|
Hermine Hug-Hellmuth
Hermine Hug-Hellmuth (born Hermine Hug Edle von Hugenstein; 31 August 1871, Vienna – 9 September 1924, Vienna) was an Austrian psychoanalyst. She is regarded as the first psychoanalyst practicing with children and the first to conceptualize the technique of psychoanalysing children. Her book, ''A Young Girl's Diary'' (1921), published in New York by Thomas Seltzer, was prefaced with an enthusiastic letter from Sigmund Freud dated 27 April 1915. Hug-Hellmuth denied authorship, however, and published the diary under the pseudonym Grete Lainer. In 1923 Hug-Hellmuth ultimately accepted title of editor for the diary in the third German edition. Written from a psychoanalyst perspective, the work which included Freudian theories to explain phenomena. It was praised within the field of psychoanalysis. It is one of the most cited contributions to child psychoanalysis. She became a member of the Vienna Psychoanalytic Society from 1913 to 1924 but was murdered by her nephew, Rudolf Hug, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermine Hug-Hellmuth
Hermine Hug-Hellmuth (born Hermine Hug Edle von Hugenstein; 31 August 1871, Vienna – 9 September 1924, Vienna) was an Austrian psychoanalyst. She is regarded as the first psychoanalyst practicing with children and the first to conceptualize the technique of psychoanalysing children. Her book, ''A Young Girl's Diary'' (1921), published in New York by Thomas Seltzer, was prefaced with an enthusiastic letter from Sigmund Freud dated 27 April 1915. Hug-Hellmuth denied authorship, however, and published the diary under the pseudonym Grete Lainer. In 1923 Hug-Hellmuth ultimately accepted title of editor for the diary in the third German edition. Written from a psychoanalyst perspective, the work which included Freudian theories to explain phenomena. It was praised within the field of psychoanalysis. It is one of the most cited contributions to child psychoanalysis. She became a member of the Vienna Psychoanalytic Society from 1913 to 1924 but was murdered by her nephew, Rudolf Hug, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vienna
en, Viennese , iso_code = AT-9 , registration_plate = W , postal_code_type = Postal code , postal_code = , timezone = CET , utc_offset = +1 , timezone_DST = CEST , utc_offset_DST = +2 , blank_name = Vehicle registration , blank_info = W , blank1_name = GDP , blank1_info = € 96.5 billion (2020) , blank2_name = GDP per capita , blank2_info = € 50,400 (2020) , blank_name_sec1 = HDI (2019) , blank_info_sec1 = 0.947 · 1st of 9 , blank3_name = Seats in the Federal Council , blank3_info = , blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD , blank_info_sec2 = .wien , website = , footnotes = , image_blank_emblem = Wien logo.svg , blank_emblem_size = Vienna ( ; german: Wien ; ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous city and state. A landlocked country, Austria is bordered by Germany to the northwest, the Czech Republic to the north, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The country occupies an area of and has a population of 9 million. Austria emerged from the remnants of the Eastern and Hungarian March at the end of the first millennium. Originally a margraviate of Bavaria, it developed into a duchy of the Holy Roman Empire in 1156 and was later made an archduchy in 1453. In the 16th century, Vienna began serving as the empire's administrative capital and Austria thus became the heartland of the Habsburg monarchy. After the dissolution of the H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychoanalyst
PsychoanalysisFrom Greek: + . is a set of theories and therapeutic techniques"What is psychoanalysis? Of course, one is supposed to answer that it is many things — a theory, a research method, a therapy, a body of knowledge. In what might be considered an unfortunately abbreviated description, Freud said that anyone who recognizes transference and resistance is a psychoanalyst, even if he comes to conclusions other than his own.… I prefer to think of the analytic situation more broadly, as one in which someone seeking help tries to speak as freely as he can to someone who listens as carefully as he can with the aim of articulating what is going on between them and why. David Rapaport (1967a) once defined the analytic situation as carrying the method of interpersonal relationship to its last consequences." Gill, Merton M. 1999.Psychoanalysis, Part 1: Proposals for the Future" ''The Challenge for Psychoanalysis and Psychotherapy: Solutions for the Future''. New York: Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Seltzer (translator)
Thomas Seltzer (22 February 1875, Russia − 11 September 1943, New York City) was a Russian-American translator, editor and book publisher. Life Born in Russia, Thomas Seltzer moved to the United States with his family as a young child. He attended the University of Pennsylvania on scholarship and graduated in 1897, going on to do post-graduate work at Columbia University. In addition to speaking his native Russian, Seltzer was conversant in Polish, Italian, German, Yiddish, and French and it was his language skills that led him to a career as a translator. He parleyed his way with words into work as a journalist and editor, writing for newspapers and magazines, notably ''Harper's Weekly'' and in 1911-1918, Seltzer worked with Max Eastman, Charles Erskine Scott Wood, and others as editor of the socialist magazine, ''The Masses''. As an editor, Seltzer gained experience at Funk & Wagnalls and beginning in 1917 the New York publishing firm Boni & Liveright. It was during his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigmund Freud
Sigmund Freud ( , ; born Sigismund Schlomo Freud; 6 May 1856 – 23 September 1939) was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a clinical method for evaluating and treating pathologies explained as originating in conflicts in the psyche, through dialogue between a patient and a psychoanalyst. Freud was born to Galician Jewish parents in the Moravian town of Freiberg, in the Austrian Empire. He qualified as a doctor of medicine in 1881 at the University of Vienna. Upon completing his habilitation in 1885, he was appointed a docent in neuropathology and became an affiliated professor in 1902. Freud lived and worked in Vienna, having set up his clinical practice there in 1886. In 1938, Freud left Austria to escape Nazi persecution. He died in exile in the United Kingdom in 1939. In founding psychoanalysis, Freud developed therapeutic techniques such as the use of free association and discovered transference, establishing its central role in the analyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vienna Psychoanalytic Society
The Vienna Psychoanalytic Society (, WPV), formerly known as the Wednesday Psychological Society, is the oldest psychoanalysis society in the world. In 1908, reflecting its growing institutional status as the international psychoanalytic authority of the time, the Wednesday group was reconstituted under its new name with Sigmund Freud as President, a position he relinquished in 1910 in favor of Alfred Adler. During its 36-year history, between 1902 and 1938, the Society had a total of 150 members. Prominent members *Sigmund Freud *Alfred Adler *Wilhelm Reich *Otto Rank *Karl Abraham *Carl Jung *Sándor Ferenczi * Guido Holzknecht * Isidor Isaak Sadger *Victor Tausk *Hanns Sachs *Ludwig Binswanger *Carl Alfred Meier *Sabina Spielrein *Margarete Hilferding *Herbert Silberer * Paul Schilder First meetings In November 1902, Sigmund Freud wrote to Alfred Adler, "A small circle of colleagues and supporters afford me the great pleasure of coming to my house in the evening (8:30 PM afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anna Freud
Anna Freud (3 December 1895 – 9 October 1982) was a British psychoanalyst of Austrian-Jewish descent. She was born in Vienna, the sixth and youngest child of Sigmund Freud and Martha Bernays. She followed the path of her father and contributed to the field of psychoanalysis. Alongside Hermine Hug-Hellmuth and Melanie Klein, she may be considered the founder of psychoanalytic child psychology. Compared to her father, her work emphasized the importance of the ego and its normal "developmental lines" as well as incorporating a distinctive emphasis on collaborative work across a range of analytical and observational contexts. After the Freud family were forced to leave Vienna in 1938 with the advent of the Nazi regime in Austria, she resumed her psychoanalytic practice and her pioneering work in child psychology in London, establishing the Hampstead Child Therapy Course and Clinic in 1952 (now the Anna Freud National Centre for Children and Families) as a centre for therapy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanie Klein
Melanie Klein (née Reizes; 30 March 1882 – 22 September 1960) was an Austrian-British author and psychoanalyst known for her work in child analysis. She was the primary figure in the development of object relations theory. Klein suggested that pre-verbal existential anxiety in infancy catalyzed the formation of the unconscious, resulting in the unconscious splitting of the world into good and bad idealizations. In her theory, how the child resolves that split depends on the constitution of the child and the character of nurturing the child experiences; the quality of resolution can inform the presence, absence, and/or type of distresses a person experiences later in life. Life Melanie Klein was born into a Jewish family and spent most of her early life in Vienna. She was the fourth and final child of parents Moriz, a doctor, and Libussa Reizes. Educated at the Gymnasium, Klein planned to study medicine. Her family's loss of wealth caused her to change her plans. At the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic (term)
The word ''catholic'' (derived via Late Latin ''catholicus'', from the Greek adjective ''katholikos'' 'universal') comes from the Greek phrase ''katholou'' 'on the whole, according to the whole, in general', and is a combination of the Greek words 'about' and 'whole'. The first known use of "Catholic" was by the church father Saint Ignatius of Antioch in his ''Letter to the Smyrnaeans'' (circa 110 AD). In the context of Christian ecclesiology, it has a rich history and several usages. The word in English can mean either "of the Catholic faith" or "relating to the historic doctrine and practice of the Western Church". "Catholicos", the title used for the head of some churches in Eastern Christian traditions, is derived from the same linguistic origin. In non-ecclesiastical use, it derives its English meaning directly from its root, and is currently used to mean the following: * including a wide variety of things, or all-embracing; * universal or of general inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Vienna
The University of Vienna (german: Universität Wien) is a public research university located in Vienna, Austria. It was founded by Duke Rudolph IV in 1365 and is the oldest university in the German-speaking world. With its long and rich history, the university has developed into one of the largest universities in Europe, and also one of the most renowned, especially in the Humanities. It is associated with 21 Nobel prize winners and has been the academic home to many scholars of historical as well as of academic importance. History From the Middle Ages to the Enlightenment The university was founded on March 12, 1365, by Rudolf IV, Duke of Austria, hence the name "Alma Mater Rudolphina". After the Charles University in Prague and Jagiellonian University in Kraków, the University of Vienna is the third oldest university in Central Europe and the oldest university in the contemporary German-speaking world; it remains a question of definition as the Charles University in Pra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isidor Sadger
Isidor Isaak Sadger (29 October 1867 – 21 December 1942), born in Neu Sandez, Galicia, was a forensic doctor and psychoanalyst in Vienna. A leader in the early development of psychoanalysis, he began his career as a neurological specialist and, in 1894, began publishing a series of articles on psychophysiology. He studied with Sigmund Freud from 1895 to 1904 with a concentration in homosexuality and fetishism and coined the term ''Sadomasochismus'' ( sadomasochism) in 1913. He also coined the term "Narcissmus" (narcissism). In September 1942, he was deported to the Theresienstadt concentration camp, where he died. Work Sadger published "Fragment der Psychoanalyse eines Homosexuellen" in the ''Jahrbuch für sexuellen Zwischenstufen'' in 1908. It described his analysis of a melancholy Danish count who was homosexual. The analysis lasted for only thirteen days before being terminated by the patient, whose sexual orientation was not changed. Later in 1908, Sadger published "Ist die ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


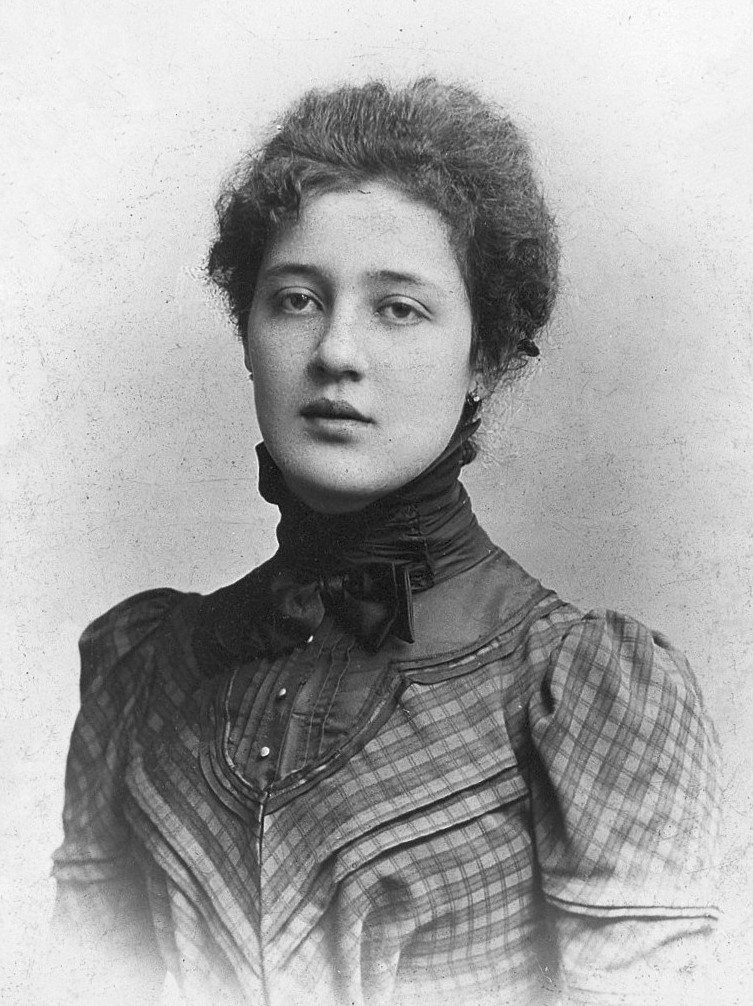
.jpg)
