|
Həsənriz
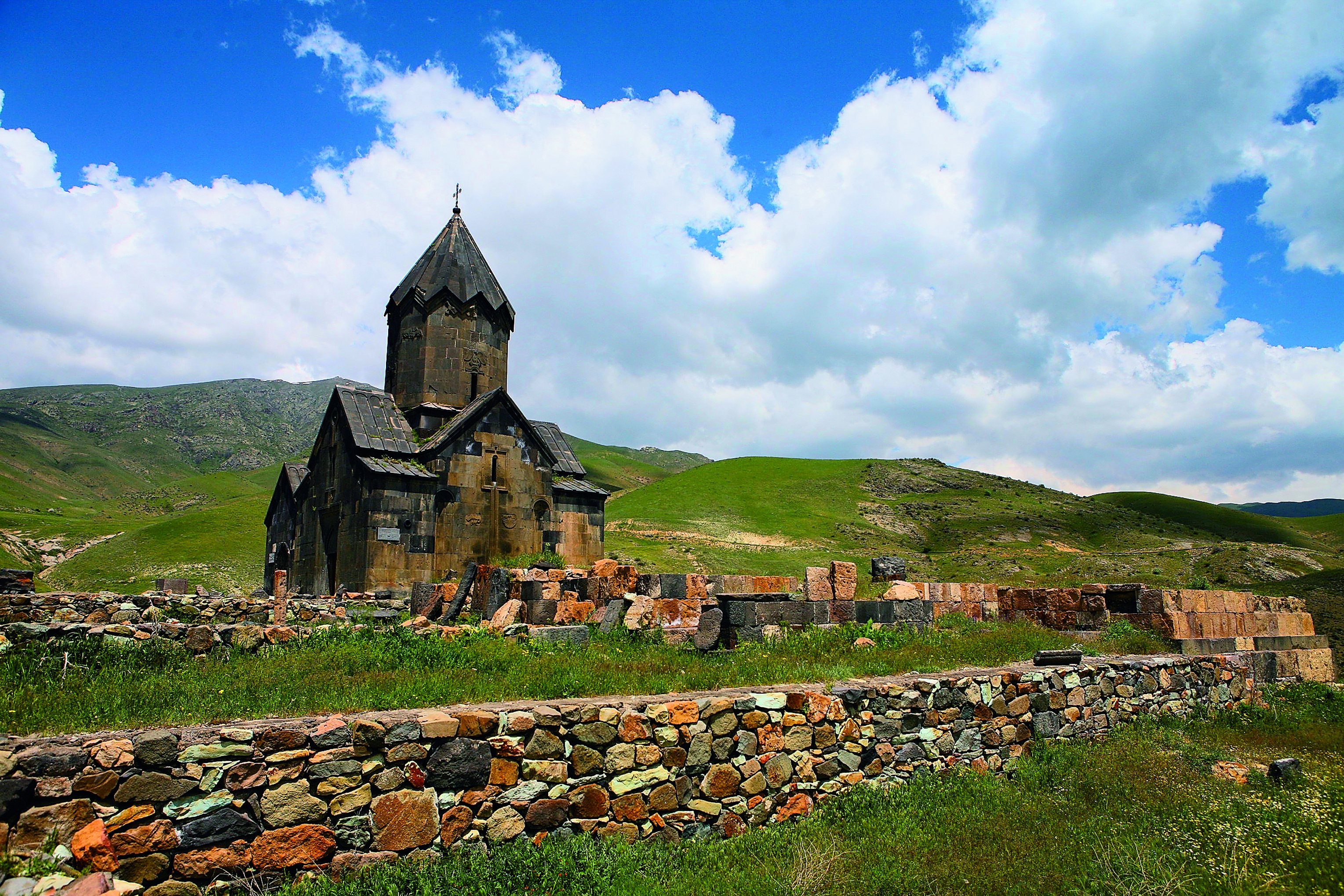
Haterk () or Hasanriz () is a village in the Aghdara District of Azerbaijan, in the region of Nagorno-Karabakh. Until 2023 it was controlled by the breakaway Republic of Artsakh. The village had an ethnic Armenian-majority population until the exodus of the Armenian population of Nagorno-Karabakh following the 2023 Azerbaijani offensive in Nagorno-Karabakh. History After the Battle of Manzikert in 1071, the Seljuks conquered most of the remnants of Bagratid Armenia, which had been largely annexed by the Byzantine Empire in the 11th century. The Syunik, Khachen (Artsakh) and Tashir principalities remained unconquered however. The Syunik and Khachen principalities had close ties, their royal families intermarried, and their respective principalities functioned as refuges and bastions for each other during times of need. During the end of the 12th century, Seljuk power declined, and forces of the Georgian-Armenian Zakarian princes moved southwards and established Zakarid Armenia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Divisions Of Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan is administratively divided into 67 districts () and 11 cities () that are subordinate to the Republic. Out of these districts and cities, 7 districts and 1 city are located within the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. The districts are further divided into Municipalities of Azerbaijan, municipalities (). Additionally, the districts of Azerbaijan are grouped into 14 Economic regions of Azerbaijan, Economic Regions (). On 7 July 2021, President of Azerbaijan Ilham Aliyev signed a decree "On the new division of economic regions in the Republic of Azerbaijan". Administrative divisions Contiguous Azerbaijan The list below represents the districts of contiguous Azerbaijan. For those of the Nakhchivan exclave, see further below. Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic The seven districts and one municipality of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic are listed below. Economic regions Nagorno-Karabakh The territory of former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast presently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Tashir-Dzoraget
The Kingdom of Tashir-Dzoraget ( ''Tashir-Dzorageti t'agavorut'yun''), alternatively known as the Kingdom of Lori or Kiurikian Kingdom by later historians, was a medieval Armenian kingdom formed in the year 979 by the Kiurikian dynasty, a branch of the Bagratuni dynasty, as a vassal kingdom of the Bagratid Kingdom of Armenia. The first capital of the kingdom was Matsnaberd, currently part of modern-day Azerbaijan. It was located on the territories of modern-day northern Armenia, northwestern Azerbaijan and southern Georgia. The founder of the kingdom and the Kiurikian dynasty was king Kiurike I (also known as Gurgen I). In 979 King Smbat II of Armenia granted the province of Tashir to his brother Kiurike with the title of king. The branch went on to outlive the main one in Ani. It became especially strong during the reign of King David I Anhoghin who succeeded his father Kiurike and ruled between 989 and 1048. David I Anhoghin conquered some territories from Emirates o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aq Qoyunlu
The Aq Qoyunlu or the White Sheep Turkomans (, ; ) was a culturally Persianate society, Persianate,Kaushik Roy, ''Military Transition in Early Modern Asia, 1400–1750'', (Bloomsbury, 2014), 38; "Post-Mongol Persia and Iraq were ruled by two tribal confederations: Akkoyunlu (White Sheep) (1378–1507) and Qaraoyunlu (Black Sheep). They were Persianate Turkoman Confederations of Anatolia (Asia Minor) and Azerbaijan." Sunni Islam, SunniMichael M. Gunter, ''Historical dictionary of the Kurds'' (2010), p. 29 Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman tribal confederation. Founded in the Diyar Bakr, Diyarbakir region by Qara Yuluk Uthman Beg, they ruled parts of present-day eastern Turkey from 1378 to 1508, and in their last decades also ruled Armenia, Azerbaijan, much of Iran, Iraq, and Oman where the ruler of Kingdom of Ormus, Hormuz recognised Aq Qoyunlu suzerainty. The Aq Qoyunlu empire reached its zenith under Uzun Hasan. History Etymology The name Aq Qoyunlu, literally meaning "those with w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qara Qoyunlu
The Qara Qoyunlu or Kara Koyunlu (, ; ), also known as the Black Sheep Turkomans, were a culturally Persianate, Muslim Turkoman "Kara Koyunlu, also spelled Qara Qoyunlu, Turkish Karakoyunlular, English Black Sheep, Turkmen tribal federation that ruled Azerbaijan, Armenia, and Iraq from about 1375 to 1468." "Better known as Turkomans... the interim Ak-Koyunlu and Karakoyunlu dynasties..." monarchy that ruled over the territory comprising present-day Azerbaijan, Armenia, northwestern Iran, eastern Turkey, and northeastern Iraq from about 1374 to 1468. History Etymology The name Qara Qoyunlu literally means "hose withblack sheep". It has been suggested that this name refers to old totemic symbols, but according to Rashid al-Din Hamadani, the Turks were forbidden to eat the flesh of their totem-animals, and so this is unlikely given the importance of mutton in the diet of pastoral nomads. Another hypothesis is that the name refers to the predominant color of their flocks. Origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkoman (ethnonym)
Turkoman, also known as Turcoman (), was a term for the people of Oghuz Turkic origin, widely used during the Middle Ages. Oghuz Turks were a western Turkic people that, in the 8th century A.D, formed a tribal confederation in an area between the Aral and Caspian seas in Central Asia, and spoke the Oghuz branch of the Turkic language family. Today, much of the populations of Turkey, Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan are descendants of Oghuz Turks. ''Turkmen'', originally an exonym, dates from the High Middle Ages, along with the ancient and familiar name " Turk" (), and tribal names such as " Bayat", " Bayandur", " Afshar", and " Kayi". By the 10th century, Islamic sources were referring to Oghuz Turks as Muslim Turkmens, as opposed to Tengrist or Buddhist Turks. It entered into the usage of the Western world through the Byzantines in the 12th century, since by that time Oghuz Turks were overwhelmingly Muslim. Later, the term "Oghuz" was gradually supplanted by "Turkmen" among Og ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goshavank
Goshavank (; meaning "Monastery of Gosh"; previously known as Nor Getik) is a 12–13th-century Armenian monastery located in the village of Gosh, Armenia, Gosh in the Tavush Province of Armenia. The monastery which has remained in relatively good condition also houses one of the world's finest examples of a khachkar. History Goshavank was erected in the place of an older monastery once known as ''Nor Getik'', which had been destroyed by an earthquake in 1188. Mkhitar Gosh, a statesman, scientist and author of numerous fables and parables as well as The Lawcode (Datastanagirk') of Mkhitar Gosh, the first criminal code, took part in the rebuilding of the monastery. At Goshavank, Mkhitar Gosh founded a school. One of its alumni, an Armenian scientist by the name of Kirakos Gandzaketsi wrote ''The History of Armenia''. The architect Mkhitar the Carpenter and his disciple Hovhannes also took an active part in the building of the monastery. The complex was later renamed Goshavan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dadivank
Dadivank () or Khutavank (Dominique Auzias, Jean-Paul Labourdette, ''Petit fûté Arménie''. Paris: Nouvelles éditions de l'Université, 2005, p. 203.) is an Armenian Apostolic monastery in the Kalbajar District of Azerbaijan. It was built between the 9th and 13th centuries and is one of the main monastic complexes of medieval Armenia. In Azerbaijan, the monastery is called Dadivəng or Xudavəng. Azerbaijan denies the monastery's Armenian religious and cultural heritage, instead falsely referring to it as a "Caucasian Albanian temple." History and architecture The monastery is said to have been founded by St. Dadi, a disciple of Thaddeus the Apostle who spread Christianity in Eastern Armenia during the first century AD. However, the monastery is only first mentioned in the 9th century. In July 2007, the grave said to belong to St. Dadi was discovered under the holy altar of the main church. The princes of Upper Khachen are also buried at Dadivank, under the church's '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tartar (river)
The Tartar (, ) is one of the tributaries of the Kura river located in Azerbaijan. It passes through the districts of Kalbajar, Barda and Tartar. Overview The Tartar is a left tributary of the Kura, the largest river in the Caucasus. The river originates in the area where Qonqur, Alaköz and Mıxtökən mountain ranges meet on the Karabakh Plateau in the vicinity of the hot springs village of Istisu located in Kalbajar Rayon of Azerbaijan. The river originates from mountain springs at above sea level. The river flows eastward through the whole Kalbajar Rayon (de facto Martakert Province), passing through Kalbajar city, Tartar and Barda raions and through Tartar and Barda cities before discharging into the Kura. The river has two left tributaries: the Levçay () and the Ağdabançay (), and one right tributary, the Turağayçay (). Sarsang reservoir was built on Tartar river in 1976 for electricity generation and irrigation purposes. Statistical information The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vayots Dzor
Vayots Dzor (, ) is a province (''marz'') of Armenia. It lies at the southeastern end of the country, bordering the Nakhchivan exclave of Azerbaijan to the west and the Kalbajar District of Azerbaijan to the east. It covers an area of . With a population of only 52,324 (2011 census), it is the most sparsely populated province in the country. The capital and largest city of the province is the town of Yeghegnadzor. A major wine-producing region in Armenia, Vayots Dzor is home to many ancient landmarks and historical attractions. Among them are the Areni-1 cave complex and Areni-1 winery of the Chalcolithic period, the 8th-century Tanahat Monastery, the 10th-century fortress of Smbataberd, and the 13th-century monastery of Noravank. The province is also home to the spa-town of Jermuk and the village of Gladzor, known for the 13th and 14th-century University of Gladzor. Etymology The province is named after the Vayots Dzor canton of historic Syunik, the ninth province of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khokhanaberd
Khokhanaberd (, ), also known as Khanabert () and Tarkhanaberd (), is a 9th-century mountaintop fortress near the village of Vank, Nagorno-Karabakh, Vank, in the Political status of Nagorno-Karabakh, disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh, in the Kalbajar District of Azerbaijan. Historically a part of the Lower Khachen (Nerkin Khachen) province of the Armenian Principality of Khachen, it served as a castle and residence of several rulers of the House of Hasan-Jalalyan. Etymology A local folk etymology holds that Hasan Jalal I Dawla, founder of the Hasan-Jalalyan dynasty, named it upon hearing news of his son's birth (in the local Karabakh dialect of Armenian, ''khokha'' means child). The fortress has historically been referred to by various names besides Khokhanaberd, including Tarakhana, Khavanaberd, Khokh, Khoyakhan, and Havaptuk. History The fortress is believed to have been constructed from the 7th to 9th centuries, during the period of Arminiya, Arab rule in Armenia. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zar, Azerbaijan
Zar (; ; , also ''Tzar'') is a village in the Kalbajar District of Azerbaijan. Etymology Armenian architectural historian Samvel Karapetyan writes that the settlement was first mentioned as "Tsar" in 1289. In the records of Dadivank Monastery in 1763, it is referred to as ''Mets Tsar'' (, ), and in the 18th century, with an increased nomadic presence in the region, ''Zar'', a derivative of ''Tsar'', began to be used as a name for the village. An Azerbaijani legend suggests a different origin. A poor young man named Zaza once lived in this village. He was in love with a girl named Nazı, but her parents were against their relationship. Zaza then decided to seek assistance from Nadir Shah. He planted a watermelon in a narrow-necked jar. The surprised shah approved and ordered that Nazı be given to Zaza. However, as soon as Nadir Shah left town, Nazı's family went to Zaza's house and murdered him before throwing his body into a well. Zaza's mother cried for several days after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |