|
Hurricane Belle
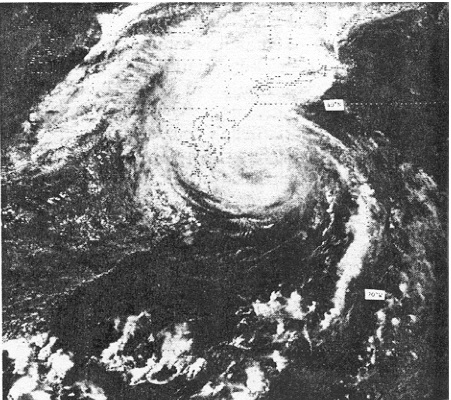
Hurricane Belle was a strong tropical cyclone that caused moderate damage across the East Coast of the United States in August 1976. In late July, a tropical wave emerged off the west coast of Africa. Traversing the Atlantic Ocean for more than a week, the system eventually consolidated into a tropical depression near the Bahamas on August 6. Remaining nearly stationary for a day, the depression strengthened into a tropical storm on August 7 and a hurricane later that day as it acquired a northwest motion. Formation of an eye accompanied quick intensification and Belle reached its peak the following day with winds of 120 mph (195 km/h). The hurricane subsequently turned north and accelerated, skirting the Outer Banks of North Carolina. Early on August 10, Belle made landfall on Long Island, New York, as a minimal hurricane crossing Long Island Sound and hitting the central coast of Connecticut as strong tropical storm. Thereafter, Belle transitio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1976 Atlantic Hurricane Season
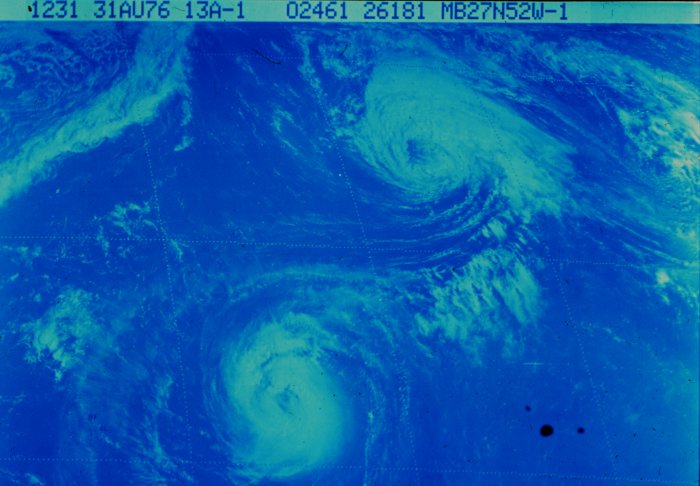
The 1976 Atlantic hurricane season featured only one fully tropical storm throughout both the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico, a rare occurrence. The season officially began on June 1 and lasted until November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. However, the first system, a subtropical storm, developed in the Gulf of Mexico on May 21, several days before the official start of the season. The system spawned nine tornadoes in Florida, resulting in about $628,000 (1976 USD) in damage, though impact was minor otherwise. The season was near average, with ten tropical storm forming, of which six became hurricanes. Two of those six became major hurricanes, which are Category 3 or higher on the Saffir–Simpson scale. The strongest hurricane of the season was Hurricane Belle, which reached Category 3 intensity east of North Carolina. Belle later struck Long Island, New York, as a Category 1 h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and South Carolina to the south, and Tennessee to the west. In the 2020 census, the state had a population of 10,439,388. Raleigh is the state's capital and Charlotte is its largest city. The Charlotte metropolitan area, with a population of 2,595,027 in 2020, is the most-populous metropolitan area in North Carolina, the 21st-most populous in the United States, and the largest banking center in the nation after New York City. The Raleigh-Durham-Cary combined statistical area is the second-largest metropolitan area in the state and 32nd-most populous in the United States, with a population of 2,043,867 in 2020, and is home to the largest research park in the United States, Research Triangle Park. The earliest evidence of human occupation i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone Warnings And Watches
Tropical cyclone warnings and watches are alerts issued by national weather forecasting bodies to coastal areas threatened by the imminent approach of a tropical cyclone of tropical storm or hurricane intensity. They are notices to the local population and civil authorities to make appropriate preparation for the cyclone, including evacuation of vulnerable areas where necessary. It is important that interests throughout the area of an alert make preparations to protect life and property, and do not disregard it on the strength of the detailed forecast track. Western hemisphere New tropical cyclone position and forecast information is available at least every twelve hours in the Southern Hemisphere and at least every six hours in the Northern Hemisphere from Regional Specialized Meteorological Centers and Tropical Cyclone Warning Centers. In conjunction with the National Hurricane Center, the national meteorological and hydrological services of Central America, the northern Atlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone Naming
Tropical cyclones and subtropical cyclones are named by various warning centers to simplify communication between forecasters and the general public regarding forecasts, watches and warnings. The names are intended to reduce confusion in the event of concurrent storms in the same basin. Once storms develop sustained wind speeds of more than , names are generally assigned to them from predetermined lists, depending on the basin in which they originate. Some tropical depressions are named in the Western Pacific; while tropical cyclones must contain a significant amount of gale-force winds before they are named in the Southern Hemisphere. Before it became standard practice to give personal (first) names to tropical cyclones, they were named after places, objects, or the saints' feast days on which they occurred. Credit for the first usage of personal names for weather systems is generally given to Queensland Government Meteorologist Clement Wragge, who named systems between 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gale
A gale is a strong wind; the word is typically used as a descriptor in nautical contexts. The U.S. National Weather Service defines a gale as sustained surface winds moving at a speed of between 34 and 47 knots (, or ).National Weather Service Glossary s.v "gale" Forecasters typically issue s when winds of this strength are expected. In the , a gale warning is specifically a maritime warning; the land-based equivalent in N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nassau, Bahamas
Nassau ( ) is the capital and largest city of the Bahamas. With a population of 274,400 as of 2016, or just over 70% of the entire population of the Bahamas, Nassau is commonly defined as a primate city, dwarfing all other towns in the country. It is the centre of commerce, education, law, administration, and media of the country. Lynden Pindling International Airport, the major airport for the Bahamas, is located about west of the city centre of Nassau, and has daily flights to major cities in Canada, the Caribbean, the United Kingdom and the United States. The city is located on the island of New Providence. Nassau is the site of the House of Assembly and various judicial departments and was considered historically to be a stronghold of pirates. The city was named in honour of William III of England, Prince of Orange-Nassau. Nassau's modern growth began in the late eighteenth century, with the influx of thousands of Loyalists and their slaves to the Bahamas following the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time or UTC is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is within about one second of mean solar time (such as UT1) at 0° longitude (at the IERS Reference Meridian as the currently used prime meridian) and is not adjusted for daylight saving time. It is effectively a successor to Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). The coordination of time and frequency transmissions around the world began on 1 January 1960. UTC was first officially adopted as CCIR Recommendation 374, ''Standard-Frequency and Time-Signal Emissions'', in 1963, but the official abbreviation of UTC and the official English name of Coordinated Universal Time (along with the French equivalent) were not adopted until 1967. The system has been adjusted several times, including a brief period during which the time-coordination radio signals broadcast both UTC and "Stepped Atomic Time (SAT)" before a new UTC was adopted in 1970 and implemented in 1972. This change also a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outflow (meteorology)
Outflow, in meteorology, is air that flows outwards from a storm system. It is associated with ridging, or anticyclonic flow. In the low levels of the troposphere, outflow radiates from thunderstorms in the form of a wedge of rain-cooled air, which is visible as a thin rope-like cloud on weather satellite imagery or a fine line on weather radar imagery. For observers on the ground, a thunderstorm outflow boundary often approaches in otherwise clear skies as a low, thick cloud that brings with it a gust front. Low-level outflow boundaries can disrupt the center of small tropical cyclones. However, outflow aloft is essential for the strengthening of a tropical cyclone. If this outflow is restricted or undercut, the tropical cyclone weakens. If two tropical cyclones are in close proximity, the upper-level outflow from the upwind system can limit the development of the other system. Thunderstorms For thunderstorms, outflow tends to indicate the development of a system. Large quan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc between the Greater Antilles to the north-west and the continent of South America."West Indies." ''Merriam-Webster's Geographical Dictionary'', 3rd ed. 2001. () Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster Inc., p. 1298. The islands of the Lesser Antilles form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea where it meets the Atlantic Ocean. Together, the Lesser Antilles and the Greater Antilles make up the Antilles. (Somewhat confusingly, the word Caribbean is sometimes used to refer only to the Antilles, and sometimes used to refer to a much larger region.) The Lesser and Greater Antilles, together with the Lucayan Archipelago, are collectively known as the West Indies. History after European arrival The Spanish were the first Europeans to arrive on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-pressure Area
In meteorology, a low-pressure area, low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather (such as cloudy, windy, with possible rain or storms), while high-pressure areas are associated with lighter winds and clear skies. Winds circle anti-clockwise around lows in the northern hemisphere, and clockwise in the southern hemisphere, due to opposing Coriolis force, Coriolis forces. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence that occur in the upper levels of the Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere (aloft). The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as cyclogenesis. In Meteorology#Dynamic meteorology, meteorology, atmospheric divergence aloft occurs in two kinds of places: * The first is in the area on the east side of upper Trough (meteorology), troughs, which form half of a Rossby wave within the Westerlies (a trough (meteorology), trough with la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Convection
Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability, or temperature difference layer in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air masses lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day which expands the height of the planetary boundary layer leads to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points. Moist convection leads to thunderstorm development, which is often responsible for severe weather throughout the world. Special threats from thunderstorms include hail, downbursts, and tornadoes. Overview There are a few general archetypes of atmospheric instability that are used to explain convection (or lack thereof). A necessary (but not sufficient) condition for convection is that the environmental lapse rate (the rate of decrease of temperature with height) is steeper than the lapse rate experienced by a rising parcel of air. When this condition is met, upward-displaced air parcels can become buoyant and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. It is the only province with both English and French as its official languages. New Brunswick is bordered by Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to the west. New Brunswick is about 83% forested and its northern half is occupied by the Appalachians. The province's climate is continental with snowy winters and temperate summers. New Brunswick has a surface area of and 775,610 inhabitants (2021 census). Atypically for Canada, only about half of the population lives in urban areas. New Brunswick's largest cities are Moncton and Saint John, while its capital is Fredericton. In 1969, New Brunswick passed the Official Languages Act which began recognizing French as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




.jpg)

