|
Hainleite
The Hainleite is a Muschelkalk ridge of hills up to in northern Thuringia, Germany. Geography This heavily wooded landscape lies between Bleicherode in Nordhausen district, Sondershausen in Kyffhäuser district, Bad Frankenhausen, Dingelstädt, Oldisleben, Kindelbrück and Schernberg. It is bordered to the north by the Kyffhäuser Hills (german: Kyffhäuser Gebirge) on the other side of the Wipper, to the east – beyond the so-called Thuringian Gate, a gorge carved out by the Unstrut near little ''Sachsenburg'' – by the Schmücke and the Hohe Schrecke, and to the south and southwest by the Thuringian Basin. Important towns * Sondershausen, capital of Kyffhäuser district * Bad Frankenhausen Hills The highest elevationsee the discussion at German Wikipedia is the point located in the western part of the Hainleite between Immenrode and Straußberg. Other hills include the Possen (420 m), the Heidelberg (403 m) and the Kuhberg (406 m). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schmücke
The Schmücke is a ridge of hills in Thuringia, Germany. Geography Together with the Hohe Schrecke, the Finne and the Hainleite, the Schmücke borders the northern rim of the Thuringian Basin. It lies between Hauteroda, Oberheldrungen, Heldrungen Heldrungen is a town and a former municipality in the Kyffhäuserkreis district, Thuringia, Germany. Since 1 January 2019, it is part of the town An der Schmücke. Nearby rivers are the Unstrut and the Wipper. It is known for its fortification ..., Heldrungen station, Gorsleben and Hemleben. It is separated from the Hainleite in the west by the Sachsenburg Gate (''Sachsenburger Pforte''). Hills *Stubenberg 198 m AMSL *Scharfer Berg 249 m AMSL Hills of Thuringia Forests and woodlands of Thuringia [Baidu] |
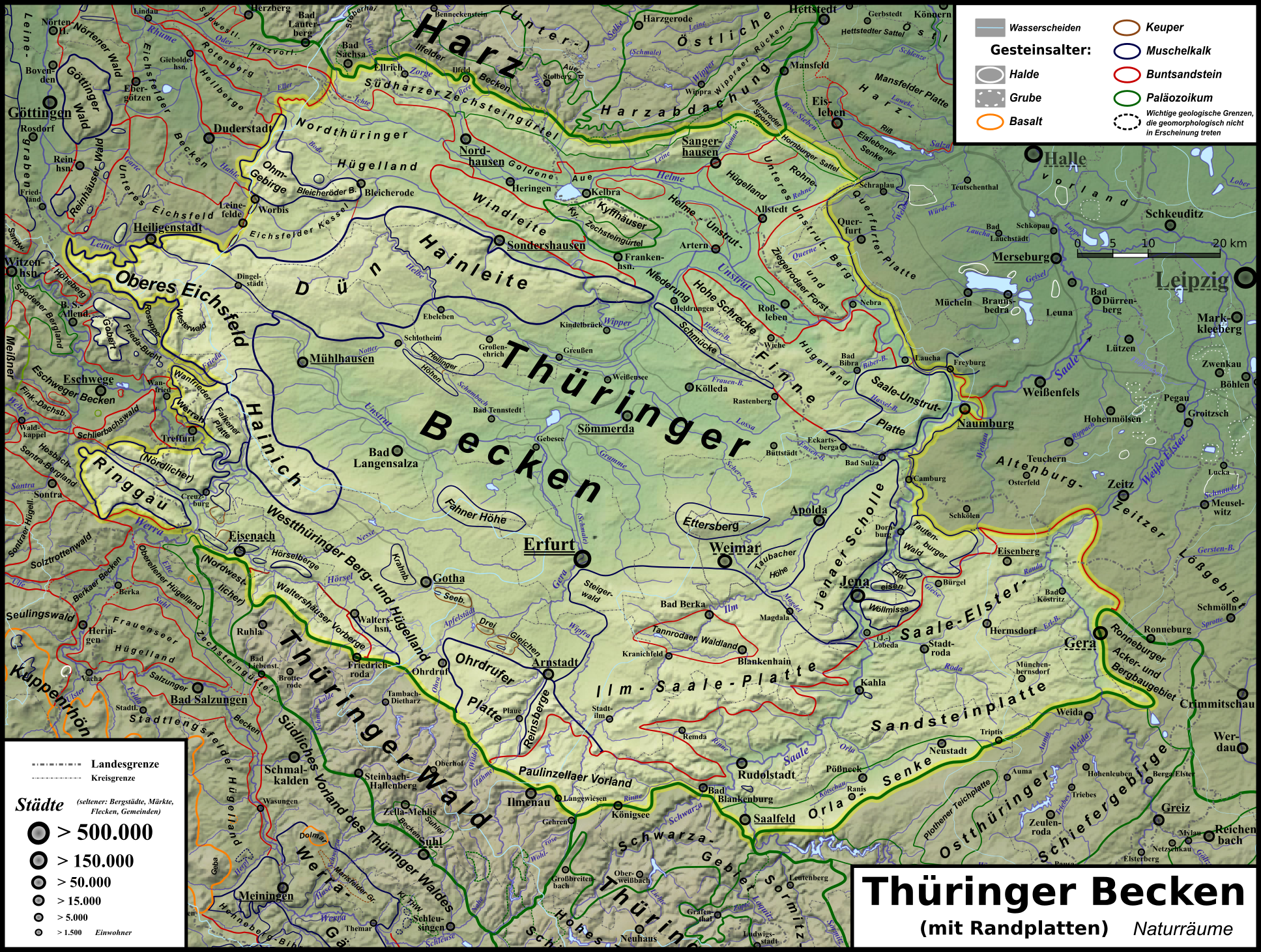
Thuringian Basin
The Thuringian Basin (german: Thüringer Becken) is a depression in the central and northwest part of Thuringia in Germany which is crossed by several rivers, the longest of which is the Unstrut. It stretches about from north to south and around from east to west. Its height varies from about 150 to . The Basin is surrounded by a wide outer girdle of limestone (Muschelkalk) ridges (including Hainich, Dün, Hainleite, Hohe Schrecke, Schmücke, Finne), and to the southwest by the Thuringian Forest and to the southeast by sharply divided terraces (the Ilm-Saale and Ohrdruf Muschelkalk plateaus, and the Saale-Elster Bunter sandstone plateau). The Thuringian Basin belongs to the triassic period, during which horizontal beds of Bunter sandstone, Muschelkalk and Keuper were laid down. Below those lie the salt and gypsum layers of Magnesian Limestone (Zechstein). In the Cenozoic era the surrounding ridges were uplifted, whilst the Thuringian Basin sank to form a saucer-shaped depress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyffhäuser Hills
The Kyffhäuser (,''Duden - Das Aussprachewörterbuch, 7. Auflage (German)'', Dudenverlag, sometimes also referred to as ''Kyffhäusergebirge'', is a hill range in Central Germany, shared by Thuringia and Saxony-Anhalt, southeast of the Harz mountains. It reaches its highest point at the Kulpenberg with an elevation of . The range is the site of medieval Kyffhausen Castle (''Reichsburg Kyffhausen'') and the 19th century Kyffhäuser Monument; it has significance in German traditional mythology as the legendary resting place of Emperor Frederick Barbarossa. Etymology The origin of the name has not been conclusively established. ''Kyffhäuser'' (formerly also ''Kiffhäuser'') probably stems from the Low German word ''cuf'', meaning "head" or "peak", and ''huse'', "house". Other explanations refer to ''kiff'', "quarrel" and the historic castles at the site. Geography The Kyffhäuser is a small ''Mittelgebirge'' located in the Kyffhäuserkreis district of Thuringia and the Mansfel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hohe Schrecke
The Hohe Schrecke is a ridge of hills in central Germany. It lies mainly within Thuringia; however, the southeastern part around Lossa belongs to the state of Saxony-Anhalt. Geography Together with the Schmücke, the Finne and the Hainleite, the Hohe Schrecke forms the northern rim of the Thuringian Basin. It lies between Braunsroda, Reinsdorf, Gehofen, Donndorf, Wiehe, Lossa, Hauteroda and Oberheldrungen. Hills and high points The highest point of the Hohe Schrecke in its wider sense is the Wetzelshain (). Among its hills and high points are the following– sorted by height in metres (m) above sea level (NHN; unless otherwise stated): * Wetzelshain (370.1 m), between Hauteroda and Garnbach * Beerberg (362.7 m), between Hauteroda and Langenroda * Drei-Lindenberg (357.6 m), near Garnbach * Seligenbornsberg (356.0 m), near Lossa in the area of the Finne with Saxony-Anhalt * Erbsland (353.6 m), near Ostramondra in the area of the Finne * Heidenkopf (353.2 m), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordhausen District
Nordhausen is a ''Kreis'' (district) in the north of Thuringia, Germany. Neighboring districts are (from the north clockwise): Harz and Mansfeld-Südharz in Saxony-Anhalt; Kyffhäuserkreis and Eichsfeld in Thuringia; and Göttingen and Goslar in Lower Saxony. History The district was created in 1815, when the Prussian province of Saxony was created. The area of Lohra-Clettenberg (the former dukedom County Hohnstein) and the previously free imperial city of Nordhausen were thereafter administrated together. In 1882-3 Nordhausen left the district, which led to its renaming as the ''Kreis Grafschaft Hohenstein'' (district county of Hohenstein) in 1888. After World War II the name reverted to ''Landkreis Nordhausen'', and in 1950 the city of Nordhausen was reincorporated into the district. In the administrative reform of 1952 several municipalities changed districts: a number were transferred from the district of Sangerhausen to that of Nordhausen, while others were transferred from N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sondershausen
Sondershausen is a town in Thuringia, central Germany, capital of the Kyffhäuserkreis district, situated about 50 km north of Erfurt. On 1 December 2007, the former municipality Schernberg was incorporated by Sondershausen. Until 1918 it was part of the principality of Schwarzburg-Sondershausen. Geography Sondershausen is situated in North Thuringia and lies in low mountain range between Hainleite (in the north) and Windleite (in the south). The highest mountain is the Frauenberg to the west of the town. A little river called Wipper flows through Sondershausen. Around the town there are mixed forests (especially with beech trees). Subdivisions The city districts are: Culture and main sights Museums In the Sondershausen Palace there is a large museum with three different exhibit areas. Special exhibits are the Golden Coach, the only of its kind in Germany, and the legendary Püstrich. There are possible special guided tours of demonstrationdepot, cellar, tower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thuringia
Thuringia (; german: Thüringen ), officially the Free State of Thuringia ( ), is a state of central Germany, covering , the sixth smallest of the sixteen German states. It has a population of about 2.1 million. Erfurt is the capital and largest city. Other cities are Jena, Gera and Weimar. Thuringia is bordered by Bavaria, Hesse, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It has been known as "the green heart of Germany" () from the late 19th century due to its broad, dense forest. Most of Thuringia is in the Saale drainage basin, a left-bank tributary of the Elbe. Thuringia is home to the Rennsteig, Germany's best-known hiking trail. Its winter resort of Oberhof makes it a well-equipped winter sports destination – half of Germany's 136 Winter Olympic gold medals had been won by Thuringian athletes as of 2014. Thuringia was favoured by or was the birthplace of three key intellectuals and leaders in the arts: Johann Sebastian Bach, Johann Wolfgang von Goet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyffhäuser
The Kyffhäuser (,''Duden - Das Aussprachewörterbuch, 7. Auflage (German)'', Dudenverlag, sometimes also referred to as ''Kyffhäusergebirge'', is a hill range in Central Germany, shared by Thuringia and Saxony-Anhalt, southeast of the Harz mountains. It reaches its highest point at the Kulpenberg with an elevation of . The range is the site of medieval Kyffhausen Castle (''Reichsburg Kyffhausen'') and the 19th century Kyffhäuser Monument; it has significance in German traditional mythology as the legendary resting place of Emperor Frederick Barbarossa. Etymology The origin of the name has not been conclusively established. ''Kyffhäuser'' (formerly also ''Kiffhäuser'') probably stems from the Low German word ''cuf'', meaning "head" or "peak", and ''huse'', "house". Other explanations refer to ''kiff'', "quarrel" and the historic castles at the site. Geography The Kyffhäuser is a small ''Mittelgebirge'' located in the Kyffhäuserkreis district of Thuringia and the Mansf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thuringian Gate
The Thuringian Gate (german: Thüringer Pforte) near Sachsenburg, a district of Oldisleben, west of Heldrungen in central Germany, is where the gorge of the river Unstrut breaks out of the Thuringian Basin through the Hainleite and Schmücke hills to the north. It is also known as the Sachsenburg Gate. This topographical feature carved out by the Unstrut has always been used as a communication route. Today the B 85 and B 86 federal roads and the Sangerhausen–Erfurt railway pass through the gorge. The Thuringian Gate was guarded in medieval In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ... times by the fortresses of Upper and Lower Sachsenburg. Valleys of Europe Valleys of Thuringia [Baidu] |
Kyffhäuser District
The Kyffhäuser (,''Duden - Das Aussprachewörterbuch, 7. Auflage (German)'', Dudenverlag, sometimes also referred to as ''Kyffhäusergebirge'', is a hill range in Central Germany, shared by Thuringia and Saxony-Anhalt, southeast of the Harz mountains. It reaches its highest point at the Kulpenberg with an elevation of . The range is the site of medieval Kyffhausen Castle (''Reichsburg Kyffhausen'') and the 19th century Kyffhäuser Monument; it has significance in German traditional mythology as the legendary resting place of Emperor Frederick Barbarossa. Etymology The origin of the name has not been conclusively established. ''Kyffhäuser'' (formerly also ''Kiffhäuser'') probably stems from the Low German word ''cuf'', meaning "head" or "peak", and ''huse'', "house". Other explanations refer to ''kiff'', "quarrel" and the historic castles at the site. Geography The Kyffhäuser is a small ''Mittelgebirge'' located in the Kyffhäuserkreis district of Thuringia and the Mansfel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) because they are the most resistant minerals to weathering processes at the Earth's surface. Like uncemented sand, sandstone may be any color due to impurities within the minerals, but the most common colors are tan, brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white, and black. Since sandstone beds often form highly visible cliffs and other topographic features, certain colors of sandstone have been strongly identified with certain regions. Rock formations that are primarily composed of sandstone usually allow the percolation of water and other fluids and are porous enough to store large quantities, making them valuable aquifers and petroleum reservoirs. Quartz-bearing sandstone can be changed into quartzite through metamorphism, usually relate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sachsenburg
Sachsenburg is a market town in the district of Spittal an der Drau in Carinthia, Austria. Geography The municipal area stretches along the valley of the Drava river, where it enters the Lurnfeld plain between the Kreuzeck group of the Hohe Tauern mountain range in the north and Gailtal Alps in the south. The municipality comprises the cadastral communities of Sachsenburg and Obergottesfeld. History The origin of the name is uncertain: an affiliation with the far apart mediæval Duchy of Saxony has never been established; however the coat of arms probably awarded in the 16th century shows a ''Saxe'', a kind of pan formerly used for gold prospecting within the nearby Hohe Tauern range. The strategically important narrow place of the Drava valley (''Sachsenburger Klause'') probably was guarded already in Roman times, when the area was part of the ''Noricum'' province. Two fortresses blocking the passage along the river were first mentioned in a 1213 deed. Sachsenburg is documen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




Saunders_Quarry-1.jpg)