|
Histoplasmosis
Histoplasmosis is a fungal infection caused by ''Histoplasma capsulatum''. Symptoms of this infection vary greatly, but the disease affects primarily the lungs. Occasionally, other organs are affected; called disseminated histoplasmosis, it can be fatal if left untreated. Histoplasmosis is common among AIDS patients because of their suppressed immunity. In immunocompetent individuals, past infection results in partial protection against ill effects if reinfected. ''Histoplasma capsulatum'' is found in soil, often associated with decaying bat guano or bird droppings. Disruption of soil from excavation or construction can release infectious elements that are inhaled and settle into the lung. From 1938 to 2013 in the US, 105 outbreaks were reported in a total of 26 states plus Puerto Rico. In 1978 to 1979 during a large urban outbreak in which 100,000 people were exposed to the fungus in Indianapolis, victims had pericarditis, rheumatological syndromes, esophageal and vocal cord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histoplasma Capsulatum
''Histoplasma capsulatum'' is a species of dimorphic fungus. Its sexual form is called ''Ajellomyces capsulatus''. It can cause pulmonary and disseminated histoplasmosis. ''H. capsulatum'' is "distributed worldwide, except in Antarctica, but most often associated with river valleys" and occurs chiefly in the "Central and Eastern United States" followed by "Central and South America, and other areas of the world". It is most prevalent in the Ohio and Mississippi River valleys. It was discovered by Samuel Taylor Darling in 1906. Growth and morphology ''H. capsulatum'' is an ascomycetous fungus closely related to ''Blastomyces dermatitidis''. It is potentially sexual, and its sexual state, ''Ajellomyces capsulatus'', can readily be produced in culture, though it has not been directly observed in nature. ''H. capsulatum'' groups with ''B. dermatitidis'' and the South American pathogen ''Paracoccidioides brasiliensis'' in the recently recognized fungal family Ajellomycetaceae. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
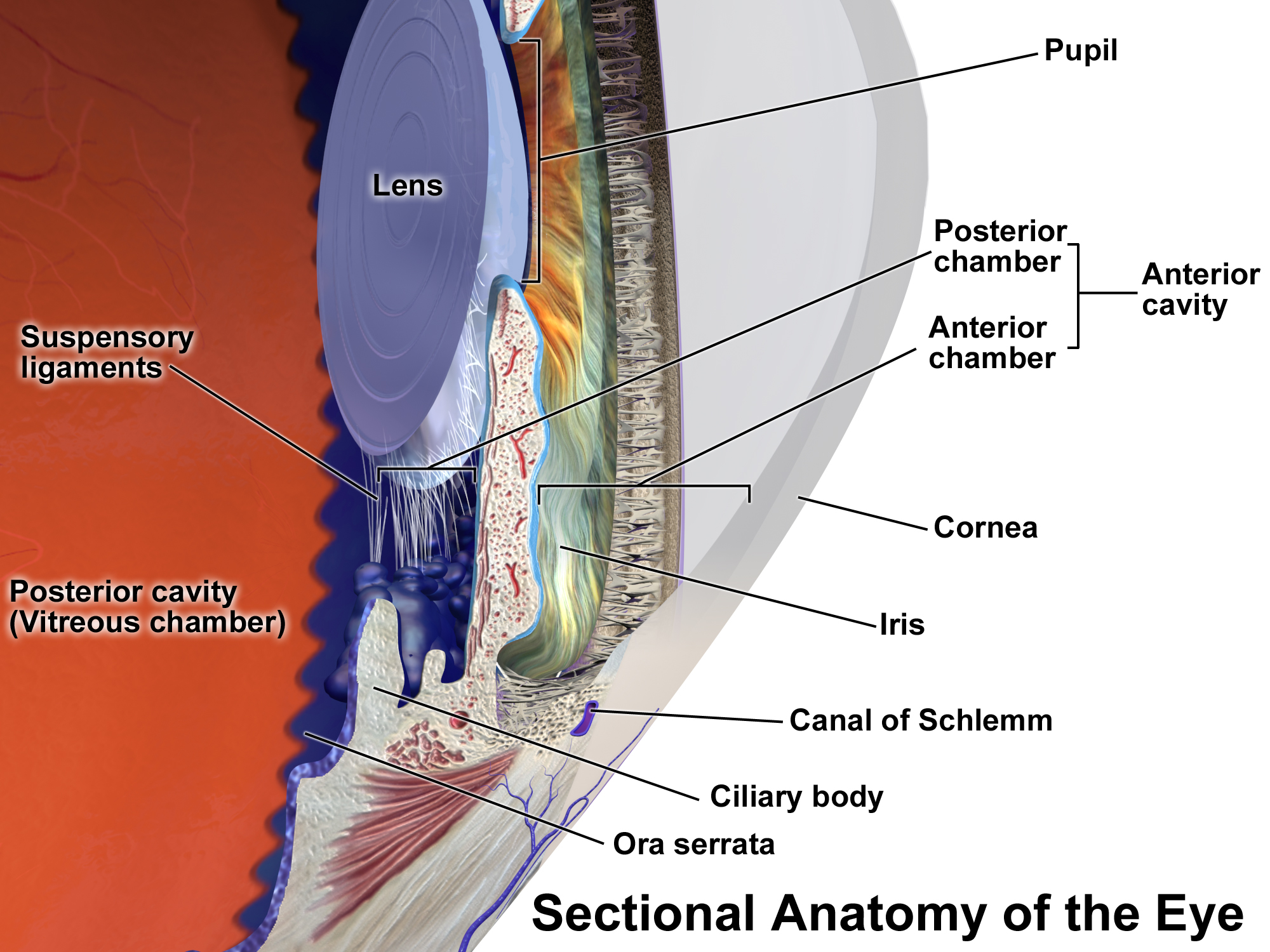
Presumed Ocular Histoplasmosis Syndrome
Presumed ocular histoplasmosis syndrome (POHS) is a syndrome affecting the eye, which is characterized by peripheral atrophic chorioretinal scars, atrophy or scarring adjacent to the optic disc and maculopathy. The loss of vision in POHS is caused by choroidal neovascularization. Presentation The diagnosis of POHS is based on the clinical triad of multiple white, atrophic choroidal scars, peripapillary pigment changes (dark spots around optic disc of the eye), and a maculopathy caused by choroidal neovascularization. Completely distinct from POHS, acute ocular histoplasmosis may rarely occur in immunodeficiency. Causes Despite its name, the "presumed" relationship of POHS to ''Histoplasma capsulatum'' is controversial and has been questioned by a number of medical professionals. The fungus has rarely been isolated from cases with POHS, Presumed Ocular Histoplasmosis Syndrome [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungal Infection
Fungal infection, also known as mycosis, is disease caused by fungi. Different types are traditionally divided according to the part of the body affected; superficial, subcutaneous, and systemic. Superficial fungal infections include common tinea of the skin, such as tinea of the body, groin, hands, feet and beard, and yeast infections such as pityriasis versicolor. Subcutaneous types include eumycetoma and chromoblastomycosis, which generally affect tissues in and beneath the skin. Systemic fungal infections are more serious and include cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, pneumocystis pneumonia, aspergillosis and mucormycosis. Signs and symptoms range widely. There is usually a rash with superficial infection. Fungal infection within the skin or under the skin may present with a lump and skin changes. Pneumonia-like symptoms or meningitis may occur with a deeper or systemic infection. Fungi are everywhere, but only some cause disease. Fungal infection occurs after spores are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guano
Guano (Spanish from qu, wanu) is the accumulated excrement of seabirds or bats. As a manure, guano is a highly effective fertilizer due to the high content of nitrogen, phosphate, and potassium, all key nutrients essential for plant growth. Guano was also, to a lesser extent, sought for the production of gunpowder and other explosive materials. The 19th-century seabird guano trade played a pivotal role in the development of modern input-intensive farming. The demand for guano spurred the human colonization of remote bird islands in many parts of the world. Unsustainable seabird guano mining processes can result in permanent habitat destruction and the loss of millions of seabirds. Bat guano is found in caves throughout the world. Many cave ecosystems are wholly dependent on bats to provide nutrients via their guano which supports bacteria, fungi, invertebrates, and vertebrates. The loss of bats from a cave can result in the extinction of species that rely on their guano. U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parotitis
Parotitis is an inflammation of one or both parotid glands, the major salivary glands located on either side of the face, in humans. The parotid gland is the salivary gland most commonly affected by inflammation. Etymology From Greek παρωτῖτις (νόσος), parōtĩtis (nósos) : (disease of the) parotid gland < παρωτίς (stem παρωτιδ-) : (gland) behind the ear < παρά - pará : behind, and οὖς - ous (stem ὠτ-, ōt-) : ear. Causes Dehydration ''Dehydration:'' This is a common, non-infectious cause of parotitis. It may occur in elderly or after surgery.Infectious parotitis ''Acute bacterial parotitis:'' is most often caused by a bacterial infection of but may be caused by any |
Chorioretinitis
Chorioretinitis is an inflammation of the choroid (thin pigmented vascular coat of the eye) and retina of the eye. It is a form of posterior uveitis. If only the choroid is inflamed, not the retina, the condition is termed choroiditis. The ophthalmologist's goal in treating these potentially blinding conditions is to eliminate the inflammation and minimize the potential risk of therapy to the patient. Symptoms Symptoms may include the presence of floating black spots, blurred vision, pain or redness in the eye, sensitivity to light, or excessive tearing. Causes Chorioretinitis is often caused by toxoplasmosis and cytomegalovirus infections (mostly seen in immunodeficient subjects such as people with HIV/AIDS or on immunosuppressant drugs). Congenital toxoplasmosis via transplacental transmission can also lead to sequelae such as chorioretinitis along with hydrocephalus and cerebral calcifications. Other possible causes of chorioretinitis are syphilis, sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Uveitis is described anatomically, by the part of the eye affected, as anterior, intermediate or posterior, or panuveitic if all parts are involved. Anterior uveitis ( iridocyclytis) is the most common, with the incidence of uveitis overall affecting approximately 1:4500, most commonly those between the ages of 20-60. Symptoms include eye pain, eye redness, floaters and blurred vision, and ophthalmic examination may show dilated ciliary blood vessels and the presence of cells in the anterior chamber. Uveitis may arise spontaneously, have a genetic component, or be associated with an autoimmune disease or infection. While the eye is a relatively protected environment, its immune mechanisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
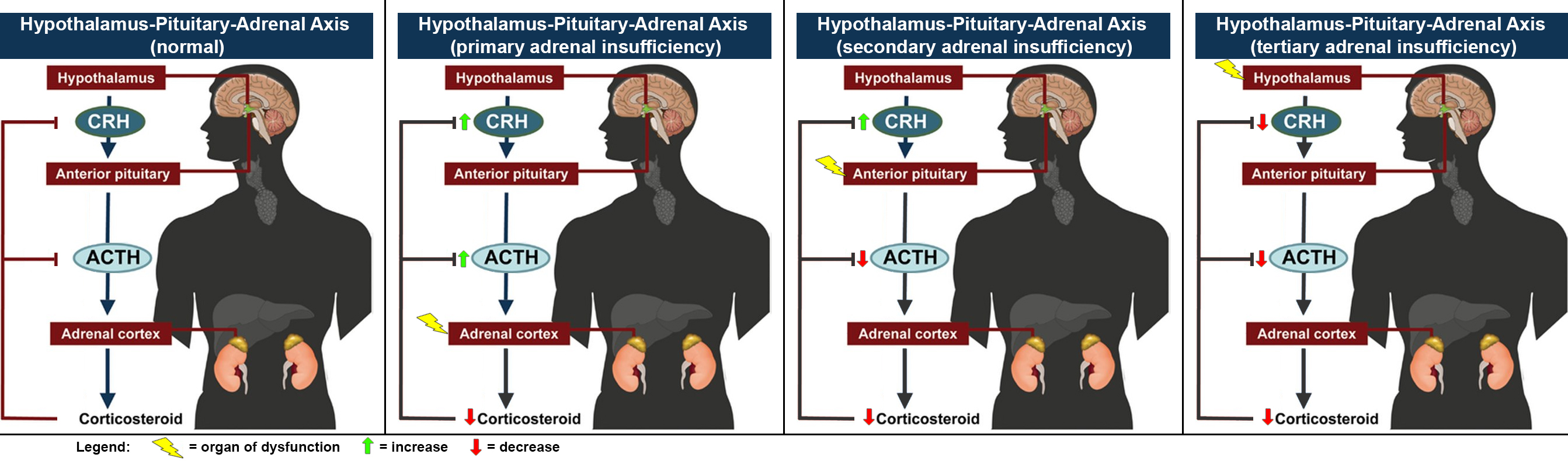
Adrenal Insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones. The adrenal gland normally secretes glucocorticoids (primarily cortisol), mineralocorticoids (primarily aldosterone), and androgens. These hormones are important in regulating blood pressure, electrolytes, and metabolism as a whole. Deficiency of these hormones leads to symptoms ranging from abdominal pain, vomiting, muscle weakness and fatigue, low blood pressure, depression, mood and personality changes (in mild cases) to organ failure and shock (in severe cases). An adrenal crisis may occur if the body is subjected to stress, such as an accident, injury, surgery, or severe infection; this is a life-threatening medical condition resulting from severe deficiency of cortisol in the body. Death may quickly follow. Adrenal insufficiency can be caused by dysfunction of the adrenal gland itself, whether by destruction (e.g. Addison's disease), failure of development ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spelunk
Caving – also known as spelunking in the United States and Canada and potholing in the United Kingdom and Ireland – is the recreational pastime of exploring wild cave systems (as distinguished from show caves). In contrast, speleology is the scientific study of caves and the cave environment.Caving in New Zealand (from Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand, Accessed 2012-11.) The challenges involved in caving vary according to the cave being visited; in addition to the total absence of light beyond the entrance, negotiating pitches, squeezes, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. It was historically referred to as consumption due to the weight loss associated with the disease. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is spread from one person to the next through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with Latent TB do not spread the disease. Active infection occurs more often in people with HIV/AIDS and in those who smoke. Diagnosis of active TB is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
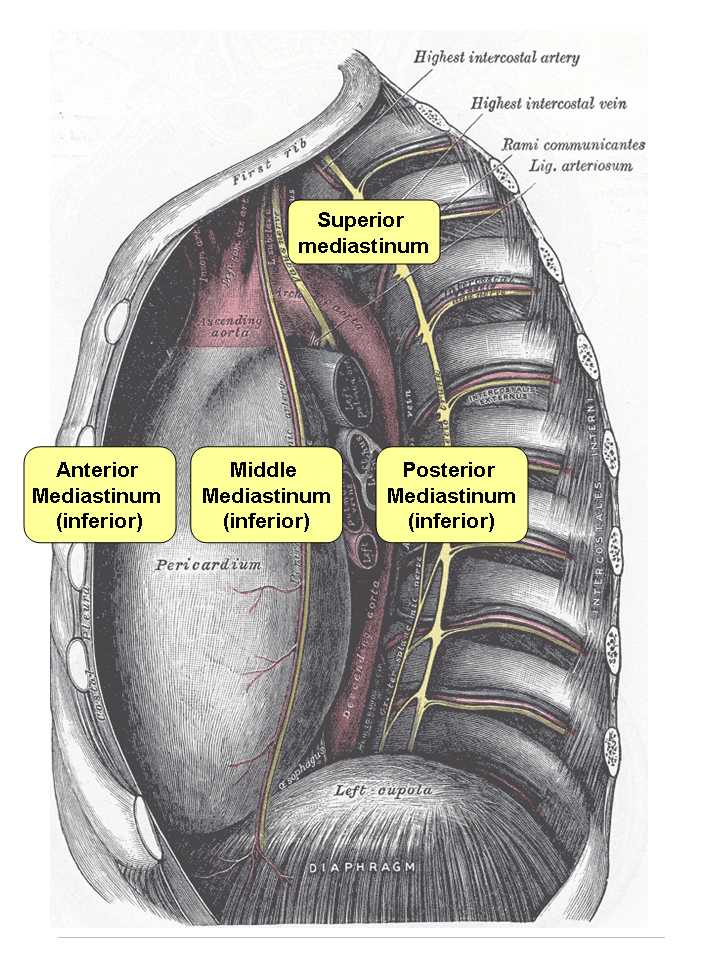
Fibrosing Mediastinitis
Mediastinitis is inflammation of the tissues in the mid-chest, or mediastinum. It can be either acute or chronic. It is thought to be due to four different etiologies: * direct contamination * hematogenous or lymphatic spread * extension of infection from the neck or retroperitoneum * extension from the lung or pleura Acute mediastinitis is usually caused by bacteria and is most often due to perforation of the esophagus. As the infection can progress rapidly, this is considered a serious condition. Chronic sclerosing (or fibrosing) mediastinitis, while potentially serious, is caused by a long-standing inflammation of the mediastinum, leading to growth of acellular collagen and fibrous tissue within the chest and around the central vessels and airways. It has a different cause, treatment, and prognosis than acute infectious mediastinitis. Space infections: Pretracheal space – lies anterior to trachea. Pretracheal space infection leads to mediastinitis. Here, the fascia fuses w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediastinitis
Mediastinitis is inflammation of the tissues in the mid-chest, or mediastinum. It can be either Acute (medical), acute or Chronic (medical), chronic. It is thought to be due to four different etiologies: * direct contamination * hematogenous or Lymphatic system, lymphatic spread * extension of infection from the neck or Retroperitoneal space, retroperitoneum * extension from the lung or pleura Acute mediastinitis is usually caused by bacteria and is most often due to perforation of the esophagus. As the infection can progress rapidly, this is considered a serious condition. Chronic Sclerosis (medicine), sclerosing (or fibrosis, fibrosing) mediastinitis, while potentially serious, is caused by a long-standing inflammation of the mediastinum, leading to growth of acellular collagen and fibrous tissue within the chest and around the central vessels and airways. It has a different cause, treatment, and prognosis than acute infectious mediastinitis. Space infections: Pretracheal space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |