|
Honing (metalworking)
Honing is an abrasive machining process that produces a precision surface on a metal workpiece by scrubbing an abrasive grinding stone or grinding wheel against it along a controlled path. Honing is primarily used to improve the geometric form of a surface, but can also improve the surface finish. Typical applications are the finishing of cylinders for internal combustion engines, air bearing spindles and gears. There are many types of hones, but all consist of one or more abrasive stones that are held under pressure against the surface they are working on. Other similar processes are lapping and superfinishing. Honing stones Honing uses a special tool, called a ''honing stone'' or a ''hone'', to achieve a precision surface. The hone is composed of abrasive grains that are bound together with an adhesive. Generally, honing grains are irregularly shaped and about 10 to 50 micrometers in diameter (300 to 1500 mesh grit). Smaller grain sizes produce a smoother surface on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-pass Bore Finishing
Single-pass bore finishing is a machining process similar to honing to finish a bore, except the tool only takes a single pass. The process was originally developed to improve bore quality in cast iron workpieces.. Process This process uses multiple diamond-plated, barrel-shaped tools to finish a bore. The tool has a single layer of diamonds bonded to the tool, with about half of each diamond exposed. These special tools are made to a specific diameter and are only meant to open up the hole to that size.. The tools are usually mounted in a dedicated bore finishing machine, however they can also be mounted in a milling machine. In either case the tool, workpiece, or both are rotated and the tool is plunged into the bore and removed. The part is then transferred to the next station or a larger tool is mounted and a larger bore machined, and the process repeated until the desired bore geometry is reached. The number of tools required to achieve the desired bore size is dependent on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bore Honing
Bore or Bores often refer to: *Boredom * Drill Relating to holes * Boring (manufacturing), a machining process that enlarges a hole ** Bore (engine), the diameter of a cylinder in a piston engine or a steam locomotive ** Bore (wind instruments), the interior chamber of a wind instrument ** Gauge (firearms), the inner diameter of the barrel of a firearm ** Nominal bore, a pipe size standard ** Water well, known as a bore in Australia Places * Bore (woreda), a district of Ethiopia that includes the town of Bore * Bore, Emilia-Romagna, a commune in Emilia-Romagna, Italy * Boré, Mali, a village in Dangol Boré commune in the Mopti Region of Mali * Bore, Norway, a small village in Klepp municipality in Rogaland county, Norway * Bore Track, a track in the South Australian outback * Bore Valley, South Georgia, Antarctica People * Bore (surname) * Francisco Bores (1898–1972), Spanish artist Maritime shipping * Steamship Company Bore, a Finnish company that operated for a time with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flat Honing
Flat honing is a metalworking grinding process used to provide high quality flat surfaces. It combines the speed of grinding or honing with the precision of lapping. It has also been known under the terms high speed lapping and high precision grinding. Origin of term The term is derived from honing cylinders and holes. A flat workpiece surface is processed, hence the word flat; the word honing is used because the cutting speed is low compared to grinding. A fixed abrasive is used to provide accuracy and optical appearance of the surface finish. Sometimes it is also called fine grinding or surface grinding using planetary kinematics. History The technology is relatively young, having appeared in the 1980s. In the industry, production lapping is being replaced by flat honing in an ever-expanding array of applications. The flat honing process allows for an equivalent quality result, but at a significant reduction in manufacturing costs per workpiece. Savings result from reduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grinding (abrasive Cutting)
Grinding is a type of abrasive machining process which uses a grinding wheel as Cutting tool (machining), cutting tool. A wide variety of machines are used for grinding, best classified as portable or stationary: * Portable power tools such as angle grinders, die grinders and abrasive saw, cut-off saws * Stationary power tools such as bench grinders and abrasive saw, cut-off saws * Stationary hydropower, hydro- or human power, hand-powered grindstone (tool), sharpening stones Milling practice is a large and diverse area of manufacturing and Tool and die maker, toolmaking. It can produce very fine finishes and very accurate dimensions; yet in mass production contexts, it can also rough out large volumes of metal quite rapidly. It is usually better suited to the machining of very Hardness, hard materials than is "regular" machining (that is, cutting larger chips with cutting tools such as tool bits or milling cutters), and until recent decades it was the only practical way to mach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauge (engineering)
A gauge, in science and engineering, is a device used to make measurements or in order to display certain dimensional information. A wide variety of tools exist which serve such functions, ranging from simple pieces of material against which sizes can be measured to complex pieces of machinery. Depending on usage, a gauge can be described as "a device for measuring a physical quantity",Richard Talman, ''Geometric Mechanics'' (2008), p. 255-56: "a "gauge" is a device for measuring a physical quantity—a thermometer is a temperature gauge, a ruler is a length gauge".. for example "to determine thickness, gap in space, diameter of materials, or pressure of flow",Ray Herren, ''Agricultural Mechanics: Fundamentals & Applications'' (2009), p. 109: "A gauge is a device used to determine thickness, gap in space, diameter of materials, or pressure of flow". or "a device that displays the measurement of a monitored system by the use of a needle or pointer that moves along a calibrated scale" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutting Fluid
Cutting fluid is a type of coolant and lubricant designed specifically for metalworking processes, such as machining and stamping. There are various kinds of cutting fluids, which include oils, oil-water emulsions, pastes, gels, aerosols (mists), and air or other gases. Cutting fluids are made from petroleum distillates, animal fats, plant oils, water and air, or other raw ingredients. Depending on context and on which type of cutting fluid is being considered, it may be referred to as cutting fluid, cutting oil, cutting compound, coolant, or lubricant. Most metalworking and machining processes can benefit from the use of cutting fluid, depending on workpiece material. Common exceptions to this are cast iron and brass, which may be machined dry (though this is not true of all brasses, and any machining of brass will likely benefit from the presence of a cutting fluid). The properties that are sought after in a good cutting fluid are the ability to: * Keep the workpiece at a sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the Chemical stability, chemically stable form of carbon at Standard conditions for temperature and pressure, room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest Scratch hardness, hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. They are also the reason that diamond anvil cells can subject materials to pressures found deep in the Earth. Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen). Small numbers of lattice defect, defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) color diamond blue (bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
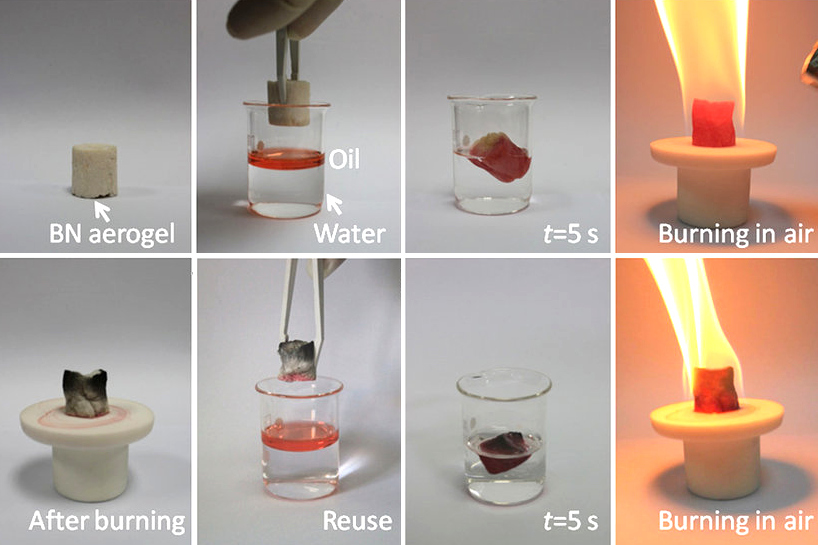
Cubic Boron Nitride
Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula BN. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice. The hexagonal form corresponding to graphite is the most stable and soft among BN polymorphs, and is therefore used as a lubricant and an additive to cosmetic products. The cubic ( zincblende aka sphalerite structure) variety analogous to diamond is called c-BN; it is softer than diamond, but its thermal and chemical stability is superior. The rare wurtzite BN modification is similar to lonsdaleite but slightly softer than the cubic form. Because of excellent thermal and chemical stability, boron nitride ceramics are used in high-temperature equipment and metal casting. Boron nitride has potential use in nanotechnology. Structure Boron nitride exists in multiple forms that differ in the arrangement of the boron and nitrogen atoms, giving rise to varyin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder and crystal since 1893 for use as an abrasive. Grains of silicon carbide can be bonded together by sintering to form very hard ceramics that are widely used in applications requiring high endurance, such as car brakes, car clutches and ceramic plates in bulletproof vests. Large single crystals of silicon carbide can be grown by the Lely method and they can be cut into gems known as synthetic moissanite. Electronic applications of silicon carbide such as light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and Cat's whisker detector, detectors in early radios were first demonstrated around 1907. SiC is used in semiconductor electronics devices that operate at high temperatures or high voltages, or both. Natural occurrence Naturally occurring moissanite is found in only minut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corundum
Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminium oxide () typically containing traces of iron, titanium, vanadium and chromium. It is a rock-forming mineral. It is a naturally transparent material, but can have different colors depending on the presence of transition metal impurities in its crystalline structure. Corundum has two primary gem varieties: ruby and sapphire. Rubies are red due to the presence of chromium, and sapphires exhibit a range of colors depending on what transition metal is present. A rare type of sapphire, padparadscha sapphire, is pink-orange. The name "corundum" is derived from the Tamil- Dravidian word ''kurundam'' (ruby-sapphire) (appearing in Sanskrit as ''kuruvinda''). Because of corundum's hardness (pure corundum is defined to have 9.0 on the Mohs scale), it can scratch almost all other minerals. It is commonly used as an abrasive on sandpaper and on large tools used in machining metals, plastics, and wood. Emery, a variety of corundum with no value a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |