or other pathologic processes. Fluids can be replaced with oral rehydration therapy (drinking), intravenous therapy, rectally such as with a Murphy drip, or by ''hypodermoclysis'', the direct injection of fluid into the subcutaneous tissue. Fluids administered by the oral and hypodermic routes are absorbed more slowly than those given intravenously. By mouth Oral rehydration therapy (ORT) is a simple treatment for dehydration associated with diarrhea, particularly gastroenteritis/gastroenteropathy, such as that caused by cholera or rotavirus. ORT consists of a solution of salts and sugars which is taken by mouth. For most mild to moderate dehydration in children, the preferable treatment in an emergency department is ORT over intravenous replacement of fluid., which cites: * It is used around the world, but is most important in the developing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavoring
A flavoring (or flavouring), also known as flavor (or flavour) or flavorant, is a food additive used to improve the taste or smell of food. It changes the perceptual impression of food as determined primarily by the chemoreceptors of the gustatory and olfactory systems. Along with additives, other components like sugars determine the taste of food. A flavoring is defined as a substance that gives another substance taste, altering the characteristics of the solute, causing it to become sweet, sour, tangy, etc. Although the term, in common language, denotes the combined chemical sensations of taste and smell, the same term is used in the fragrance and flavors industry to refer to edible chemicals and extracts that alter the flavor of food and food products through the sense of smell. Owing to the high cost, or unavailability of natural flavor extracts, most commercial flavorings are "nature-identical", which means that they are the chemical equivalent of natural flavors, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calories
The calorie is a unit of energy. For historical reasons, two main definitions of "calorie" are in wide use. The large calorie, food calorie, or kilogram calorie was originally defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one kilogram of water by one degree Celsius (or one kelvin). The small calorie or gram calorie was defined as the amount of heat needed to cause the same increase in one gram of water. Thus, 1 large calorie is equal to 1000 small calories. In nutrition and food science, the term ''calorie'' and the symbol ''cal'' almost always refers to the large unit. It is generally used in publications and package labels to express the energy value of foods in per serving or per weight, recommended dietary caloric intake, metabolic rates, etc. Some authors recommend the spelling ''Calorie'' and the symbol ''Cal'' (both with a capital C) to avoid confusion; however, this convention is often ignored. In physics and chemistry the word ''calorie'' and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present. Humidity depends on the temperature and pressure of the system of interest. The same amount of water vapor results in higher relative humidity in cool air than warm air. A related parameter is the dew point. The amount of water vapor needed to achieve saturation increases as the temperature increases. As the temperature of a parcel of air decreases it will eventually reach the saturation point without adding or losing water mass. The amount of water vapor contained within a parcel of air can vary significantly. For example, a parcel of air near saturation may contain 28 g of water per cubic metre of air at , but only 8 g of water per cubic metre of air at . Three primary measurements of humidity are widely employed: absolute, relative, and specific. Ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), the latter being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible to extract energy as heat from a body at that temperature. Temperature is important in all fields of natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Cubes
An ice cube is a small piece of ice, which is typically rectangular as viewed from above and trapezoidal as viewed from the side. Ice cubes are products of mechanical refrigeration and are usually produced to cool beverages. They may be produced at home in a freezer with an ice tray or in an automated ice-making accessory. They may also be produced industrially and sold commercially. Origin of production American physician and inventor John Gorrie built a refrigerator in 1844 with the purpose of producing ice to cool air. His refrigerator produced ice which hung from the ceiling in a basin to lower the ambient room temperature. During his time, bad air quality was thought to cause disease. Therefore, in order to help prevent and treat sickness, he pushed for the draining of swamps and the cooling of sickrooms. Production Trays and bags Ice cube trays are designed to be filled with water, then placed in a freezer until the water freezes into ice, producing ice cube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
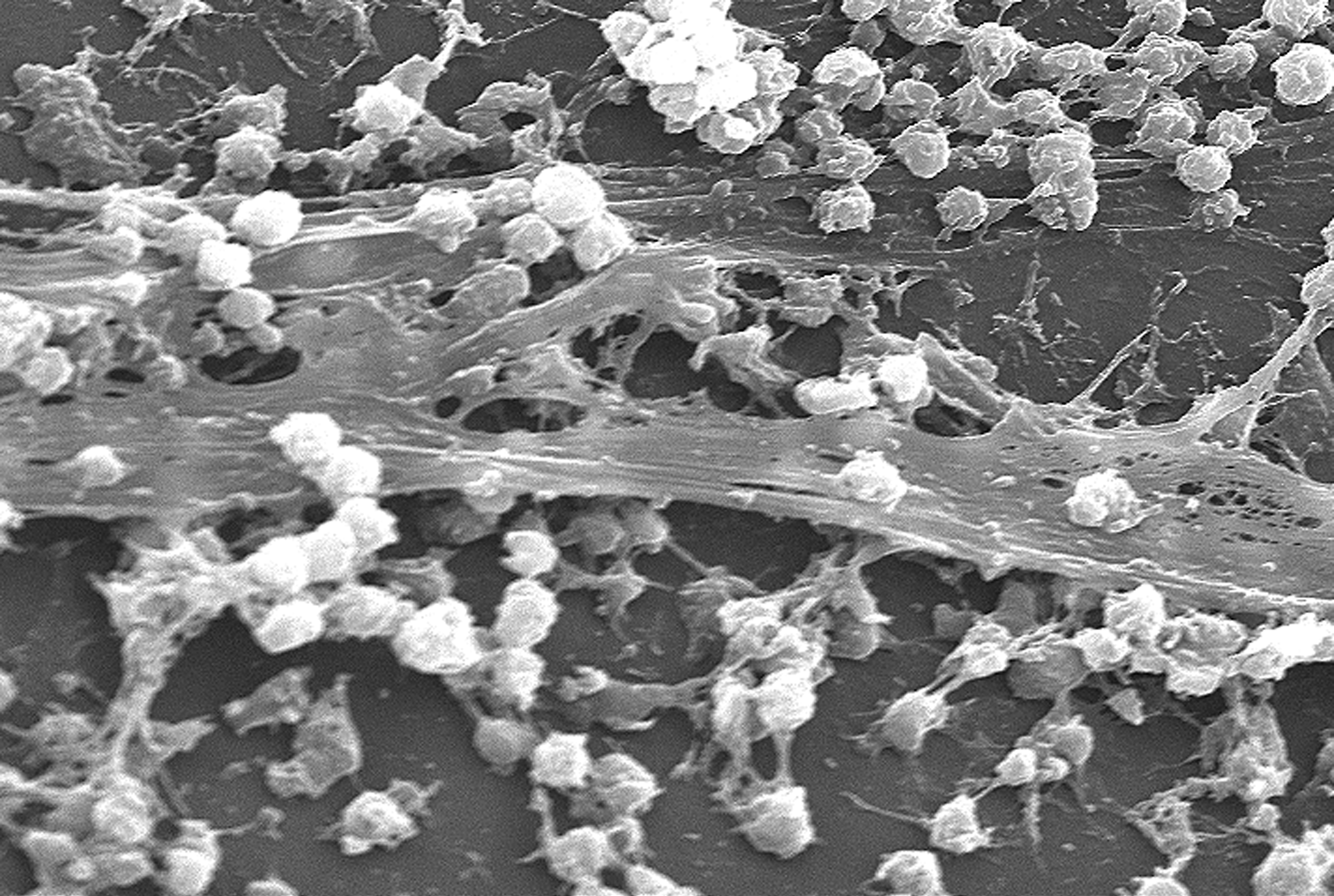
Biofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs). The cells within the biofilm produce the EPS components, which are typically a polymeric conglomeration of extracellular polysaccharides, proteins, lipids and DNA. Because they have three-dimensional structure and represent a community lifestyle for microorganisms, they have been metaphorically described as "cities for microbes". Biofilms may form on living or non-living surfaces and can be prevalent in natural, industrial, and hospital settings. They may constitute a microbiome or be a portion of it. The microbial cells growing in a biofilm are physiologically distinct from planktonic cells of the same organism, which, by contrast, are single cells that may float or swim in a liquid medium. Biofilms can form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylindrical
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base. A cylinder may also be defined as an infinite curvilinear surface in various modern branches of geometry and topology. The shift in the basic meaning—solid versus surface (as in ball and sphere)—has created some ambiguity with terminology. The two concepts may be distinguished by referring to solid cylinders and cylindrical surfaces. In the literature the unadorned term cylinder could refer to either of these or to an even more specialized object, the ''right circular cylinder''. Types The definitions and results in this section are taken from the 1913 text ''Plane and Solid Geometry'' by George Wentworth and David Eugene Smith . A ' is a surface consisting of all the points on all the lines which are parallel to a given line and which pass through a fixed plane curve in a pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Safety Research
Mountain Safety Research, or MSR, is a producer of camping, hiking and mountaineering equipment, such as portable stoves, water filters, snowshoes, and tents. While specializing in lightweight and technical equipment, MSR's gear is designed for a wide range of outdoor enthusiasts from novice to expert mountaineers. It is located in Seattle, Washington and owned by Cascade Designs. History MSR began as a newsletter in 1969 that covered topics around mountaineering Mountaineering or alpinism, is a set of outdoor activities that involves ascending tall mountains. Mountaineering-related activities include traditional outdoor climbing, skiing, and traversing via ferratas. Indoor climbing, sport climbing, a ... safety. In 1973, Larry Penberthy (1916–2001) developed the MSR Model 9 camp stove, a design which was relatively efficient in cold weather. He separated the stove burner from then small fuel tanks, and then pressurized auxiliary fuel bottles as the tank, and used a bett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
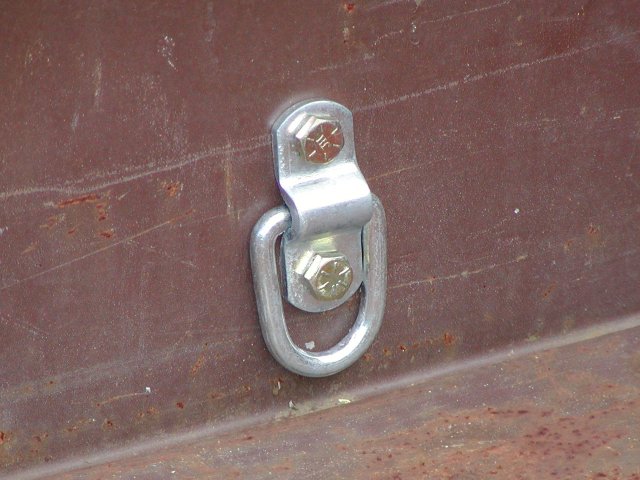
D-rings
A D-ring is a D-shaped metal ring used primarily as a lashing point in a tie-down system. Depending on their function D-rings may vary in composition, geometry, weight, finish, and load capacity. They may be screwed or welded in place, or attached to the end of a cord or a strap. In permanent applications recessed tie-down rings minimize obstruction when the ring is not in use. A D-ring may be also used as a permanent lifting point, or as a part of a tether. The most basic carabiner is a D-ring with a pivoting gate. References {{DEFAULTSORT:D-Ring Hardware (mechanical) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |