|
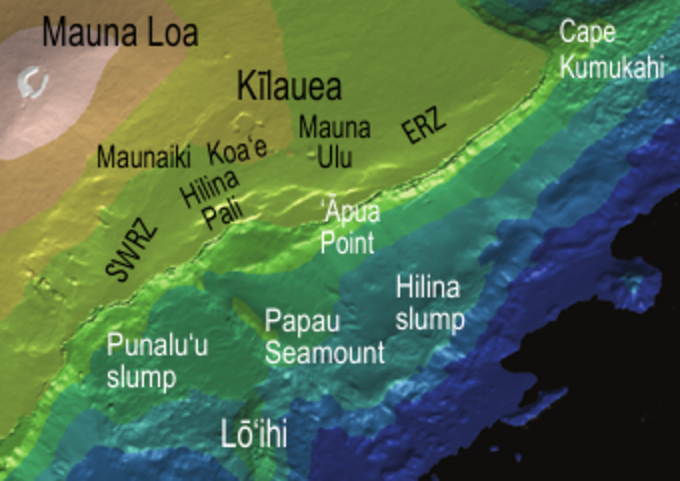
Hilina Slump
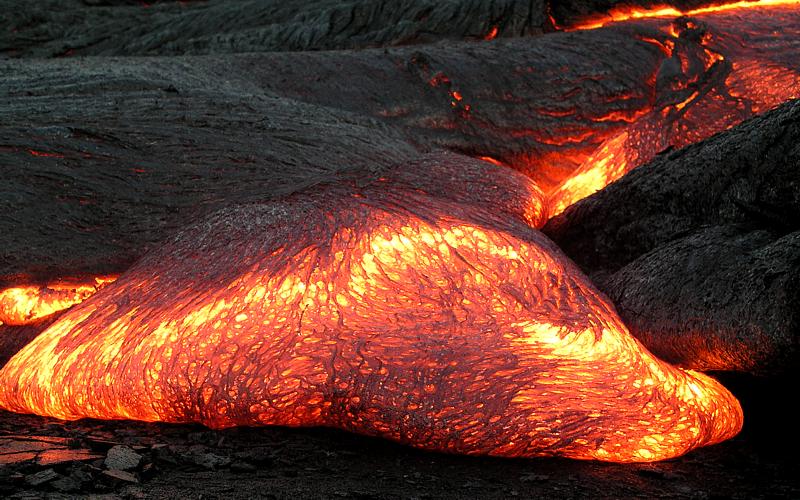
The Hilina Slump, on the south flank of the Kīlauea Volcano on the southeast coast of the Big Island of Hawaiʻi, is the most notable of several landslides that ring each of the Hawaiian Islands. These landslides are the means by which material deposited at a volcano's vents are transferred downward and seaward, eventually spilling onto the seabed to broaden the island. Kīlauea's entire south flank, extending out to Cape Kumukahi, is currently sliding seaward, with some parts of the central portion (over looking the Hilina slump) moving as much as per year, pushed by the forceful injection of magma and pulled by gravity. Current movement of the Hilina slump and recent volcanic activity, coupled with evidence of massive submarine slides in the geological past, has led to claims that megatsunamis might result if the south flank of Kīlauea should suddenly fail. Geology The Hawaiian Islands are volcanoes, the newest part of the Hawaiian-Emperor seamount chain, created ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kīlauea
Kīlauea ( , ) is an active shield volcano in the Hawaiian Islands. Located along the southeastern shore of the Big Island of Hawaii, the volcano is between 210,000 and 280,000 years old and emerged above sea level about 100,000 years ago. Historically, it is the most active of the five volcanoes that together form Hawaii island. Kīlauea is also one of the most active volcanoes on Earth, and the most recent and currently ongoing eruption began on September 29, 2021, when several vents began to erupt lava within Halemaʻumaʻu, a pit crater in the volcano's summit caldera. Kīlauea is the second-youngest product of the Hawaiian hotspot and the current eruptive center of the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain. Because it lacks topographic prominence and its activities historically coincided with those of Mauna Loa, Kīlauea was once thought to be a satellite of its much larger neighbor. Structurally, Kīlauea has a large, fairly recently formed caldera at its summit and two act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the Crust (geology), crust of a Planet#Planetary-mass objects, planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and volcanic gas, gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where list of tectonic plates, tectonic plates are divergent boundary, diverging or convergent boundary, converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1868 Hawaii Earthquake
The 1868 Hawaii earthquake was the largest recorded in the history of Hawaii island, with an estimated magnitude of 7.9 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of X (''Extreme''). The earthquake occurred at 4 p.m. local time on April 2, 1868 and caused a landslide and tsunami that led to 77 deaths. The aftershock sequence for this event has continued up to the present day. Background The island of Hawaii (commonly called the "Big Island") is the currently active volcanic center of the Hawaiian Islands formed over the Hawaii hotspot. Two of the active volcanoes on the Big Island are Kīlauea and Mauna Loa with a newer submarine volcano forming the Kamaʻehuakanaloa Seamount (formerly Loihi) to the southeast of the island. Continued growth of the southeastern part of the island is accompanied by major slumping and southeastward movement of the flanks of the two volcanoes. This flank displacement is linked to extension within the rift zones associated with both of the active volcanoes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Décollement
Décollement () is a gliding plane between two rock masses, also known as a basal detachment fault. Décollements are a deformational structure, resulting in independent styles of deformation in the rocks above and below the fault. They are associated with both compressional settings (involving folding and overthrusting) and extensional settings. Origin The term was first used by geologists studying the structure of the Swiss Jura Mountains, coined in 1907 by A. Buxtorf, who released a paper that theorized that the Jura is the frontal part of a décollement at the base of a nappe, rooted in the faraway Swiss Alps. Marcel Alexandre Bertrand published a paper in 1884 that dealt with Alpine nappism. Thin-skinned tectonics was implied in that paper but the actual term was not used until Buxtorf's 1907 publication. Formation Décollements are caused by surface forces, which 'push' at converging plate boundaries, facilitated by body forces (gravity sliding). Mechanically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dip-slip
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tephra
Tephra is fragmental material produced by a volcanic eruption regardless of composition, fragment size, or emplacement mechanism. Volcanologists also refer to airborne fragments as pyroclasts. Once clasts have fallen to the ground, they remain as tephra unless hot enough to fuse into pyroclastic rock or tuff. Tephrochronology is a geochronological technique that uses discrete layers of tephra—volcanic ash from a single eruption—to create a chronological framework in which paleoenvironmental or archaeological records can be placed. When a volcano explodes, it releases a variety of tephra including ash, cinders, and blocks. These layers settle on the land and, over time, sedimentation occurs incorporating these tephra layers into the geologic record. Often, when a volcano explodes, biological organisms are killed and their remains are buried within the tephra layer. These fossils are later dated by scientists to determine the age of the fossil and its place within the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural satellites. Besides molten rock, magma may also contain suspended crystals and gas bubbles. Magma is produced by melting of the mantle or the crust in various tectonic settings, which on Earth include subduction zones, continental rift zones, mid-ocean ridges and hotspots. Mantle and crustal melts migrate upwards through the crust where they are thought to be stored in magma chambers or trans-crustal crystal-rich mush zones. During magma's storage in the crust, its composition may be modified by fractional crystallization, contamination with crustal melts, magma mixing, and degassing. Following its ascent through the crust, magma may feed a volcano and be extruded as lava, or it may solidify underground to form an intrusion, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a conical volcano built up by many layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile with a summit crater and periodic intervals of explosive eruptions and effusive eruptions, although some have collapsed summit craters called calderas. The lava flowing from stratovolcanoes typically cools and hardens before spreading far, due to high viscosity. The magma forming this lava is often felsic, having high-to-intermediate levels of silica (as in rhyolite, dacite, or andesite), with lesser amounts of less-viscous mafic magma. Extensive felsic lava flows are uncommon, but have travelled as far as . Stratovolcanoes are sometimes called composite volcanoes because of their composite stratified structure, built up from sequential outpourings of erupted materials. They are among the most common types of volcanoes, in contrast to the less common shield volcano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shield Volcano
A shield volcano is a type of volcano named for its low profile, resembling a warrior's shield lying on the ground. It is formed by the eruption of highly fluid (low viscosity) lava, which travels farther and forms thinner flows than the more viscous lava erupted from a stratovolcano. Repeated eruptions result in the steady accumulation of broad sheets of lava, building up the shield volcano's distinctive form. Shield volcanoes are found wherever fluid low-silica lava reaches the surface of a rocky planet. However, they are most characteristic of ocean island volcanism associated with hot spots or with continental rift volcanism. They include the largest volcanoes on earth, such as Tamu Massif and Mauna Loa. Giant shield volcanoes are found on other planets of the Solar System, including Olympus Mons on Mars and Sapas Mons on Venus. Etymology The term 'shield volcano' is taken from the German term ''Schildvulkan'', coined by the Austrian geologist Eduard Suess in 1888 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |