|
Henry Royce Institute
The Henry Royce Institute (often referred to as ‘Royce’) is the UK’s national institute for advanced materials research and innovation. Its vision is to identify challenges and to stimulate innovation in advanced materials research to support sustainable growth and development. Royce aims to be a "single front door" to the UK’s materials research community. Its stated mission is to “support world-recognised excellence in UK materials research, accelerating commercial exploitation of innovations, and delivering positive economic and societal impact for the UK.” Operating from its Hub at the University of Manchester, Royce is a partnership of eleven leading UK institutions. Royce operates as a hub and spoke collaboration between the University of Manchester (the hub), and the spokes of the founding Partners National Nuclear Laboratory, UK Atomic Energy Authority, Imperial College London, University of Cambridge, University of Leeds, University of Liverpool, University o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sustainable Growth
Sustainable development is an organizing principle for meeting human development goals while also sustaining the ability of natural systems to provide the natural resources and ecosystem services on which the economy and society depend. The desired result is a state of society where living conditions and resources are used to continue to meet human needs without undermining the integrity and stability of the natural system. Sustainable development was defined in the 1987 Brundtland Report as "Development that meets the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs".United Nations General Assembly (1987''Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development: Our Common Future'' Transmitted to the General Assembly as an Annex to document A/42/427 – Development and International Co-operation: Environment. As the concept of sustainable development developed, it has shifted its focus more towards the economi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Royce
Sir Frederick Henry Royce, 1st Baronet, (27 March 1863 – 22 April 1933) was an English engineer famous for his designs of car and aeroplane engines with a reputation for reliability and longevity. With Charles Rolls (1877–1910) and Claude Johnson (1864–1926), he founded Rolls-Royce. Rolls-Royce initially focused on large 40-50 horsepower motor cars, the Silver Ghost and its successors. Royce produced his first aero engine shortly after the outbreak of the First World War and aircraft engines became Rolls-Royce's principal product. Royce's health broke down in 1911 and he was persuaded to leave his factory in the Midlands at Derby and, taking a team of designers, move to the south of England spending winters in the south of France. He died at his home in Sussex in the spring of 1933. Early life Royce was born in Alwalton, Huntingdonshire, near Peterborough in 1863 to James and Mary Royce (née King). He was the youngest of their five children. His father ran a flour mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Graphene Institute
The National Graphene Institute is a research institute and building at the University of Manchester that is focused on the research of graphene. Construction of the building to house the institute started in 2013 and finished in 2015. Institute The creation of the institute, including the construction of the building, cost £61 million. Funded by the Government of the United Kingdom, UK Government (£38m) and the European Union's European Regional Development Fund (£23m), the building is the national centre for graphene research in the UK. It provides facilities for industry and university academics to collaborate on graphene applications and the commercialisation of graphene. The building was opened on 20 March 2015 by George Osborne. Building The five-story glass-fronted building provides of research space. This includes 1,500 square metres (16,000 sq ft) of class 100 and class 1000 clean rooms, one of which occupies the entire lower ground floor (in order to mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Turing Building
The Alan Turing Building, named after the mathematician and founder of computer science Alan Turing, is a building at the University of Manchester, in Manchester, England. It houses the School of Mathematics, the Photon Science Institute and the Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics (part of the School of Physics and Astronomy). The building is located in the Chorlton-on-Medlock district of Manchester, on Upper Brook Street, and is adjacent to University Place and the Henry Royce Institute. While under construction the project was known as AMPPS : Astronomy, Mathematics, Physics and Photon Science. The building was shortlisted for the Greater Manchester Building of the Year 2008 prize, which is awarded by the Greater Manchester Chamber of Commerce. The manager of the building project was awarded a silver medal in the Chartered Institute of Building "Construction Manager of the Year" awards. Architecture The £43 m building was completed in July 2007, and was designed by archite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maths And Social Sciences Building
The Maths and Social Sciences Building is a high-rise tower in Manchester, England. It was part of the University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology (UMIST) until that university merged with the Victoria University of Manchester, to form the University of Manchester, in 2004. It was vacated by the university in 2010 but is currently in use by the School of Materials while waiting for a new building to be constructed. The MSS Building was built in 1969, as part of the UMIST campus. Constructed from reinforced concrete and designed by architects Cruikshank and Seward, it has fifteen stories and an overall height of , making it the tallest building on the former UMIST campus. Unlike many examples of Brutalist architecture on university campuses of that period, the building deviates from a purely cuboid outline with decorative towers at either end (now used as convenient locations for mobile phone antennae) and the floors up to the 10th being larger, which also brea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Triangle (universities)
The golden triangle refers to the triangle formed by the university cities of Cambridge, London and Oxford in the southeast of England. The triangle is occasionally referred to as the Loxbridge triangle, a portmanteau of London and Oxbridge or, when limited to five members, the G5. The golden triangle universities are: * University of Oxford * University of Cambridge * University College London (UCL) * Imperial College London (ICL) * King's College London (KCL) * London School of Economics (LSE) The list of universities considered to be members of the golden triangle varies between sources, but typically comprises the University of Cambridge, the University of Oxford, Imperial College London, University College London, King's College London, and the London School of Economics. Some sources omit either or both of King's College London and the London School of Economics. while occasionally other universities are included, e.g. the London Business School and the London School o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Powerhouse
The Northern Powerhouse is a proposal to boost economic growth in the North of England by the 2010–15 coalition government and 2015–2016 Conservative government in the United Kingdom, particularly in the " Core Cities" of Hull, Manchester, Liverpool, Leeds, Sheffield and Newcastle. The proposal is based on the benefits of agglomeration and aims to reposition the British economy away from London and the South East. The spatial footprint of the Northern Powerhouse is defined as the 11 Local enterprise partnership areas of the North of England. The proposal involves improvement to transport links, investment in science and innovation, and devolution of powers in City Deals. Former MP for Stockton South, James Wharton, was appointed as minister responsible for the proposal in May 2015. A 2018 investigation by The Guardian indicated he rarely left London to visit the northern areas, however. In October 2015 during General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party Xi Jinpin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
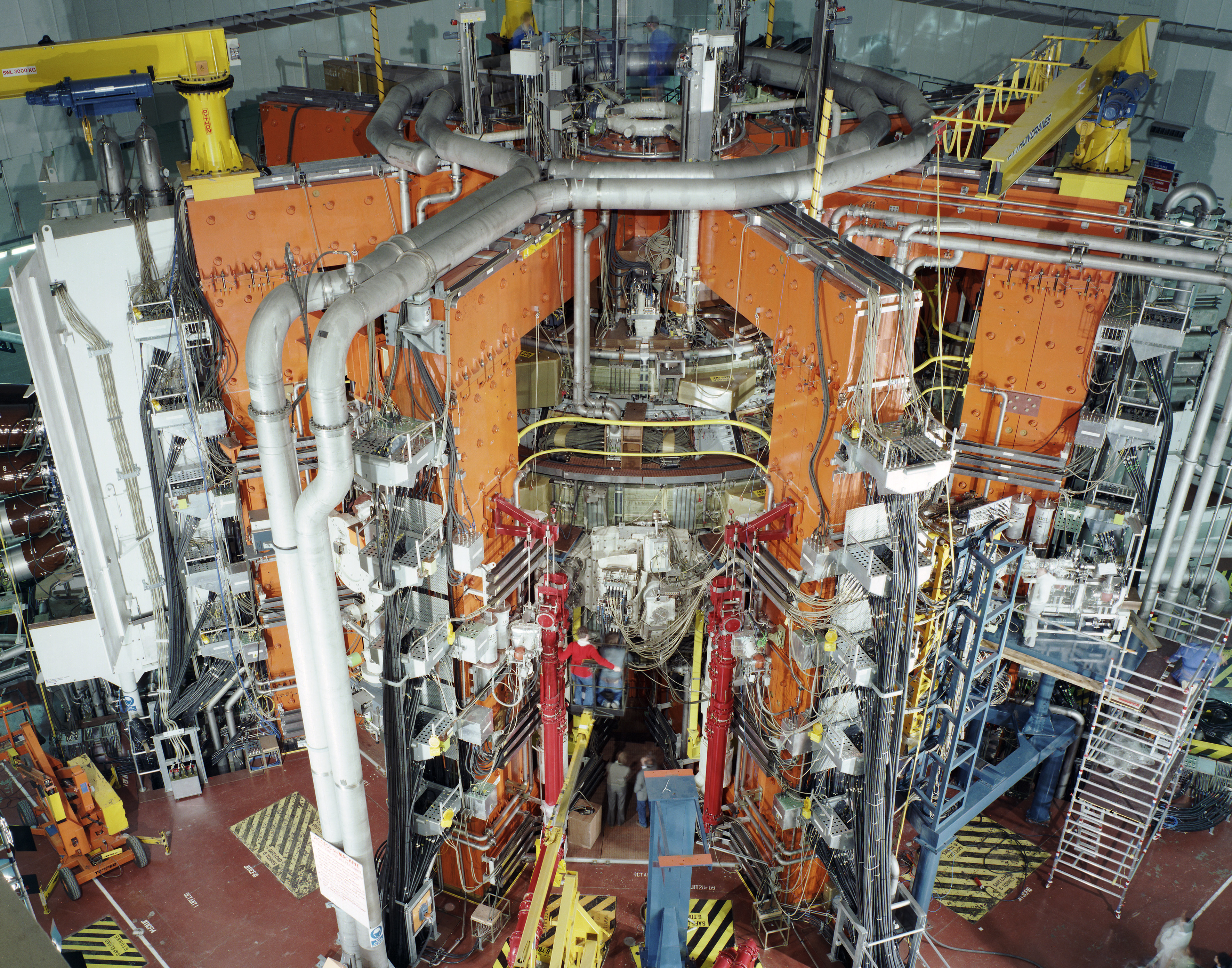
UKAEA
The United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority is a UK government research organisation responsible for the development of fusion energy. It is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS). The authority focuses on United Kingdom and European fusion energy research programmes at Culham in Oxfordshire, including the world's most powerful operating fusion device, the Joint European Torus (JET). The research aims to develop fusion power as a commercially viable, environmentally responsible energy source for the future. record59 megajoules of sustained fusion energy was demonstrated by scientists and engineers working on JET in December 2021. United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority owns the Culham Science Centre and has a stake in the Harwell Campus, and is involved in the development of both sites as locations for science and innovation-based business. On its formation in 1954, the authority was responsible for the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine, also referred to as precision medicine, is a medical model that separates people into different groups—with medical decisions, practices, interventions and/or products being tailored to the individual patient based on their predicted response or risk of disease. The terms personalized medicine, precision medicine, stratified medicine and P4 medicine are used interchangeably to describe this concept though some authors and organisations use these expressions separately to indicate particular nuances. While the tailoring of treatment to patients dates back at least to the time of Hippocrates, the term has risen in usage in recent years given the growth of new diagnostic and informatics approaches that provide understanding of the molecular basis of disease, particularly genomics. This provides a clear evidence base on which to stratify (group) related patients. Among the 14 Grand Challenges for Engineering, an initiative sponsored by National Academy of En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Economy
A circular economy (also referred to as circularity and CE) is a model of production and consumption, which involves sharing, leasing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing and recycling existing materials and products as long as possible. CE aims to tackle global challenges as climate change, biodiversity loss, waste, and pollution by emphasizing the design-based implementation of the three base principles of the model. The three principles required for the transformation to a circular economy are: eliminating waste and pollution, circulating products and materials, and the regeneration of nature. CE is defined in contradistinction to the traditional linear economy. The idea and concepts of circular economy (CE) have been studied extensively in academia, business, and government over the past ten years. CE has been gaining popularity since it helps to minimize emissions and consumption of raw materials, open up new market prospects and principally, increase the sustainability of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Technology
Quantum technology is an emerging field of physics and engineering, encompassing technologies that rely on the properties of quantum mechanics, especially quantum entanglement, quantum superposition, and quantum tunneling. Quantum computing, sensors, cryptography, simulation, measurement, and imaging are all examples of emerging quantum technologies. The development of quantum technology also heavily impacts established fields such as space exploration. Secure communications Quantum secure communication is a method that is expected to be 'quantum safe' in the advent of quantum computing systems that could break current cryptography systems using methods such as Shor's algorithm. These methods include quantum key distribution (QKD), a method of transmitting information using entangled light in a way that makes any interception of the transmission obvious to the user. Another method is the quantum random number generator, which is capable of producing truly random numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusion Power
Fusion power is a proposed form of power generation that would generate electricity by using heat from nuclear fusion reactions. In a fusion process, two lighter atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, while releasing energy. Devices designed to harness this energy are known as fusion reactors. Research into fusion reactors began in the 1940s, but as of 2022, only one design, an inertial confinement laser-driven fusion machine at the US National Ignition Facility, has conclusively produced a positive fusion energy gain factor, i.e. more power output than input. Fusion processes require fuel and a confined environment with sufficient temperature, pressure, and confinement time to create a plasma in which fusion can occur. The combination of these figures that results in a power-producing system is known as the Lawson criterion. In stars, the most common fuel is hydrogen, and gravity provides extremely long confinement times that reach the conditions needed for fusion e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |