|
Healthy Community Design
Healthy community design is planning and designing communities that make it easier for people to live healthy lives. Healthy community design offers important benefits: * Decreases dependence on the automobile by building homes, businesses, schools, churches and parks closer to each other so that people can more easily walk or bike between them. * Provides opportunities for people to be physically active and socially engaged as part of their daily routine, improving the physical and mental health of its citizens. * Allows persons, if they choose, to age in place and remain all their lives in a community that reflects their changing lifestyles and changing physical capabilities. Health benefits Healthy places are those designed and built to improve the quality of life for all people who live, work, learn, and play within their borders—person is free to make choices amid a variety of healthy, available, accessible, and affordable options. Healthy community design can provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
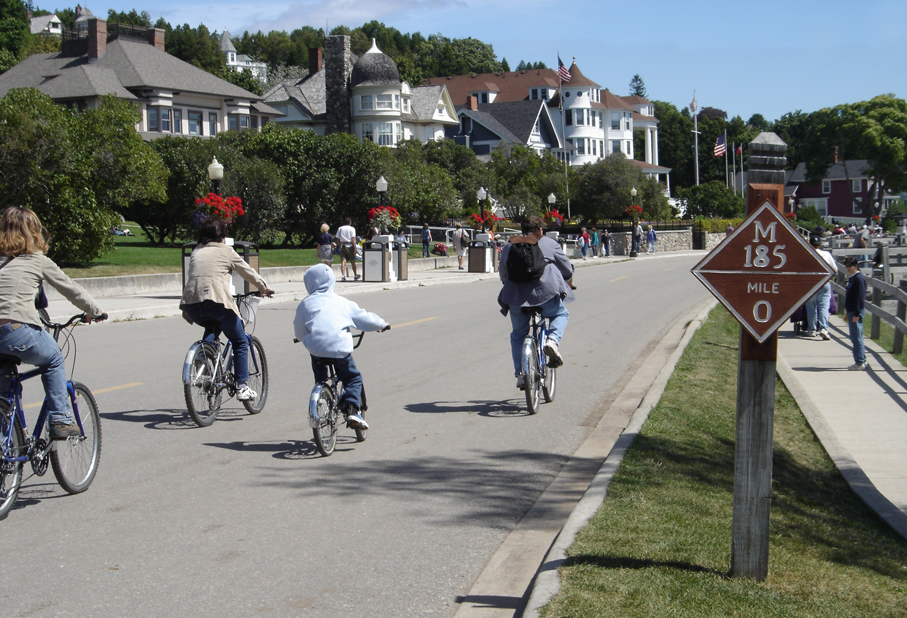
M-185 Mile 0 On Mackinac Island August 2004
M-185 is a state trunkline highway in the U.S. state of Michigan that circles Mackinac Island, a popular tourist destination on the Lake Huron side of the Straits of Mackinac, along the island's shoreline. A narrow paved road of , it offers scenic views of the straits that divide the Upper and the Lower peninsulas of Michigan and Lakes Huron and Michigan. It has no connection to any other Michigan state trunkline highways—as it is on an island—and is accessible only by passenger ferry. The City of Mackinac Island, which shares jurisdiction over the island with the Mackinac Island State Park Commission (MISPC), calls the highway Main Street within the built-up area on the island's southeast quadrant, and Lake Shore Road elsewhere. M-185 passes by several important sites within Mackinac Island State Park, including Fort Mackinac, Arch Rock, British Landing, and Devil's Kitchen. Lake Shore Road carries the highway next to the Lake Huron shoreline, running between the wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
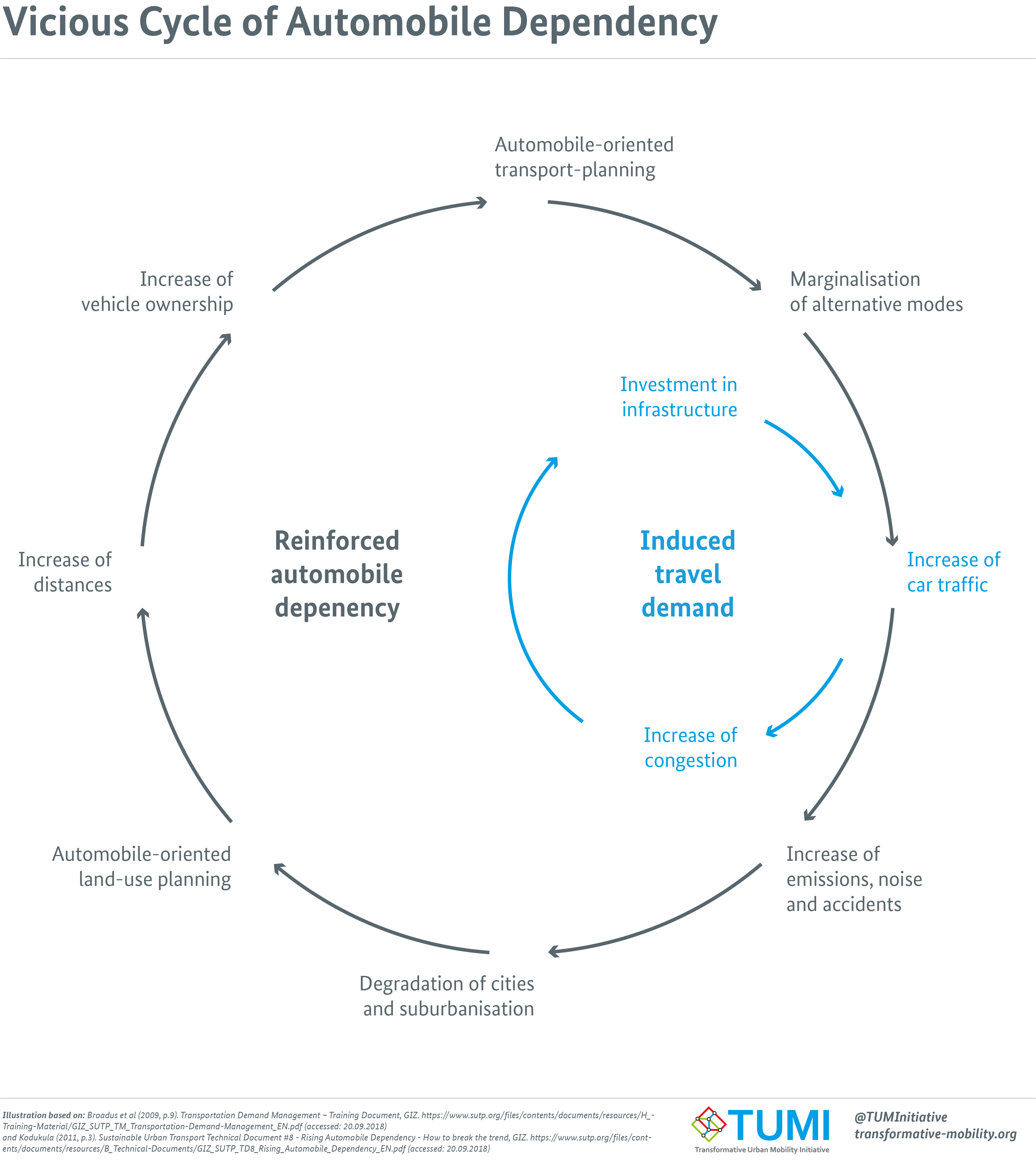
Automobile Dependence
Car dependency is the concept that some city layouts cause cars to be favoured over alternate forms of transportation, such as bicycles, public transit, and walking. Overview In many modern cities, automobiles are convenient and sometimes necessary to move easily. When it comes to automobile use, there is a spiraling effect where traffic congestion produces the 'demand' for more and bigger roads and removal of 'impediments' to traffic flow. For instance, pedestrians, signalized crossings, traffic lights, cyclists, and various forms of street-based public transit, such as trams. These measures make automobile use more pleasurable and advantageous at the expense of other modes of transport, so greater traffic volumes are induced. Additionally, the urban design of cities adjusts to the needs of automobiles in terms of movement and space. Buildings are replaced by parking lots. Open-air shopping streets are replaced by enclosed shopping malls. Walk-in banks and fast-food stores a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aging In Place
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention defines aging in place as "the ability to live in one's own home and community safely, independently, and comfortably, regardless of age, income, or ability level". Environmental gerontology Research in environmental gerontology indicates the importance of the physical and social environment of housing and the neighborhood (public space), as well as its implications for aging in place. Preference Most adults would prefer to age in place—that is, remain in their home of choice as long as possible. In fact, 90 percent of adults over the age of 65 report that they would prefer to stay in their current residence as they age. One-third of American households are home to one or more residents 60 years of age or older. Technology can be an enabler for aging in place—there are four categories of technology that acts as an enabler—Communication and Engagement, Health and Wellness, Learning and Contribution, and Safety and Secu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycling Infrastructure
Cycling infrastructure is all infrastructure cyclists are allowed to use. Bikeways include bike paths, bike lanes, cycle tracks, rail trails and, where permitted, sidewalks. Roads used by motorists are also cycling infrastructure, except where cyclists are barred such as many freeways/motorways. It includes amenities such as bike racks for parking, shelters, service centers and specialized traffic signs and signals. The more cycling infrastructure, the more people get about by bicycle. Good road design, road maintenance and traffic management can make cycling safer and more useful. Settlements with a dense network of interconnected streets tend to be places for getting around by bike. Their cycling networks can give people direct, fast, easy and convenient routes. History The history of cycling infrastructure starts from shortly after the bike boom of the 1880s when the first short stretches of dedicated bicycle infrastructure were built, through to the rise of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Interest Design
Public interest design is a human-centered and participatory design practice that places emphasis on the “triple bottom line” of sustainable design that includes ecological, economic, and social issues and on designing products, structures, and systems that address issues such as economic development and the preservation of the environment. Projects incorporating public interest design focus on the general good of the local citizens with a fundamentally collaborative perspective. Starting in the late 1990s, several books, convenings, and exhibitions have generated new momentum and investment in public interest design. Since then, public interest design—frequently described as a movement or field—has gained public recognition. History Public interest design grew out of the community design movement, which got its start in 1968 after American civil rights leader Whitney Young issued a challenge to attendees of the American Institute of Architects (AIA) national convention: " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban Vitality
Urban vitality is the quality of those spaces in cities that are capable of attracting heterogeneous people for different types of activities throughout varied time schedules. The areas of the city with high vitality are perceived as alive, lively or vibrant and they tend to attract people to carry out their activities, stroll or stay. However, the areas of low vitality repel people and can be perceived as unsafe. The urban vitality index is a measure of this quality and in recent years it has become a fundamental tool for planning urban policies, especially for the intervention of spaces with low vitality. In addition, it is used for proper management of spaces with high vitality, as the success of certain areas can lead to processes of gentrification and touristification that, paradoxically, end up reducing the vitality that made them popular. The concept of urban vitality is based on the contributions of Jane Jacobs, especially those of her most influential work, ''The Deat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Promotion
Health promotion is, as stated in the 1986 World Health Organization (WHO) Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion, the "process of enabling people to increase control over, and to improve their health." Scope The WHO's 1986 Ottawa Charter for Health Promotion and then the 2005 Bangkok Charter for Health Promotion in a Globalized World defines health promotion as "the process of enabling people to increase control over their health and its determinants, and thereby improve their health".Participants at the 1st Global Conference on Health Promotion in Ottawa, Canada, Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, 1986. Accessed 2021 Sept 15. Health promotion involves public policy that addresses health determinants such as income, housing, food security, employment, and quality working conditions. More recent work has used the term Health in All Policies (HiAP) to refer to the actions that incorporate health into all public policies. Health promotion is aligned with health equity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |