|
Han Shantong
Han Shantong ({{zh, t=韓山童, p=Hán Shāntóng; died 1351), born in Luancheng, Hebei, was one of the early leaders of the Red Turban Rebellions. He claimed to be the descendant of Emperor Huizong of Song (1082–1135), the penultimate emperor of the Northern Song dynasty, and rebelled against the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. Background of the rise to popularity The Yellow River flood of 1344 caused heavy casualties, displacement, hunger, epidemics, and the crisis in Dadu, the Yuan capital. The popular discontent with the ruling Yuan dynasty was triggered by the major construction project of the Yellow River rerouting 1351. Rebellion leader's career During the works, he claimed to have found a stone image with only one eye and a prophecy about the revolt inscribed on its back (''Caomuzi''). This was probably the reflection of some popular beliefs already widespread in Henan of the time. Han proclaimed the rebirth of Maitreya Buddha and the near coming of the "King of Light" (天 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han (Chinese Surname)
Han () is a common Chinese surname. The spelling "Han" is based on China's pinyin system and so used throughout Mainland China. Spelling can vary from 'Hon' in Cantonese-speaking areas to 'Hang' in Hainan. It is the 15th name on the '' Hundred Family Surnames'' poem. In 2003, Han (韩) is ranked 25th in China in terms of the number of bearers at around 8 million persons. In 2019 it was the 28th most common surname in Mainland China. Less common Chinese surnames romanized as ''Han'' include: 寒 (Hán) and 汉/漢 (Hàn). Four Chinese Origins of '韩' From '姬' surname ' 姬' (Jì) is an ancient Chinese surname. It is an alternate surname of the Yellow Emperor (Gongsun Xuanyuan) and the Zhou ruling family. A descendant of King Wu of Zhou, Wan, was given land in Hanyuan. Wan's descendants created the State of Han during the Warring States period. When the state was conquered by Qin in 230 BC, members of the ruling family adopted Han '韩' as their surname. From the transcr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Lin'er
Han may refer to: Ethnic groups * Han Chinese, or Han People (): the name for the largest ethnic group in China, which also constitutes the world's largest ethnic group. ** Han Taiwanese (): the name for the ethnic group of the Taiwanese people who may be fully or partially Han Chinese descent. * Han Minjok, or Han people (): the Korean native name referring to Koreans. * Hän: one of the First Nations peoples of Canada. Former states * Han (Western Zhou state) (韓) (11th century BC – 757 BC), a Chinese state during the Spring and Autumn period * Han (state) (韓) (403–230 BC), a Chinese state during the Warring States period * Han dynasty (漢/汉) (206 BC – 220 AD), a dynasty split into two eras, Western Han and Eastern Han ** Shu Han (蜀漢) (221–263), a Han Chinese dynasty that existed during the Three Kingdoms Period * Former Zhao (304–329), one of the Sixteen Kingdoms, known as Han (漢) before 319 * Cheng Han (成漢) (304–347), one of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Turban Rebels
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondary color (made from magenta and yellow) in the CMYK color model, and is the complementary color of cyan. Reds range from the brilliant yellow-tinged scarlet and vermillion to bluish-red crimson, and vary in shade from the pale red pink to the dark red burgundy. Red pigment made from ochre was one of the first colors used in prehistoric art. The Ancient Egyptians and Mayans colored their faces red in ceremonies; Roman generals had their bodies colored red to celebrate victories. It was also an important color in China, where it was used to color early pottery and later the gates and walls of palaces. In the Renaissance, the brilliant red costumes for the nobility and wealthy were dyed with kermes and cochineal. The 19th century brou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Youliang
Chen Youliang (陳友諒; 1320 – 3 October 1363For those cross-referencing the Mingshi, in the old Chinese calendar 至正二十三年 refers to the year 1363 CE, 七月二十日 refers to 8月29日 or 29 August, and 八月二十六日 refers to 10月3日 or 3 October.) was the founder and first emperor of the dynastic state of Chen Han in Chinese history. He was one of the military leaders and heroes of the people's revolution at the end of the Yuan dynasty. Biography Chen was born to a fishing family in Mianyang (沔陽) in present-day Hubei. Some say he was born with surname Chen (陳), while others say he was born with surname Xie (謝). Vietnamese records say that Chen Youliang was the son of Chen Yiji (陳益稷) or Trần Ích Tắc, a Trần dynasty leader who settled in the Yuan dynasty. In his childhood, he grew up poor, and he and his family were relatively unsuccessful fishermen. Chen once served as a district official before becoming a general under Ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xu Shouhui
Xu Shouhui () (1320–1360) was a 14th-century Chinese rebel leader who proclaimed himself emperor of the Tianwan dynasty (天完) during the late Yuan dynasty period of China. He was also known as Xu Zhenyi (徐真一 or 徐真逸, romanized in Wade–Giles as Hsü Chen-i). Born in Luotian (羅田, now in Hubei), Xu was a cloth vendor by profession. Emperor In August 1351, he worked with others in Qízhōu () to establish the rebel army of Red Turbans under the pretense of the Buddhist White Lotus Society. In the following months of the Red Turban Rebellion, they captured Qishui () and made it the command centre of the Red Turbans and the capital of the newly declared Empire of Tianwan (), originally called Song ()Chan, Hok-Lam. “The ‘Song’ Dynasty Legacy: Symbolism and Legitimation from Han Liner to Zhu Yuanzhang of the Ming Dynasty.” Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies 68, no. 1 (2008): 91–133. http://www.jstor.org/stable/40213653. with himself as the emperor wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Lotus
The White Lotus () is a syncretic religious and political movement which forecasts the imminent advent of the "King of Light" (), i.e., the future Buddha Maitreya. As White Lotus sects developed, they appealed to many Han Chinese who found solace in the worship of Wusheng Laomu (). History Background The religious background of the White Lotus Sect goes back to the founding of the first White Lotus Society (白蓮社) in the Donglin Temple at Mount Lu by the Huiyuan (334–416 CE). During the Northern Song period (960–1126), White Lotus Societies were founded throughout southern China, spreading Pure Land teachings and meditation methods with them. Between 9th and 14th centuries, Chinese Manichaeans increasingly involved themselves with the Pure Land school. Through this close interaction Manichaeism had profound influence on Chinese Maitreyan Buddhist sects within the Pure Land tradition, practicing together so closely alongside the Buddhists that the two traditions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ming Dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han people, the majority ethnic group in China. Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng (who established the short-lived Shun dynasty), numerous rump regimes ruled by remnants of the Ming imperial family—collectively called the Southern Ming—survived until 1662. The Ming dynasty's founder, the Hongwu Emperor (r. 1368–1398), attempted to create a society of self-sufficient rural communities ordered in a rigid, immobile system that would guarantee and support a permanent class of soldiers for his dynasty: the empire's standing army exceeded one million troops and the navy's dockyards in Nanjing were the largest in the world. He also took great care breaking the power of the court eunuchs and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Yi Of Chu
Emperor Yi of Chu (died 206 BC), also known as King Huai II of Chu before receiving his ''de jure'' emperor title, personal name Xiong Xin, was the ruler of the Chu state in the late Qin dynasty. He was a grandson of King Huai of Chu. In 223 BC, during the Warring States period, the Chu state was conquered by the Qin state, which unified the various Chinese feudal states in a series of wars and established the Qin dynasty in 221 BC. In 209 BC, when rebellions broke out throughout China to overthrow the Qin dynasty, the Chu state was revived as an insurgent state against Qin imperial rule. Xiong Xin was discovered by Xiang Liang, a rebel leader who descended from a famous Chu general, , and installed on the Chu throne as "King Huai II of Chu". However, Xiong Xin was merely a puppet ruler because power was concentrated in Xiang Liang's hands, and was later passed on to Xiang Liang's nephew, Xiang Yu, after Xiang Liang was killed in battle. In 206 BC, the Qin dynasty was overth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
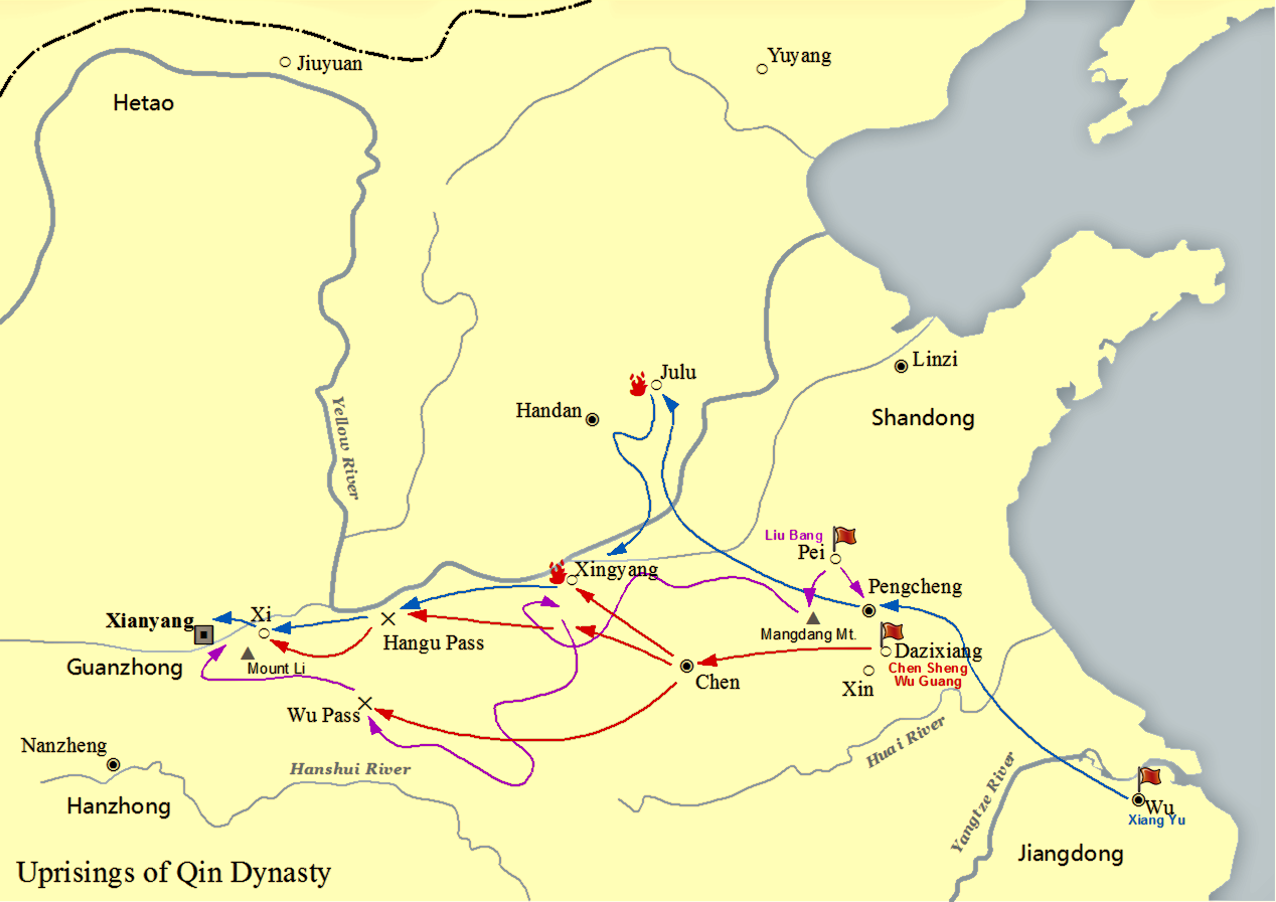
Xiang Yu
Xiang Yu (, –202 BC), born Xiang Ji (), was the Hegemon-King (Chinese: 霸王, ''Bà Wáng'') of Western Chu during the Chu–Han Contention period (206–202 BC) of China. A noble of the Chu state, Xiang Yu rebelled against the Qin dynasty and became a prominent warlord. He was granted the title of "Duke of Lu" () by King Huai II of the restoring Chu state in 208 BC. The following year, he led the Chu forces to victory at the Battle of Julu against the Qin armies led by Zhang Han. After the fall of Qin, Xiang Yu was enthroned as the "Hegemon-King of Western Chu" () and ruled a vast area covering modern-day central and eastern China, with Pengcheng as his capital. He engaged Liu Bang, the founding emperor of the Han dynasty, in a long struggle for power, known as the Chu–Han Contention, which concluded with his eventual defeat at the Battle of Gaixia and his suicide. Xiang Yu is depicted in the Wu Shuang Pu (, Table of Peerless Heroes) by Jin Guliang. Names and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandate Of Heaven
The Mandate of Heaven () is a Chinese political philosophy that was used in ancient and imperial China to legitimize the rule of the King or Emperor of China. According to this doctrine, heaven (天, '' Tian'') – which embodies the natural order and will of the universe – bestows the mandate on a just ruler of China, the " Son of Heaven". If a ruler was overthrown, this was interpreted as an indication that the ruler was unworthy and had lost the mandate. It was also a common belief that natural disasters such as famine and flood were divine retributions bearing signs of Heaven's displeasure with the ruler, so there would often be revolts following major disasters as the people saw these calamities as signs that the Mandate of Heaven had been withdrawn. The Mandate of Heaven does not require a legitimate ruler to be of noble birth, depending instead on how well that person can rule. Chinese dynasties such as the Han and Ming were founded by men of common origins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhu Yuanzhang
The Hongwu Emperor (21 October 1328 – 24 June 1398), personal name Zhu Yuanzhang (), courtesy name Guorui (), was the founding emperor of the Ming dynasty of China, reigning from 1368 to 1398. As famine, plagues and peasant revolts increased across China proper in the 14th century, Zhu Yuanzhang rose to command the Red Turban forces that conquered China proper, ending the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty and forcing the remnant Yuan court (known as Northern Yuan in historiography) to retreat to the Mongolian Plateau. Zhu claimed the Mandate of Heaven and established the Ming dynasty at the beginning of 1368 and occupied the Yuan capital, Khanbaliq (present-day Beijing), with his army that same year. Trusting only his family, he made his many sons feudal princes along the northern marches and the Yangtze valley.Chan Hok-lam.Legitimating Usurpation: Historical Revisions under the Ming Yongle Emperor (r. 14021424)". ''The Legitimation of New Orders: Case Studies in World Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Futong
/ ( or ) is an East Asian surname. pinyin: in Mandarin Chinese, in Cantonese. It is the family name of the Han dynasty emperors. The character originally meant 'kill', but is now used only as a surname. It is listed 252nd in the classic text Hundred Family Surnames. Today, it is the 4th most common surname in Mainland China as well as one of the most common surnames in the world. Distribution In 2019 劉 was the fourth most common surname in Mainland China. Additionally, it was the most common surname in Jiangxi province. In 2013 it was found to be the 5th most common surname, shared by 67,700,000 people or 5.1% of the population, with the province with the most people being Shandong.中国四百大姓, 袁义达, 邱家儒, Beijing Book Co. Inc., 1 January 2013 Origin One source is that they descend from the Qí (祁) clan of Emperor Yao. For example the founding emperor of the Han dynasty (one of China's golden ages), Liu Bang ( Emperor Gaozu of Han) was a descendant o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)