|
High Germany
High Germany is a geographical term referring to the mountainous southern part of Germany. The term is first found in medieval Latin as , for example in chapter 23 of the ''Imago mundi'' of Honorius Augustodunensis (12th century, Regensburg): , "From the Danube to the Alps is High Germany". In German In German, the term ''Hochdeutschland'' to mean Alpine Germany was not uncommon in the 16th century, and was still so used by the Brothers Grimm in the 19th, but has largely fallen out of use. However, when the Republic of Austria was founded in 1918, ''Hochdeutschland'' was one of the proposals made for a name for the new country. Ernst Bruckmüller in: Österreichische Galerie Belvedere, Günter Düriegl (Hrsg): ''Das neue Österreich. Die Ausstellung zum Staatsvertragsjubiläum 1955–2005'', Wien 2005, , S. 242ff. The adjective ''hochdeutsch'', meaning Southern German, is most commonly used in the context of language: High German refers to all dialects of the German languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honorius Augustodunensis
Honorius Augustodunensis (c. 1080 – c. 1140), commonly known as Honorius of Autun, was a very popular 12th-century Christian theologian who wrote prolifically on many subjects. He wrote in a non-scholastic manner, with a lively style, and his works were approachable for the lay community in general. He was, therefore, something of a popularizer of clerical learning. Life Very little is known of his life. He says that he is ''Honorius Augustodunensis ecclesiae presbyter et scholasticus'', but nothing else is known. "Augustodunensis" was taken to mean Autun (''Augustodunum''), but that identification is now generally rejected. However, there is no solid reasoning for any other identification (such as Augst/''Augustodunensem praesulem'' near Basle, Augsburg/''Augusta Vindelicorum'' in Swabia, or ''Augustinensis'', from St Augustine's Abbey at Canterbury), so his by-name has stuck. It is certain that he was a monk and that he traveled to England and was a student of Anselm's for some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regensburg
Regensburg or is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the Danube, Naab and Regen rivers. It is capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the state in the south of Germany. With more than 150,000 inhabitants, Regensburg is the fourth-largest city in the State of Bavaria after Munich, Nuremberg and Augsburg. From its foundation as an imperial Roman river fort, the city has been the political, economic and cultural centre of the surrounding region; it is still known in the Romance languages by a cognate of its Latin name of "Ratisbona" (the version "Ratisbon" was long current in English). Later, under the rule of the Holy Roman Empire, it housed the Perpetual Diet of Regensburg. The medieval centre of the city was made a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2006 because of its well-preserved architecture and the city's historical importance for assemblies during the Holy Roman Empire. In 2014, Regensburg was among the top sights and travel attractions in Germany. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High German
The High German dialects (german: hochdeutsche Mundarten), or simply High German (); not to be confused with Standard High German which is commonly also called ''High German'', comprise the varieties of German spoken south of the Benrath and Uerdingen isoglosses in central and southern Germany, Austria, Liechtenstein, Switzerland, Luxembourg, and eastern Belgium, as well as in neighbouring portions of France (Alsace and northern Lorraine), Italy (South Tyrol), the Czech Republic (Bohemia), and Poland (Upper Silesia). They are also spoken in diaspora in Romania, Russia, the United States, Brazil, Argentina, Mexico, Chile, and Namibia. High German is marked by the High German consonant shift, separating it from Low German (Low Saxon) and Low Franconian (including Dutch) within the continental West Germanic dialect continuum. Classification As a technical term, the "high" in High German is a geographical reference to the group of dialects that forms "High German" (i.e. "Hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
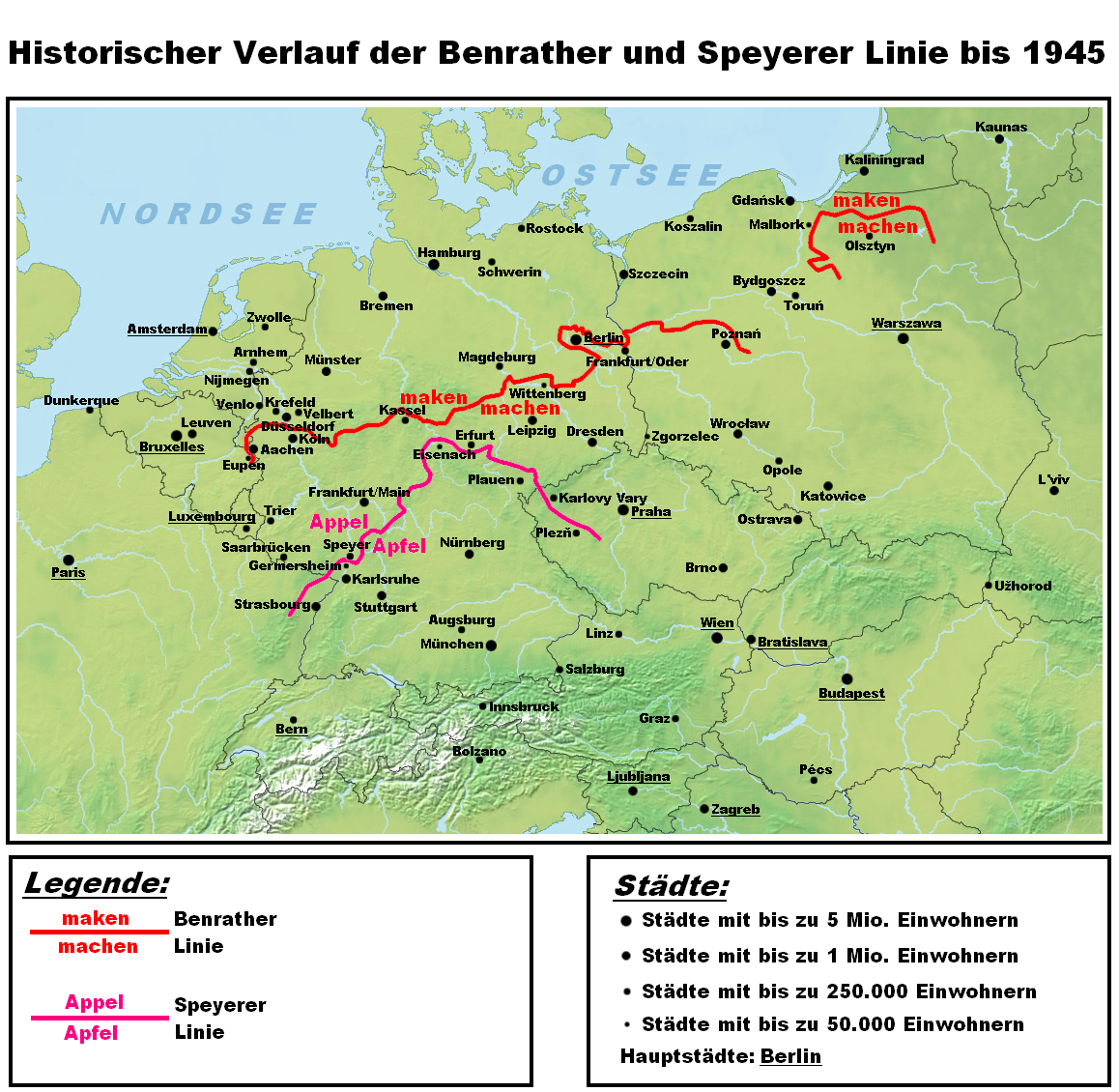
Benrath Line
In German linguistics, the Benrath line (german: Benrather Linie) is the ''maken–machen'' isogloss: dialects north of the line have the original in ''maken'' (to make), while those to the south have the innovative (''machen''). The Line runs from Aachen in the west via Benrath (south of Düsseldorf) to eastern Germany near Frankfurt an der Oder in the area of Berlin and Dessau and through former East Prussia dividing Low Prussian dialect and High Prussian dialect. It is called Benrath line because Benrath is the place where it crosses the Rhine. The High German consonant shift (3rd to 9th centuries AD), in which the (northern) Low German dialects for the most part did not participate, affected the southern varieties of the West Germanic dialect continuum. This shift is traditionally seen to distinguish the High German varieties from the other West Germanic languages. The impact of the High German consonant shift increases gradually to the South. The Benrath line does not mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hannover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German States of Germany, state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the List of cities in Germany by population, 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany after Berlin, Hamburg and Bremen. Hanover's urban area comprises the towns of Garbsen, Langenhagen and Laatzen and has a population of about 791,000 (2018). The Hanover Region has approximately 1.16 million inhabitants (2019). The city lies at the confluence of the River Leine and its tributary the Ihme, in the south of the North German Plain, and is the largest city in the Hannover–Braunschweig–Göttingen–Wolfsburg Metropolitan Region. It is the fifth-largest city in the Low German dialect area after Hamburg, Dortmund, Essen and Bremen. Before it became the capital of Lower Saxony in 1946, Hannover was the capital of the Principality of Calenberg (1636–1692), the Electorat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low German Language
: : : : : (70,000) (30,000) (8,000) , familycolor = Indo-European , fam2 = Germanic , fam3 = West Germanic , fam4 = North Sea Germanic , ancestor = Old Saxon , ancestor2 = Middle Low German , dia1 = West Low German , dia2 = East Low German , iso2 = nds , iso3 = nds , iso3comment = (Dutch varieties and Westphalian have separate codes) , lingua = 52-ACB , map = Nds Spraakrebeet na1945.svg , mapcaption = Present day Low German language area in Europe. , glotto = lowg1239 , glottoname = Low German , notice = IPA Low German or Low Saxon (in the language itself: , and other names; german: Plattdeutsch, ) is a West Germanic language variety spoken mainly in Northern Germany and the northeastern part of the Netherlands. The dialect of Plautdietsch is also spoken in the Russian Mennonite diaspora worldwi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Germany
Northern Germany (german: link=no, Norddeutschland) is a linguistic, geographic, socio-cultural and historic region in the northern part of Germany which includes the coastal states of Schleswig-Holstein, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and Lower Saxony and the three city-states Berlin, Hamburg and Bremen. It contrasts with Southern Germany, Western Germany and Eastern Germany. Language Northern Germany generally refers to the ''Sprachraum'' area north of the Uerdingen and Benrath line isoglosses, where Low German dialects are spoken. These comprise the Low Saxon dialects in the west (including the Westphalian language area up to the Rhineland), the East Low German region along the Baltic coast with Western Pomerania, the Altmark and northern Brandenburg, as well as the North Low German dialects. Although from the 19th century onwards, the use of Standard German was strongly promoted especially by the Prussian administration, Low German dialects are still present in rural areas, with an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regiolect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena: One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a characteristic of a particular group of the language's speakers. Under this definition, the dialects or varieties of a particular language are closely related and, despite their differences, are most often largely mutually intelligible, especially if close to one another on the dialect continuum. The term is applied most often to regional speech patterns, but a dialect may also be defined by other factors, such as social class or ethnicity. A dialect that is associated with a particular social class can be termed a sociolect, a dialect that is associated with a particular ethnic group can be termed an ethnolect, and a geographical/regional dialect may be termed a regiolectWolfram, Walt and Schilling, Natalie. 2016. ''American English: Dial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Germany (folk Song)
High Germany ( Roud 904), is a traditional folk song, once known throughout England, Ireland and Scotland, with a history spanning hundreds of years. There are three songs known as ''High Germany''. This page focuses on the best known one, the others being ''The Two Lovers'' or ''True Lovers'' (Roud 1445) and ''The Wars of Germany'' (Roud 5608). The song deals with a young man (usually named Willy) and his lover (Polly) lamenting over his conscription to fight in Germany, "High Germany" referring to the southern, mountainous part of the country. He attempts to convince her to join him in the war. "Polly" professes her love, but declares she is not fit for war. "Willy" attempts to persuade her to change her mind, stating that he will buy her a horse to ride, and that they will eventually wed. "Polly" still refuses and laments that her man has been drafted away from her. The historical setting of the ballad is most likely either the War of the Spanish Succession (1701–1714) or the Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Philip of Anjou and Charles of Austria, and their respective supporters, among them Spain, Austria, France, the Dutch Republic, Savoy and Great Britain. Related conflicts include the 1700–1721 Great Northern War, Rákóczi's War of Independence in Hungary, the Camisards revolt in southern France, Queen Anne's War in North America and minor trade wars in India and South America. Although weakened by over a century of continuous conflict, Spain remained a global power whose territories included the Spanish Netherlands, large parts of Italy, the Philippines, and much of the Americas, which meant its acquisition by either France or Austria potentially threatened the European balance of power. Attempts by Louis XIV of France and William III o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Delw'r_Byd.jpg)

.jpg)


