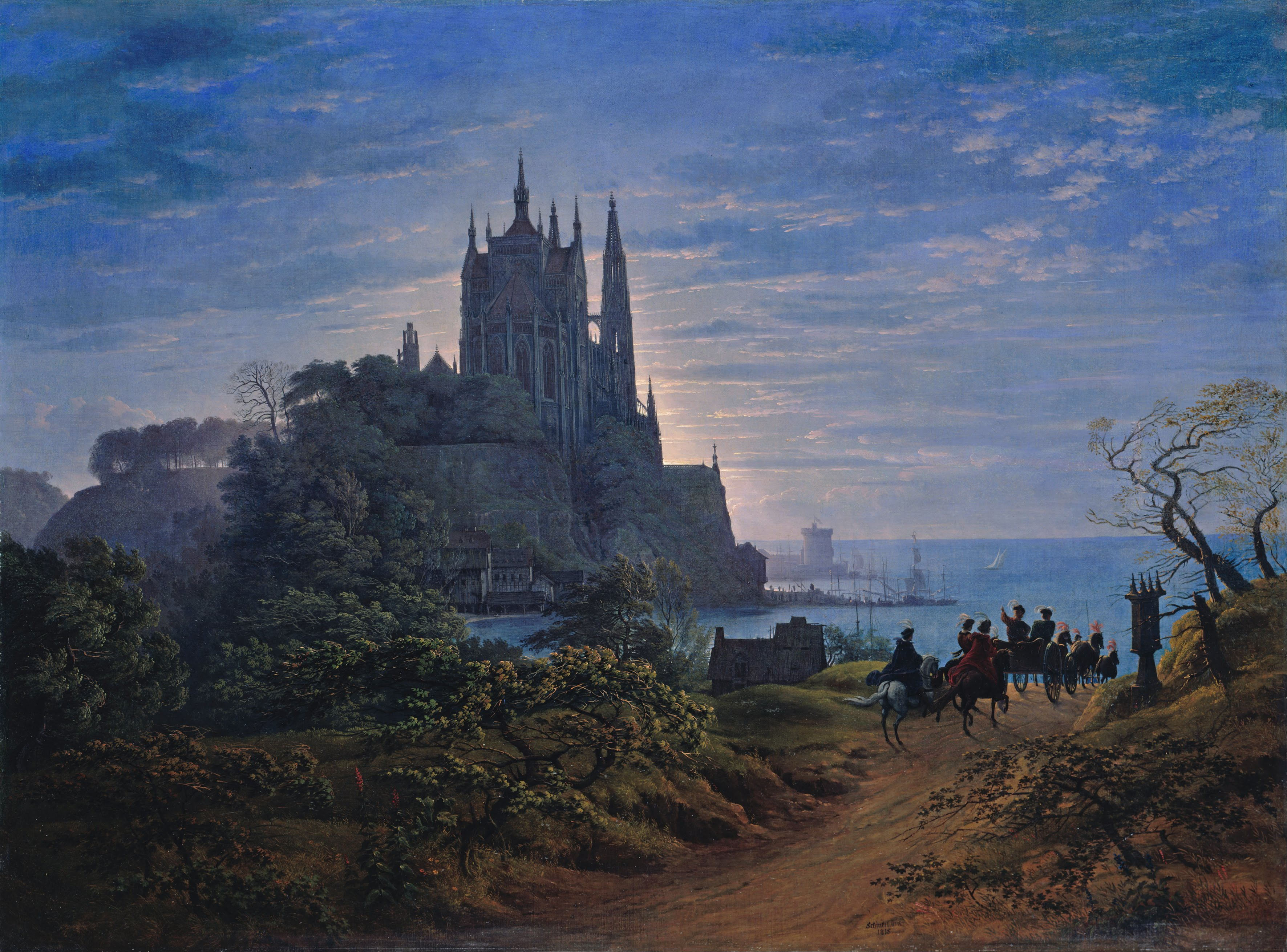|
Hütte (book)
The (originally , stylized as "HÜTTE" and pronounced ) is a reference work for engineers of various disciplines. It was compiled for the first time in 1857 by the (short , translating as "the hut") of the in Berlin, from which the association of German engineers Verein Deutscher Ingenieure (VDI) emerged. The authors were members of the association. The technical illustrations were created in woodcut technique by . It is published in constantly revised editions to this day and is therefore the oldest German reference work still available today. First edition 1857 and bibliophile reprint 2007 The book was initially divided into three sections: (Mathematics and Mechanics), (Mechanical Engineering and Technology) and (Building Science) and was originally published by the publishing house , the later , who published it until 1971. For the 150th anniversary in 2007, the first edition was reissued as a bibliophilia, bibliophile reprint. Historical development Starting wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reference Work
A reference work is a document, such as a Academic publishing#Scholarly paper, paper, book or periodical literature, periodical (or their electronic publishing, electronic equivalents), to which one can refer for information. The information is intended to be found quickly when needed. Such works are usually ''referred'' to for particular pieces of information, rather than read beginning to end. The writing style used in these works is informative; the authors avoid opinions and the use of the first person, and emphasize facts. Index (publishing), Indices are a common navigation feature in many types of reference works. Many reference works are put together by a team of contributors whose work is coordinated by one or more editors, rather than by an individual author. Updated edition (book), editions are usually published as needed, in some cases annual publication, annually, such as ''Whitaker's Almanack'', and ''Who's Who (UK), Who's Who''. Reference works include textbook ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Friedrich Schinkel
Karl Friedrich Schinkel (13 March 1781 – 9 October 1841) was a Prussian architect, urban planning, city planner and painter who also designed furniture and stage sets. Schinkel was one of the most prominent architects of Germany and designed both Neoclassical architecture, Neoclassical and Gothic revival architecture, neo-Gothic buildings. His most famous buildings are found in and around Berlin. Schinkel's Bauakademie is considered one of the forerunners of modern architecture. Biography Schinkel was born in Neuruppin, Margraviate of Brandenburg. When he was six, his father died in the disastrous Neuruppin fire of 1787. He became a student of architect Friedrich Gilly (1772–1800) (the two became close friends) and his father, David Gilly, in Berlin. At that time, the architectural taste in Prussia was shaped in Neoclassical style, mainly by Carl Gotthard Langhans, the architect of the Brandenburg Gate in Berlin. After returning to Berlin from his first trip to Italy in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century German Literature
The 19th century began on 1 January 1801 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 (MCM). It was the 9th century of the 2nd millennium. It was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was Abolitionism, abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanded beyond its British homeland for the first time during the 19th century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, France, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Catholic Church, in response to the growing influence and power of modernism, secularism and materialism, formed the First Vatican Council in the late 19th century to deal with such problems an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1857 Non-fiction Books
Events January–March * January 1 – The biggest Estonian newspaper, ''Postimees'', is established by Johann Voldemar Jannsen. * January 7 – The partly French-owned London General Omnibus Company begins operating. * January 9 – The 7.9 Fort Tejon earthquake shakes Central and Southern California, with a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (''Violent''). * January 24 – The University of Calcutta is established in Calcutta, as the first multidisciplinary modern university in South Asia. The University of Bombay is also established in Bombay, British India, this year. * February 3 – The National Deaf Mute College (later renamed Gallaudet University) is established in Washington, D.C., becoming the first school for the advanced education of the deaf. * February 5 – The Federal Constitution of the United Mexican States is promulgated. * March – The Austrian garrison leaves Bucharest. * March 3 ** France and the United Kingdom form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |