|
Hūkerenui
Hūkerenui is a settlement in Northland Region, Northland, New Zealand. New Zealand State Highway 1, State Highway 1 passes through the area. Kawakawa, New Zealand, Kawakawa is northwest, and Hikurangi is southeast. The New Zealand Ministry for Culture and Heritage gives a translation of "large cascade" for ''Hukerenui''. History The settlement began as Hukerenui South in 1886, with a request made by a group of local people for the land under the Village Homestead Special Settlement system. The village was opened to the first 25 settler families the following year. Although the main road from Whangārei to Kawakawa passed through it, the road was only a dirt track, and was impassable during winter. Gum-digger, Gum digging was one of the initial sources of income, but the Government cancelled gum-digging licences after fires in early 1888. A flax mill at Towai provided some jobs. Some were employed to build and improve the roads. The North Auckland Line, North Auckland railway l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Auckland Line
The North Auckland Line (designation NAL) is a major section of New Zealand's Rail transport in New Zealand, national rail network, and is made up of the following parts: the portion of track that runs northward from Westfield Junction to Newmarket railway station, Auckland, Newmarket Station; from there, westward to Waitakere Railway Station, Waitakere; from there, northward to Otiria via Whangārei. The first section was opened in 1868 and the line was completed in 1925. The line, or sections of it, have been known at various times as the Kaipara Line, the Waikato-Kaipara Line, the Kaipara Branch and the North Auckland Main Trunk. North Auckland Line is a designation for the section of track, not a service route. The southernmost portion from Westfield Junction to Newmarket was originally built as part of the North Island Main Trunk railway, with Newmarket serving as the junction of the two lines. The North Island Main Trunk was re-routed in 1930 via the Westfield Deviation t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whangarei District
Whangarei District is a territorial authority district in the Northland Region of New Zealand that is governed by the Whangarei District Council. The district is made up in area largely by rural land, and includes a fifth of the Northland Region. It extends southwards to the southern end of Bream Bay, northwards to Whangaruru and almost to the Bay of Islands, and westwards up the Mangakahia River valley past Pakotai and almost to Waipoua Forest. It includes the Hen and Chicken Islands and the Poor Knights Islands. The principal urban area and district seat is the city of Whangārei. Other towns include Hūkerenui, Hikurangi, Titoki, Portland, Ruakākā and Waipu. The district population was The district contains beaches such as Ngunguru, game fishing at Tutukaka, a variety of beaches along Whangārei Harbour, as well as Matakohe or Limestone Island in the Harbour, now subject to ecological restoration. The main airport for the district is Whangarei Airport. De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northland Region
Northland (), officially the Northland Region, is the northernmost of New Zealand's 16 regions of New Zealand, local government regions. New Zealanders sometimes refer to it as the Winterless North because of its mild climate all throughout the year. The major population centre is the city of Whangārei, and the largest town is Kerikeri. At the 2018 New Zealand census, Northland recorded a population growth spurt of 18.1% since the previous 2013 New Zealand census, 2013 census, placing it as the fastest growing region in New Zealand, ahead of other strong growth regions such as the Bay of Plenty Region (2nd with 15%) and Waikato (3rd with 13.5%). Geography The Northland Region occupies the northern 80% () of the Northland Peninsula, the southernmost part of which is in the Auckland region. It is bounded to the west by the Tasman Sea, and to the east by the Pacific Ocean. The land is predominantly rolling hill country. Farming and forestry occupy over half of the land and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam In New Zealand
Islam is the third-largest Religion in New Zealand, religion in New Zealand (1.5%) after Christianity in New Zealand, Christianity (32.3%) and Hinduism in New Zealand, Hinduism (2.9%). Small numbers of Muslim immigrants from South Asia and eastern Europe settled in New Zealand from the early 1900s until the 1960s. Large-scale Muslim immigration began in the 1970s with the arrival of Indo-Fijians, Indian Fijians, followed in the 1990s by refugees from various war-torn countries. According to the 2023 New Zealand census, there are 75,144 Muslim New Zealanders, representing 1.5% of the total population. The first Islamic centre in New Zealand opened in 1959 and there are now several mosques and two Islamic schools. The majority of Muslims in New Zealand are Sunni, with significant Shia and Ahmadiyya minorities. The Ahmadiyya Community has translated the Qur'an into the Māori language. History Early migration, 19th century The earliest Muslim presence in New Zealand dates bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-binary Gender
Non-binary or genderqueer gender identities are those that are outside the male/female gender binary. Non-binary identities often fall under the transgender umbrella since non-binary people typically identify with a gender that is different from the sex assigned to them at birth, although some non-binary people do not consider themselves transgender. Non-binary people may identify as an intermediate or separate third gender, identify with more than one gender or no gender, or have a fluctuating gender identity. Gender identity is separate from sexual or romantic orientation; non-binary people have various sexual orientations. Non-binary people as a group vary in their gender expressions, and some may reject gender identity altogether. Some non-binary people receive gender-affirming care to reduce the mental distress caused by gender dysphoria, such as gender-affirming surgery or hormone replacement therapy. Terms and definitions The term "genderqueer" first app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irreligion In New Zealand
Irreligion in New Zealand refers to atheism, agnosticism, deism, religious scepticism and secular humanism in New Zealand society. Post-war New Zealand has become a highly secular country, meaning that religion does not play a major role in the lives of most people. Although New Zealand has no established religion, Christianity had been the most common religion since widespread European settlement in the 19th century. Demographics Statistics New Zealand gathers information on religious affiliation in the five-yearly census. Completing a census form is compulsory by law for every person in New Zealand on census night but respondents are able to object to answering the question of religious affiliation, and around 6% do object. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Age
New Age is a range of Spirituality, spiritual or Religion, religious practices and beliefs that rapidly grew in Western world, Western society during the early 1970s. Its highly eclecticism, eclectic and unsystematic structure makes a precise definition difficult. Although many scholars consider it a religious movement, its adherents typically see it as spiritual or as a unification of mind, body, and spirit, and rarely use the term ''New Age'' themselves. Scholars often call it the New Age movement, although others contest this term and suggest it is better seen as a Social environment, ''milieu'' or ''zeitgeist''. As a form of Western esotericism, the New Age drew heavily upon esoteric traditions such as the occultism of the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, including the work of Emanuel Swedenborg and Franz Mesmer, as well as Spiritualism (movement), Spiritualism, New Thought, and Theosophy (Blavatskian), Theosophy. More immediately, it arose from mid-20th-century influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism In New Zealand
Buddhism is New Zealand's third-largest religion after Christianity and Hinduism standing at 1.5% of the population of New Zealand. Buddhism originates in Asia and was introduced to New Zealand by immigrants from East Asia. History The first Buddhists in New Zealand were Chinese diggers in the Otago goldfields in the mid-1860s. Their numbers were small, and the 1926 census, the first to include Buddhism, recorded only 169. Buddhism grew significantly as a religion in New Zealand during the 1970s and 1980s with the arrival of Southeast Asian immigrants and refugees, coinciding with increased interest in Buddhist teaching from Western communities. Buddhist associations began forming, such as the Zen Society of New Zealand in 1972 (originally known as the Denkyo-ji Society), often fundraising to organise In the 1970s travel to Asian countries and visits by Buddhist teachers sparked an interest in the religious traditions of Asia, and significant numbers of New Zealanders adopte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity In New Zealand
Christianity in New Zealand dates to the arrival of missionary, missionaries from the Church Missionary Society who were welcomed onto the beach at Rangihoua Bay in December 1814. It soon became the predominant belief amongst the indigenous people, with over half of Māori people, Māori regularly attending church services within the first 30 years. Christianity remains New Zealand's largest religious group, but no one denomination is dominant and there is no official state church. According to the 2018 New Zealand census, 2018 census 38.17% of the population identified as Christians, Christian. The largest Christian groups are Anglican Church in New Zealand, Anglican, Catholic Church in New Zealand, Catholic and Presbyterian Church in New Zealand, Presbyterian. Christian organisations are the leading non-government providers of social services in New Zealand. History The first Christian church service, service conducted in New Zealand waters was probably to be carried out by F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Sign Language
New Zealand Sign Language or NZSL () is the main language of the deaf community in New Zealand. It became an official language of New Zealand in April 2006 under the New Zealand Sign Language Act 2006. The purpose of the act was to create rights and obligations in the use of NZSL throughout the legal system and to ensure that the Deaf community had the same access to government information and services as everybody else. According to the 2013 Census, over 20,000 New Zealanders know NZSL. New Zealand Sign Language has its roots in British Sign Language (BSL), and may be technically considered a dialect of British, Australian and New Zealand Sign Language (BANZSL). There are 62.5% similarities found in British Sign Language and NZSL, compared with 33% of NZSL signs found in American Sign Language. Like other natural sign languages, it was devised by and for deaf people, with no linguistic connection to a spoken or written language. NZSL uses the same two-handed manual alphabet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian New Zealanders
Asian New Zealanders are New Zealanders of Asian ancestry (including naturalised New Zealanders who are immigrants from specific regions in Asia and descendants of such immigrants). At the 2023 census, 861,573 New Zealanders identified as being of Asian ethnicity, making up 17.3% of New Zealand's population. The first Asians in New Zealand were Chinese workers who migrated to New Zealand to work in the gold mines in the 1860s. The modern period of Asian immigration began in the 1970s when New Zealand relaxed its restrictive policies to attract migrants from Asia. Terminology Under Statistics New Zealand classification, the term refers to a pan-ethnic group that includes diverse populations who have ancestral origins in East Asia (e.g. Chinese, Korean, Japanese), Southeast Asia (e.g. Filipino, Vietnamese, Malaysian), and South Asia (e.g. Nepalese, Indian (incl. Indo-Fijians), Sri Lankan, Bangladeshi, Pakistani). New Zealanders of West Asian and Central Asi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
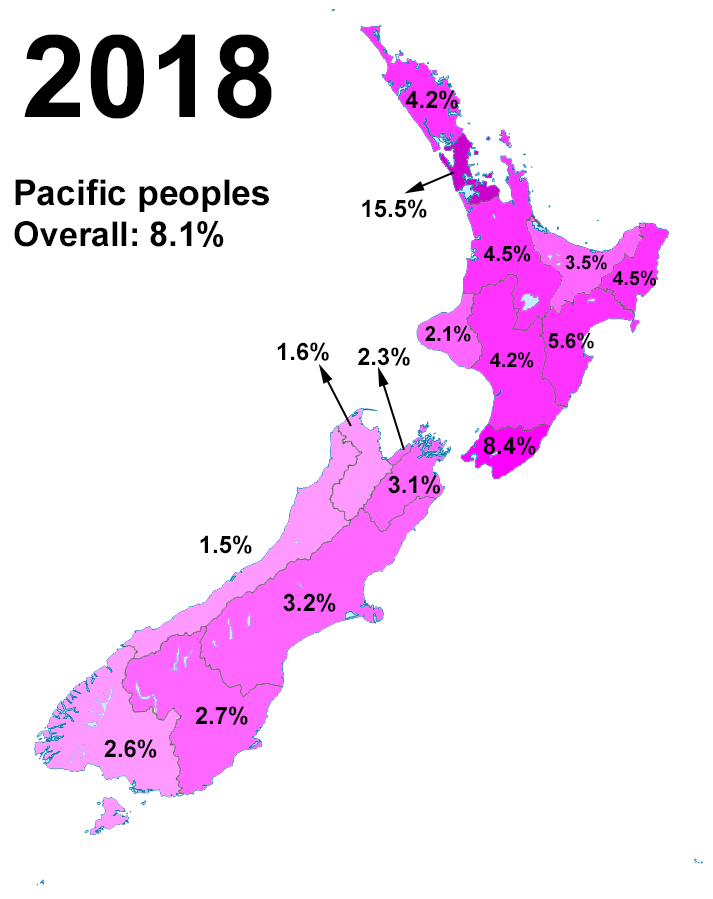
Pasifika New Zealanders
Pasifika New Zealanders (also called Pacific Peoples) are a pan-ethnic group of New Zealanders associated with, and descended from, the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Islands (also known as Pacific Islander#New Zealand, Pacific Islanders) outside New Zealand itself. They form the fourth-largest ethnic grouping in the country, after European New Zealanders, European descendants, indigenous Māori people, Māori, and Asian New Zealanders. Over 380,000 people identify as being of Pacific origin, representing 8% of the country's population, with the majority residing in Auckland. History Prior to the Second World War Pasifika in New Zealand numbered only a few hundred. Wide-scale Pasifika migration to New Zealand began in the 1950s and 1960s, typically from countries associated with the Commonwealth and the Realm of New Zealand, including Western Samoa (modern-day Samoa), the Cook Islands and Niue. In the 1970s, governments (both New Zealand Labour Party, Labour and New Zealand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |