|
Heptapolis
Middle Egypt () is the section of land between Lower Egypt (the Nile Delta) and Upper Egypt, stretching upstream from Asyut in the south to Memphis in the north. At the time, Ancient Egypt was divided into Lower and Upper Egypt, though Middle Egypt was technically a subdivision of Upper Egypt. It was not until the 19th century that archaeologists felt the need to divide Upper Egypt in two. As a result, they coined the term "Middle Egypt" for the stretch of river between Cairo and the Qena Bend. It was also associated with a region termed "Heptanomis" (; Greek: , in Ptol. iv. 5. § 55; more properly or , in Dionysius Periegetes 251; and sometimes ; meaning "Seven Nomes", a " nome" being a subdivision of ancient Egypt), generally as the district which separates the Thebaïd from the Delta. Middle Egypt today can be identified as the part of the Nile Valley that, while geographically part of Upper Egypt, is culturally closer to Lower Egypt. For instance, in terms of language, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heptanomis
Middle Egypt () is the section of land between Lower Egypt (the Nile Delta) and Upper Egypt, stretching upstream from Asyut in the south to Memphis in the north. At the time, Ancient Egypt was divided into Lower and Upper Egypt, though Middle Egypt was technically a subdivision of Upper Egypt. It was not until the 19th century that archaeologists felt the need to divide Upper Egypt in two. As a result, they coined the term "Middle Egypt" for the stretch of river between Cairo and the Qena Bend. It was also associated with a region termed " Heptanomis" (; Greek: , in Ptol. iv. 5. § 55; more properly or , in Dionysius Periegetes 251; and sometimes ; meaning "Seven Nomes", a " nome" being a subdivision of ancient Egypt), generally as the district which separates the Thebaïd from the Delta. Middle Egypt today can be identified as the part of the Nile Valley that, while geographically part of Upper Egypt, is culturally closer to Lower Egypt. For instance, in terms of language, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
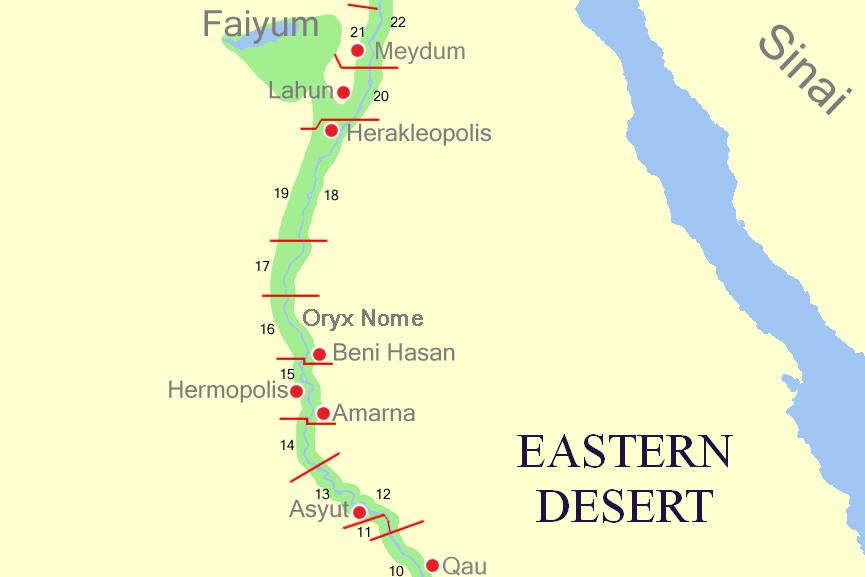
Middle Egypt Nomes
Middle or The Middle may refer to: * Centre (geometry), the point equally distant from the outer limits. Places * Middle (sheading), a subdivision of the Isle of Man * Middle Bay (other) * Middle Brook (other) * Middle Creek (other) * Middle Island (other) * Middle Lake (other) * Middle Mountain, California * Middle Peninsula, Chesapeake Bay, Virginia * Middle Range, a former name of the Xueshan Range on Taiwan Island * Middle River (other) * Middle Rocks, two rocks at the eastern opening of the Straits of Singapore * Middle Sound, a bay in North Carolina * Middle Township (other) * Middle East Music * "Middle" (song), 2015 * "The Middle" (Jimmy Eat World song), 2001 * "The Middle" (Zedd, Maren Morris and Grey song), 2018 *"Middle", a song by Rocket from the Crypt from their 1995 album ''Scream, Dracula, Scream!'' *"The Middle", a song by Demi Lovato from their debut album ''Don't Forget'' *"The Middle", a song ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nome (Egypt)
A nome (, from grc, νομός, ''nomós'', "district") was a territorial division in ancient Egypt. Each nome was ruled by a nomarch ( egy, ḥrj tp ꜥꜣ Great Chief). The number of nomes changed through the various periods of the history of ancient Egypt. Etymology The term ''nome'' comes from Ancient Greek νομός, ''nomós'', meaning "district"; the Ancient Egyptian term was ''sepat'' or ''spAt''. Today's use of the Ancient Greek rather than the Ancient Egyptian term came about during the Ptolemaic period, when the use of Greek was widespread in Egypt. The availability of Greek records on Egypt influenced the adoption of Greek terms by later historians. History Dynastic Egypt The division of ancient Egypt into nomes can be traced back to prehistoric Egypt (before 3100 BC). These nomes originally existed as autonomous city-states, but later began to unify. According to ancient tradition, the ruler Menes completed the final unification. Not only did the divi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inebu-hedj
Inebu-hedj (''White Walls'', also Inbu-Hedj, ''White fortress'') was one of 42 nomes (administrative division) in Ancient Egypt., Egypt Ancient.net, accessdate=2010-07-14 Egypt tourist authority, accessdate=2010-07-14 , Ancient Egyptian religion, Philae.net, accessdate=2010-07-14 Reshafim.org, accessdate=2010-07-14 Aldokan.com, accessdate=2010-07-14 Digital Egypt for Universities, accessdate=2010-07-14 Geography< ...
|
Photios I Of Constantinople
Photios I ( el, Φώτιος, ''Phōtios''; c. 810/820 – 6 February 893), also spelled PhotiusFr. Justin Taylor, essay "Canon Law in the Age of the Fathers" (published in Jordan Hite, T.O.R., & Daniel J. Ward, O.S.B., "Readings, Cases, Materials in Canon Law: A Textbook for Ministerial Students, Revised Edition" ollegeville, MN: The Liturgical Press, 1990, p. 61 (), was the ecumenical patriarch of Constantinople from 858 to 867 and from 877 to 886. He is recognized in the Eastern Orthodox Church as Saint Photios the Great. Photios is widely regarded as the most powerful and influential church leader of Constantinople subsequent to John Chrysostom's archbishopric around the turn of the fifth century. He is also viewed as the most important intellectual of his time – "the leading light of the ninth-century renaissance". He was a central figure in both the conversion of the Slavs to Christianity and the Photian schism, and is considered " e great systematic compiler of the Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agatharchides
Agatharchides or Agatharchus ( grc-gre, Ἀγαθαρχίδης or , ''Agatharchos'') of Cnidus was a Greek historian and geographer (flourished 2nd century BC). Life Agatharchides is believed to have been born at Cnidus, hence his appellation. As Stanley M. Burstein notes, the "evidence for Agatharchides' life is meagre." Photius describes him as a ''threptos'', a kind of assistant of servile origin, to Cinnaeus and states that he was later a secretary to Heraclides Lembus. Cinnaeus served as a counselor to Ptolemy VI; Heraclides is best known for negotiating the treaty that ended Antiochus IV's invasion of Egypt in 169 BC. Agatharchides furnishes few clues about his own life. At the conclusion of his ''On the Erythraean Sea'', he apologizes for being unable to complete his work "since our age is unable to similarly bear the toil" and "as a result of the disturbances in Egypt" he could no longer access the official records (a fragment cited by Photius in his ''Bibliotheca'' C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance to later Byzantine, Islamic, and Western European science. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the ''Almagest'', although it was originally entitled the ''Mathēmatikē Syntaxis'' or ''Mathematical Treatise'', and later known as ''The Greatest Treatise''. The second is the ''Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ''Apotelesmatika'' (lit. "On the Effects") but more commonly known as the '' Tetrábiblos'', from the Koine Greek meaning "Four Books", or by its Latin equivalent ''Quadripart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebes, Egypt
, image = Decorated pillars of the temple at Karnac, Thebes, Egypt. Co Wellcome V0049316.jpg , alt = , caption = Pillars of the Great Hypostyle Hall, in '' The Holy Land, Syria, Idumea, Arabia, Egypt, and Nubia'' , map_type = Egypt , map_alt = , map_size = , relief = yes , coordinates = , location = Luxor, Luxor Governorate, Egypt , region = Upper Egypt , type = Settlement , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , height = , builder = , material = , built = , abandoned = , epochs = , cultures = , dependency_of = , occupants = , event = , excavations = , archaeologists = , condition = , ownership = , management = , public_access = , website = , notes = , designation1 = WHS , designation1_offname = Ancient T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sa'idi People
A Ṣa‘īdī (, Coptic: ⲣⲉⲙⲣⲏⲥ ''Remris'') is a person from Upper Egypt (, Coptic: ⲙⲁⲣⲏⲥ ''Maris''). Etymology The word literally means "from Ṣa‘īd" (i.e. Upper Egypt), and can also refer to a form of music originating there, or to the dialect spoken by Sa‘idis. The Arabic word ''Ṣa‘īd'', as a geographical term, means "highland, upland, plateau". The suffix "-i" denotes the adjective. The word ''Ṣa‘īdi'' is pronounced in the dialect itself as or and the plural is or , while pronounced in Egyptian Arabic (Northern Egyptian) as and the plural is . In the Sahidic (Upper Egyptian) dialect of Coptic, the name for a person from Upper Egypt is (pronounced rem/rīs) meaning "person of the South" or (pronounced rem/pma/rīs or rem/ma/rīs) "person of (the) place of the south (i.e. Upper Egypt)". Stereotypes and jokes Ṣa‘īdis and their dialect are the subject of numerous Egyptian stereotypes and ethnic jokes, mainly from the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sa'idi Arabic
A Ṣa‘īdī (, Coptic: ⲣⲉⲙⲣⲏⲥ ''Remris'') is a person from Upper Egypt (, Coptic: ⲙⲁⲣⲏⲥ ''Maris''). Etymology The word literally means "from Ṣa‘īd" (i.e. Upper Egypt), and can also refer to a form of music originating there, or to the dialect spoken by Sa‘idis. The Arabic word ''Ṣa‘īd'', as a geographical term, means "highland, upland, plateau". The suffix "-i" denotes the adjective. The word ''Ṣa‘īdi'' is pronounced in the dialect itself as or and the plural is or , while pronounced in Egyptian Arabic (Northern Egyptian) as and the plural is . In the Sahidic (Upper Egyptian) dialect of Coptic, the name for a person from Upper Egypt is (pronounced rem/rīs) meaning "person of the South" or (pronounced rem/pma/rīs or rem/ma/rīs) "person of (the) place of the south (i.e. Upper Egypt)". Stereotypes and jokes Ṣa‘īdis and their dialect are the subject of numerous Egyptian stereotypes and ethnic jokes, mainly from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |