|
Heywood Island (Antarctica)
Heywood Island is the largest of the islands off the north coast of Robert Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. It is named after Captain Peter Heywood, RN (1773–1831), commanding HMS ''Nereus'' off the east coast of South America in 1810–13, formerly a midshipman in ''HMS Bounty'' under Captain William Bligh. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers operating from nearby Clothier Harbour. Description The island lies west by north of Catharina Point, Robert Island; north-west of Hammer Point, Robert Island; north-north-east of Rogozen Island; north-north-east of Fort William, Robert Island; and east-north-east of Table Island (British mapping in 1822, 1935, 1962, and 1968, American in 1942, Argentine in 1946 and 1957, Chilean in 1957 and 1971, and Bulgarian in 2009). It is long with a surface area of .L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands.Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort William (Robert Island)
Fort William Point is the conspicuous flat-topped rocky headland forming the northwest extremity of Coppermine Peninsula and Robert Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The point is a northwest entrance point of English Strait and forms the west side of the entrance to Carlota Cove. The feature was named by the early 19th century sealers who used it as a landmark for entering English Strait from the north. Location The point is located at which is southwest of Catharina Point, north of Spark Point, north-northeast of Barrientos Island, east of Okol Rocks and southeast of Table Island (British mapping in 1821, 1962 and 1968, Argentine in 1949, Soviet Union in 1961, Chilean in 1974, and Bulgarian in 2009). See also * List of lighthouses in Antarctica * Composite Antarctic Gazetteer * Robert Island * SCAR * South Shetland Islands * Territorial claims in Antarctica Seven sovereign states – Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, New Zealand, Norway, and the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
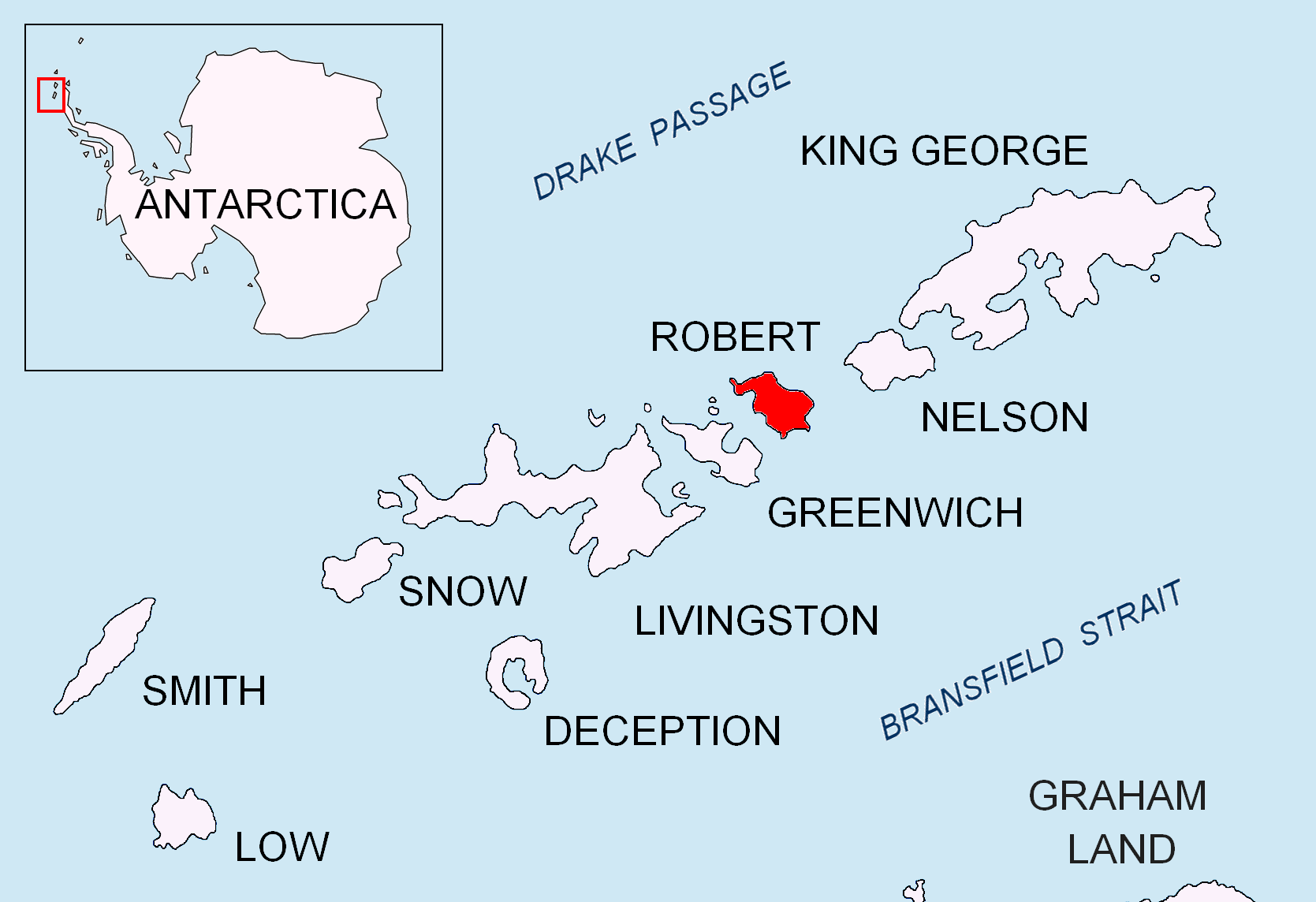
Islands Of Robert Island
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerry, skerries, cays or keys. An river island, island in a river or a lake island may be called an ait, eyot or ait, and a small island off the coast may be called a holm (island), holm. Sedimentary islands in the Ganges delta are called List of islands of Bangladesh, chars. A grouping of geographically or geologically related islands, such as the Philippines, is referred to as an archipelago. There are two main types of islands in the sea: continental and oceanic. There are also artificial islands, which are man-made. Etymology The word ''island'' derives from Middle English ''iland'', from Old English ''igland'' (from ''ig'' or ''ieg'', similarly meaning 'island' when used independently, and -land carrying its contemporary meaning; cf. Dutch language, Dutch ''eiland'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Peninsula
The Antarctic Peninsula, known as O'Higgins Land in Chile and Tierra de San Martín in Argentina, and originally as Graham Land in the United Kingdom and the Palmer Peninsula in the United States, is the northernmost part of mainland Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is part of the larger peninsula of West Antarctica, protruding from a line between Cape Adams (Weddell Sea) and a point on the mainland south of the Eklund Islands. Beneath the ice sheet that covers it, the Antarctic Peninsula consists of a string of bedrock islands; these are separated by deep channels whose bottoms lie at depths considerably below current sea level. They are joined by a grounded ice sheet. Tierra del Fuego, the southernmost tip of South America, is about away across the Drake Passage. The Antarctic Peninsula is in area and 80% ice-covered. The marine ecosystem around the western continental shelf of the Antarctic Peninsula (WAP) has been subjected to rapid climate change. Over the past 50 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Colony
A bird colony is a large congregation of individuals of one or more species of bird that nest or roost in proximity at a particular location. Many kinds of birds are known to congregate in groups of varying size; a congregation of nesting birds is called a breeding colony. Colonial nesting birds include seabirds such as auks and albatrosses; wetland species such as herons; and a few passerines such as weaverbirds, certain blackbirds, and some swallows. A group of birds congregating for rest is called a communal roost. Evidence of colonial nesting has been found in non- neornithine birds ( Enantiornithes), in sediments from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) of Romania. Variations on colonial nesting in birds Approximately 13% of all bird species nest colonially. Nesting colonies are very common among seabirds on cliffs and islands. Nearly 95% of seabirds are colonial, leading to the usage, seabird colony, sometimes called a rookery. Many species of terns nest in colonie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BirdLife International
BirdLife International is a global partnership of non-governmental organizations that strives to conserve birds and their habitats. BirdLife International's priorities include preventing extinction of bird species, identifying and safeguarding important sites for birds, maintaining and restoring key bird habitats, and empowering conservationists worldwide. It has a membership of more than 2.5 million people across 116 country partner organizations, including the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds, the Wild Bird Society of Japan, the National Audubon Society and American Bird Conservancy. BirdLife International has identified 13,000 Important Bird and Biodiversity Areas and is the official International Union for Conservation of Nature’s Red List authority for birds. As of 2015, BirdLife International has established that 1,375 bird species (13% of the total) are threatened with extinction ( critically endangered, endangered or vulnerable). BirdLife International p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Important Bird Area
An Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) is an area identified using an internationally agreed set of criteria as being globally important for the conservation of bird populations. IBA was developed and sites are identified by BirdLife International. There are over 13,000 IBAs worldwide. These sites are small enough to be entirely conserved and differ in their character, habitat or ornithological importance from the surrounding habitat. In the United States the Program is administered by the National Audubon Society. Often IBAs form part of a country's existing protected area network, and so are protected under national legislation. Legal recognition and protection of IBAs that are not within existing protected areas varies within different countries. Some countries have a National IBA Conservation Strategy, whereas in others protection is completely lacking. History In 1985, following a specific request from the European Economic Community, Birdlife International ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vrabcha Cove
Vrabcha Cove ( bg, залив Врабча, zaliv Vrabcha, ) is the 900 m wide cove indenting for 1 km the west coast of Heywood Island off the northwest coast of Robert Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The cove is named after the settlement of Vrabcha in western Bulgaria. Location Vrabcha Cove is located at . Bulgarian mapping in 2009. Map * L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands.Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. References Vrabcha Cove.SCAR A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other organs, and tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a n ... Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica. Bulgarian Antarctic Gazetteer. Antarctic Place-names Commission. (details in Bulgarianbasic datain English) External links Vrabcha Cove.Cop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Table Island (South Shetland Islands)
Table Island is a conspicuous flat-topped, rocky island lying north of Greenwich Island and north-northwest of the Aitcho group on the west side of English Strait in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The island is rising to over and extending , with a surface area of .L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands.Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. It is separated from Aitcho Islands to the south-southeast by the wide Klimash Passage. ''Turmoil Rock'' () is lying southeast of Table Island and north-northeast of Morris Rock. The area was visited by early-19th-century sealers. The island was descriptively named by sealers from its shape, while the rock was descriptively named from the breakers it creates, following a survey from ''HMS Protector'' in 1967. Location The midpoint of Table Island is located at and the island lies northwest of Fort William, Robert Island, north of Dee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |