|
Hàm Nghi
Emperor Hàm Nghi (, vi-hantu, lit. "entirely right", 3 August 1871 – 14 January 1944), personal name Nguyễn Phúc Ưng Lịch (), also Nguyễn Phúc Minh, was the eighth emperor of the Vietnamese Nguyễn dynasty. He reigned for only one year (1884–85). He was the younger brother of Emperor Kiến Phúc. In 1884, Hàm Nghi was enthroned at the age of 13 by the regents Nguyễn Văn Tường and Tôn Thất Thuyết. After the failed counterattack at the imperial capital Huế in 1885, Tôn Thất Thuyết took him out of the capital where he issued the Cần Vương edict to resist French colonial rule. In Hàm Nghi’s name, Tôn Thất Thuyết launched the Cần Vương movement, calling upon scholars and patriots to assist the Emperor by rising up to fight and save the nation, to regain independence. This movement lasted until 1888, when Hàm Nghi was captured. Afterward, he was exiled to Algiers the capital of Algeria, where he later died in 1944 from stomach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nguyễn Phúc Hồng Cai
Nguyễn Phúc Hồng Cai (阮福洪侅, 13 December 1845 – 15 May 1876) was a prince of Nguyễn dynasty, Vietnam. He was the father of three emperors: Kiến Phúc, Đồng Khánh and Hàm Nghi. Hồng Cai was the twenty-sixth son of Thiệu Trị, and his mother was Trương Thị Vĩnh. He was a filial piety, filial son and liked studying. He was granted the title Kiên Quốc Công (堅國公, "Duke of Kiên") in 1865. Tự Đức had no child, and adopted Hồng Cai's two sons, Ưng Đăng and Ưng Thị, who later became Emperor Kiến Phúc and Emperor Đồng Khánh respectively. Hồng Cai died in 1876 and received the posthumous name Thuần Nghị (純毅). He was buried in Hương Thủy. In 1885, Đồng Khánh ascended the throne, and granted him the title Kiên Vương (堅王, "Prince of Kiên") posthumously. Later, his title was elevated to Kiên Thái Vương (堅太王, "King Father Kiên") in 1888.''Đại Nam thực lục, Đại Nam Thực lục Chính ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tôn Thất Thuyết
Tôn Thất Thuyết ( 尊 室 説; 12 May 1839 in Huế – 1913 in Longzhou), Courtesy name Đàm Phu (談夫), was the regent and leading mandarin of Emperor Tự Đức of Vietnam's Nguyễn dynasty. Thuyết later led the Cần Vương movement which aimed to restore Vietnamese independence under Emperor Hàm Nghi.Charles Keith ''Catholic Vietnam: A Church from Empire to Nation'' 2012 p. 52 "In July 1885, as Qing forces were withdrawing, the regent Tôn Thất Thuyết led an attack on the French garrison at huế and escaped with the young emperor hàm nghi into the mountains. Thuyết called for a general uprising and for all of the ..." He fled to China seeking political refuge after Hàm Nghi's capture by France, and later died in Longzhou, Guangxi Guangxi,; officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China, located in South China and bordering Vietnam (Hà Giang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
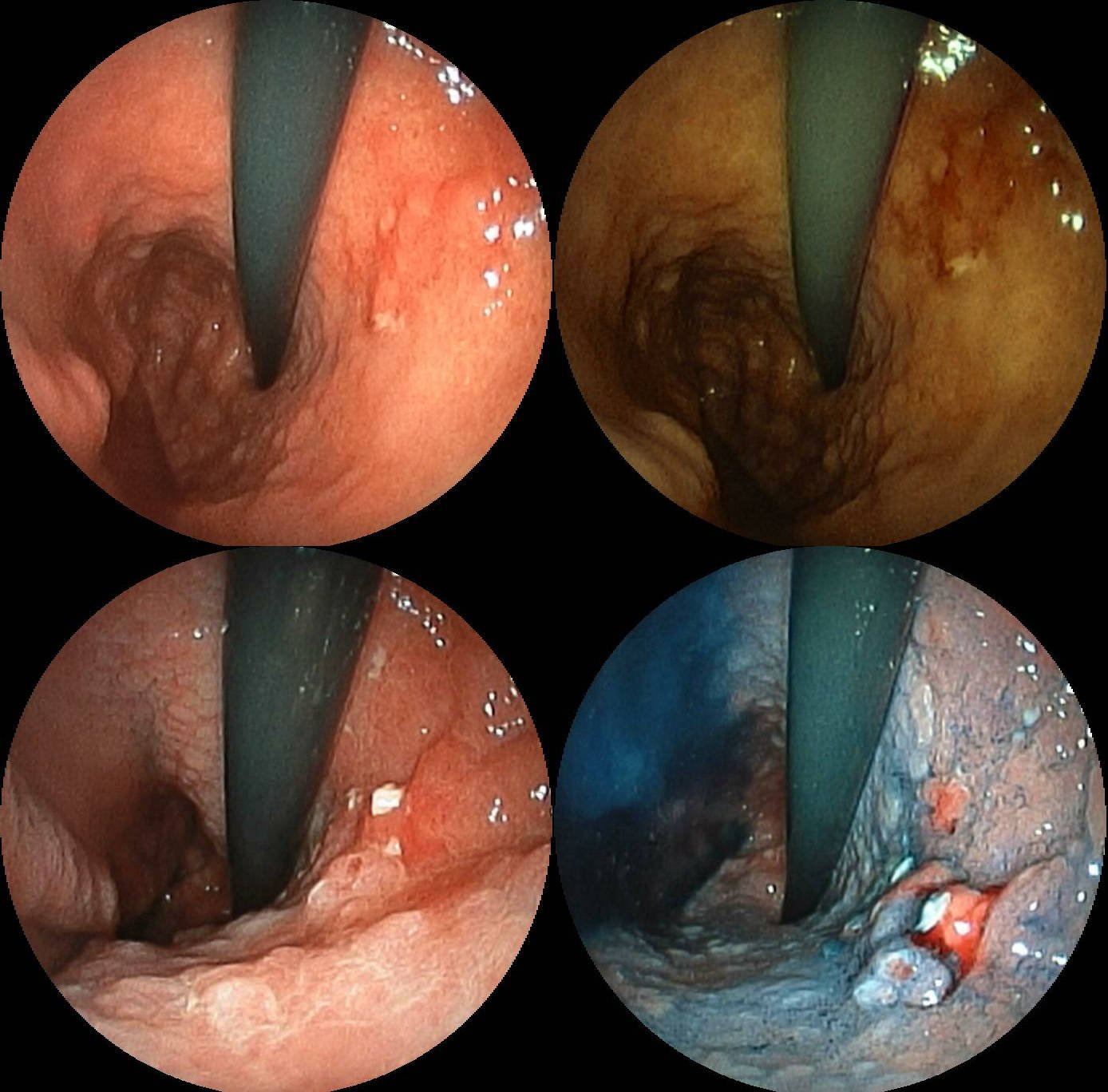
Stomach Cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a malignant tumor of the stomach. It is a cancer that develops in the Gastric mucosa, lining of the stomach. Most cases of stomach cancers are gastric carcinomas, which can be divided into a number of subtypes, including gastric adenocarcinomas. Lymphomas and mesenchymal tumors may also develop in the stomach. Early symptoms may include heartburn, upper abdominal pain, nausea, and Anorexia (symptom), loss of appetite. Later signs and symptoms may include weight loss, jaundice, yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, Hematemesis, vomiting, Dysphagia, difficulty swallowing, and Melena, blood in the stool, among others. The cancer may metastasis, spread from the stomach to other parts of the body, particularly the liver, lungs, bones, peritoneum, lining of the abdomen, and lymph nodes. The bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'' accounts for more than 60% of cases of stomach cancer. Certain strains of ''H. pylori'' have greater risk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Algeria–Niger border, the southeast by Niger; to Algeria–Western Sahara border, the southwest by Mali, Mauritania, and Western Sahara; to Algeria–Morocco border, the west by Morocco; and to the north by the Mediterranean Sea. The capital and List of cities in Algeria, largest city is Algiers, located in the far north on the Mediterranean coast. Inhabited since prehistory, Algeria has been at the crossroads of numerous cultures and civilisations, including the Phoenicians, Numidians, Ancient Rome, Romans, Vandals, and Byzantine Greeks. Its modern identity is rooted in centuries of Arab migrations to the Maghreb, Arab Muslim migration waves since Muslim conquest of the Maghreb, the seventh century and the subsequent Arabization, Arabisation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cần Vương Movement
The Cần Vương (, chữ Hán: , ) movement was a large-scale Vietnamese insurgency between 1885 and 1896 against French colonial rule. Its objective was to expel the French and install the Hàm Nghi Emperor as the leader of an independent Vietnam. The movement lacked a coherent national structure and consisted mainly of regional leaders who attacked French troops in their own provinces. The movement initially prospered as there were only a few French garrisons in Annam, but failed after the French recovered from the surprise of the insurgency and poured troops into Annam from bases in Tonkin and Cochinchina. The insurrection in Annam spread and flourished in 1886, reached its climax the following year and gradually faded out by 1889. French involvement in Vietnam 17th–18th century French involvement in Vietnam began as early as the 17th century, with missionaries such as Alexandre de Rhodes spreading the Catholic faith. This situation was to remain until the late 18th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Colonial Empire
The French colonial empire () comprised the overseas Colony, colonies, protectorates, and League of Nations mandate, mandate territories that came under French rule from the 16th century onward. A distinction is generally made between the "First French colonial empire", that existed until 1814, by which time most of it had been lost or sold, and the "Second French colonial empire", which began with the French conquest of Algeria, conquest of Algiers in 1830. On the eve of World War I, France's colonial empire was List of largest empires, the second-largest in the world after the British Empire. France began to establish colonies in the French colonization of the Americas, Americas, the Caribbean, and French India, India in the 16th century but lost most of its possessions after its defeat in the Seven Years' War. The North American possessions were lost to Britain and Spain, but Louisiana (New France), Spain later returned Louisiana to France in 1800. The territory was then Loui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tôn Thất Thuyết
Tôn Thất Thuyết ( 尊 室 説; 12 May 1839 in Huế – 1913 in Longzhou), Courtesy name Đàm Phu (談夫), was the regent and leading mandarin of Emperor Tự Đức of Vietnam's Nguyễn dynasty. Thuyết later led the Cần Vương movement which aimed to restore Vietnamese independence under Emperor Hàm Nghi.Charles Keith ''Catholic Vietnam: A Church from Empire to Nation'' 2012 p. 52 "In July 1885, as Qing forces were withdrawing, the regent Tôn Thất Thuyết led an attack on the French garrison at huế and escaped with the young emperor hàm nghi into the mountains. Thuyết called for a general uprising and for all of the ..." He fled to China seeking political refuge after Hàm Nghi's capture by France, and later died in Longzhou, Guangxi Guangxi,; officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China, located in South China and bordering Vietnam (Hà Giang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nguyễn Dynasty
The Nguyễn dynasty (, chữ Nôm: 茹阮, chữ Hán: 朝阮) was the last List of Vietnamese dynasties, Vietnamese dynasty, preceded by the Nguyễn lords and ruling unified Vietnam independently from 1802 until French protectorate in 1883. Its emperors were members of the House of Nguyễn Phúc. During its existence, the Nguyễn empire expanded into modern-day Southern Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos through a continuation of the centuries-long Nam tiến and Siamese–Vietnamese wars. With the French conquest of Vietnam, the Nguyễn dynasty was forced to give up sovereignty over parts of French Cochinchina, Southern Vietnam to France in 1862 and 1874, and after 1883 the Nguyễn dynasty only nominally ruled the French protectorates of Annam (French protectorate), Annam (Central Vietnam) as well as Tonkin (French protectorate), Tonkin (Northern Vietnam). Backed by Empire of Japan, Imperial Japan, in 1945 the last Nguyễn emperor Bảo Đại abolished the protectorate treat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifteenth-most populous country. One of two communist states in Southeast Asia, Vietnam shares land borders with China to the north, and Laos and Cambodia to the west. It shares Maritime boundary, maritime borders with Thailand through the Gulf of Thailand, and the Philippines, Indonesia, and Malaysia through the South China Sea. Its capital is Hanoi and its largest city is Ho Chi Minh City. Vietnam was inhabited by the Paleolithic age, with states established in the first millennium BC on the Red River Delta in modern-day northern Vietnam. Before the Han dynasty's invasion, Vietnam was marked by a vibrant mix of religion, culture, and social norms. The Han dynasty annexed Northern and Central Vietnam, which were subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Legge
James Legge (; 20 December 181529 November 1897) was a Scottish linguist, missionary, sinologist, and translator who was best known as an early translator of Classical Chinese texts into English. Legge served as a representative of the London Missionary Society in Malacca and Hong Kong (1840–1873) and was the first Professor of Chinese at Oxford University (1876–1897). In association with Max Müller he prepared the monumental '' Sacred Books of the East'' series, published in 50 volumes between 1879 and 1891. Early life James Legge was born at Huntly, Aberdeenshire. He enrolled in Aberdeen Grammar School at age 13 and then King's College, Aberdeen at age 15. He then continued his studies at Highbury Theological College, London. Mission to China and family Legge went, in 1839, as a missionary to China, but first stayed at Malacca three years, in charge of the Anglo-Chinese College there. The College was subsequently moved to Hong Kong, where Legge lived for n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classic Of Poetry
The ''Classic of Poetry'', also ''Shijing'' or ''Shih-ching'', translated variously as the ''Book of Songs'', ''Book of Odes'', or simply known as the ''Odes'' or ''Poetry'' (; ''Shī''), is the oldest existing collection of Chinese poetry, comprising 305 works dating from the 11th to 7th centuries BC. It is one of the " Five Classics" traditionally said to have been compiled by Confucius, and has been studied and memorized by scholars in China and neighboring countries over two millennia. It is also a rich source of '' chengyu'' (four-character classical idioms) that are still a part of learned discourse and even everyday language in modern Chinese. Since the Qing dynasty, its rhyme patterns have also been analysed in the study of Old Chinese phonology. Name Early references refer to the anthology as the ''300 Poems'' ('' shi''). ''The Odes'' first became known as a ''jīng'', or a "classic book", in the canonical sense, as part of the Han dynasty's official adoption of Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century Before the Common Era, BCE. It is the Major religious groups, world's fourth-largest religion, with about 500 million followers, known as Buddhists, who comprise four percent of the global population. It arose in the eastern Gangetic plain as a movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia. Buddhism has subsequently played a major role in Asian culture and spirituality, eventually spreading to Western world, the West in the 20th century. According to tradition, the Buddha instructed his followers in a path of bhavana, development which leads to Enlightenment in Buddhism, awakening and moksha, full liberation from ''Duḥkha, dukkha'' (). He regarded this path as a Middle Way between extremes su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |