|
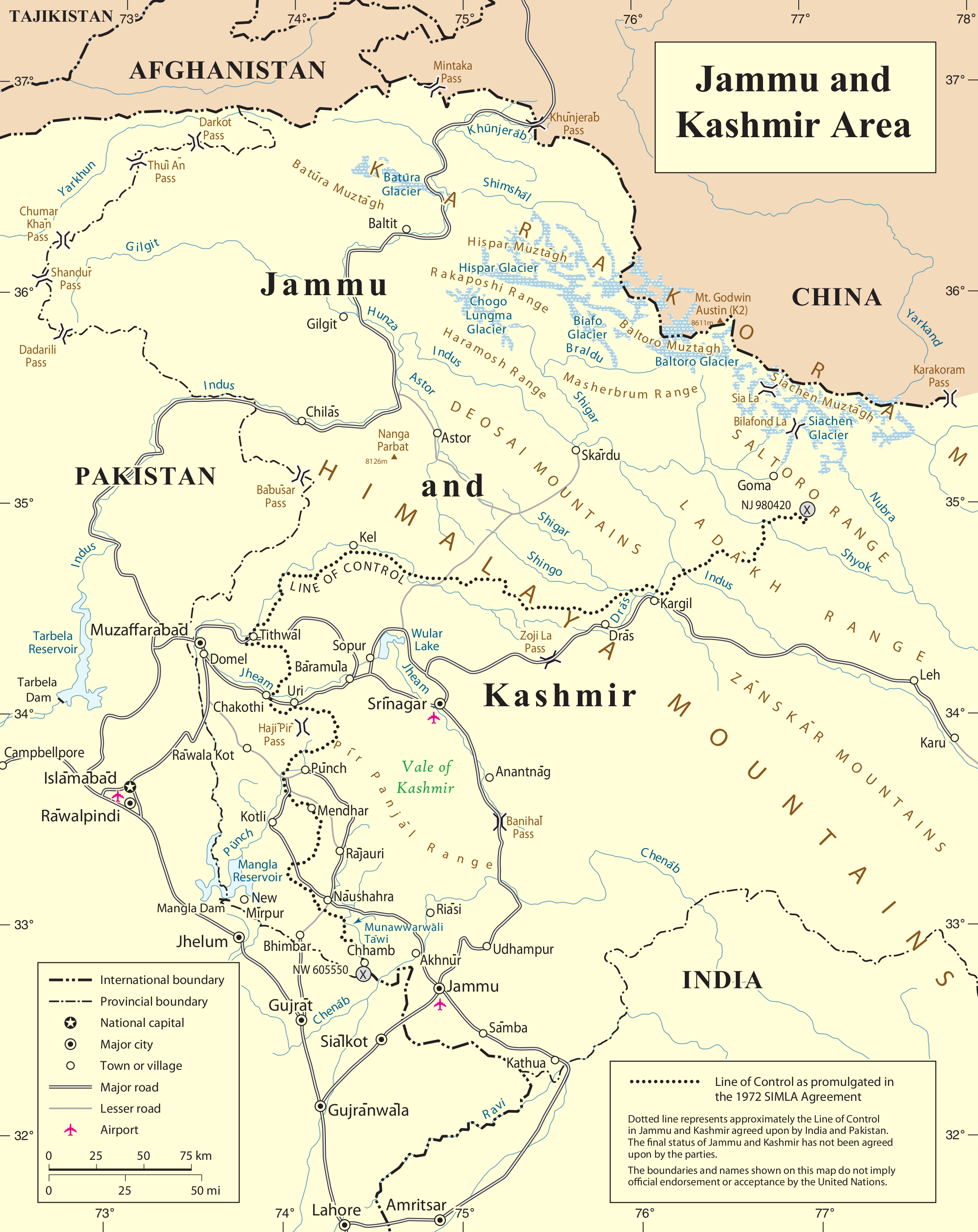
Hunza (princely State)
Hunza (, ), also known as Kanjut (; ), was a Burushaski, Burusho princely state in the present-day Gilgit-Baltistan, Gilgit Baltistan region of Pakistan. Although under the suzerainty of the Kashmir (princely state), Jammu and Kashmir (princely state), it was not a part of it and had status of a separate state. Initially, it functioned as a principality and subsequently became a princely state under a subsidiary alliance with the British India starting in 1892 and continuing until August 1947. For a brief period of three months, it remained unaligned after gaining independence, and then from November 1947 until 1974, it retained its status as a princely state within Pakistan. The territory of Hunza now constitutes the northernmost part of Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan. The princely state bordered the Gilgit Agency to the south, the former Nagar (princely state), princely state of Nagar to the east, Xinjiang, China, to the northeast and Afghanistan to the northwest. The state's c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Language
Persian ( ), also known by its endonym and exonym, endonym Farsi (, Fārsī ), is a Western Iranian languages, Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian languages, Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and used officially within Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan in three mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible standard language, standard varieties, respectively Iranian Persian (officially known as ''Persian''), Dari, Dari Persian (officially known as ''Dari'' since 1964), and Tajik language, Tajiki Persian (officially known as ''Tajik'' since 1999).Siddikzoda, S. "Tajik Language: Farsi or not Farsi?" in ''Media Insight Central Asia #27'', August 2002. It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population within Uzbekistan, as well as within other regions with a Persianate society, Persianate history in the cultural sphere o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
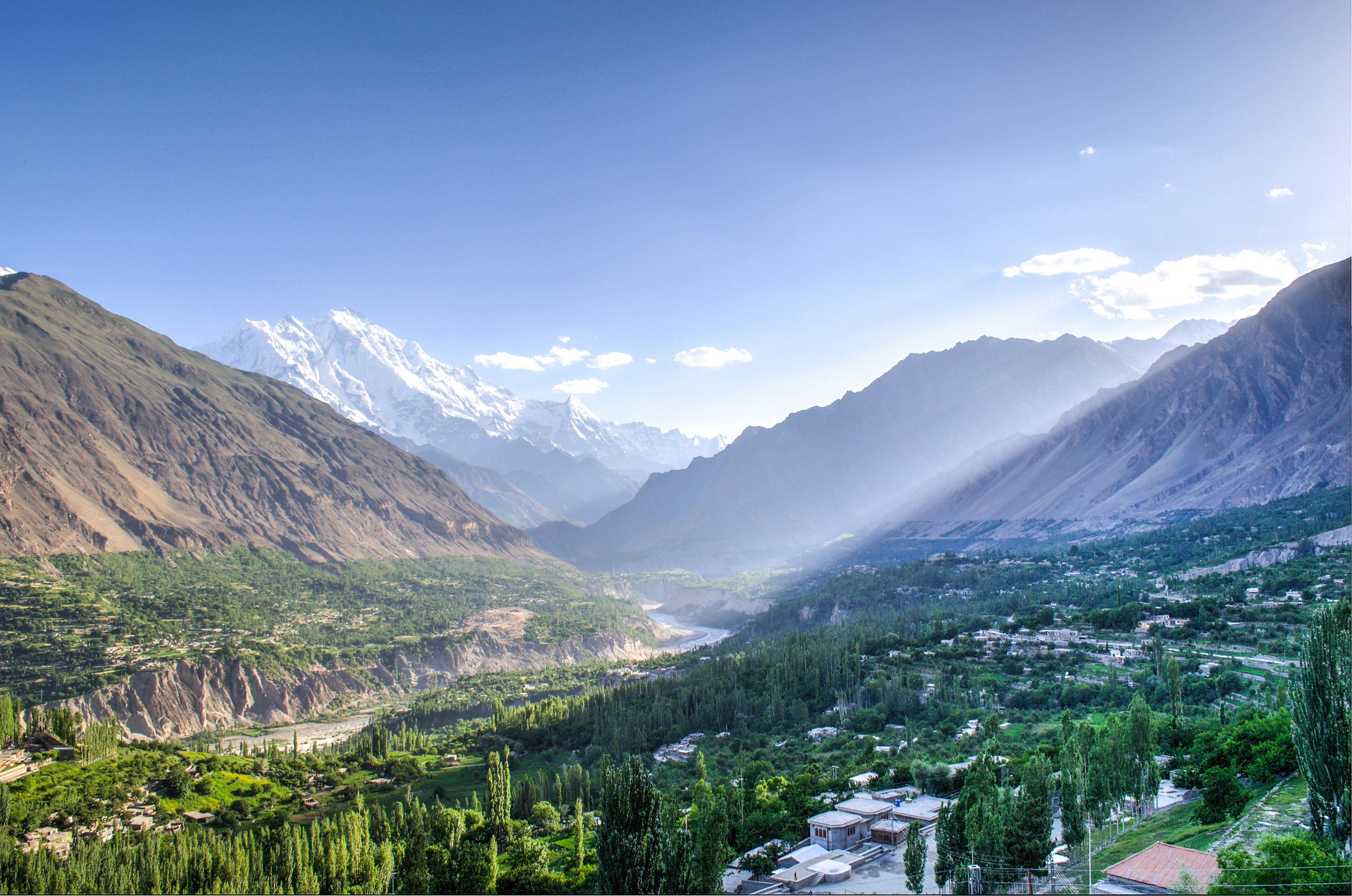
Karimabad (Hunza)
Karimabad (), formerly known as Baltit, is the capital of the Hunza District in Pakistan-administered Gilgit-Baltistan in the disputed Kashmir region. Etymology Karimabad was named in honour of Karim Aga Khan, the late spiritual leader of the Shia Ismaili Nizari community. Geography Karimabad town is situated on the western bank of the Hunza River, opposite Nagar Valley nestled in the lower Hunza Valley. It lies at an elevation of 8,200 feet (2,500 meters) above sea level. The town is characterized by its construction on stone-walled and steep-sloping terraces. Historically, Karimabad served as a caravan stop for travelers journeying through the Hindu Kush mountains en route to the Vale of Kashmir. The town is framed by deep gorges and is set against the backdrop of snow-clad mountain peaks like Rakaposhi, which stands at an altitude of approximately 25,000 feet (7,600 meters), Diran, Golden Peak and Ultar Peak. All four peaks have dedicated view points in and around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dogra Dynasty
The Dogra dynasty of Dogra Rajputs from the Shivalik hills created Jammu and Kashmir through the treaties with the East India Company following the First Anglo-Sikh war. Events led the Sikh Empire to recognise Jammu as a vassal state in 1820, and later the British added Kashmir to Jammu with the Treaty of Amritsar in 1846. The founder of the dynasty, Gulab Singh, was an influential noble in the court of the Sikh emperor Maharaja Ranjit Singh, while his brother Dhian Singh served as the prime minister of the Sikh Empire. Appointed by Ranjit Singh as the hereditary Raja of the Jammu principality, Gulab Singh established his supremacy over all the hill states surrounding the Kashmir Valley. After the First Anglo-Sikh War in 1846, under the terms of the Treaty of Lahore, 1846, the British East India Company acquired Kashmir from the Sikh Empire and transferred it to Gulab Singh, recognising him as an independent Maharaja. Thus, Jammu and Kashmir was established as one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarkant (town)
Yarkant County,, National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also Shache County,, National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also SASM/GNC romanization#Uyghur, transliterated from Uyghur as Yakan County, is a county in the Xinjiang, Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, China, located on the southern rim of the Taklamakan Desert in the Tarim Basin. It is one of 11 counties administered under Kashgar Prefecture. The county, usually referred to as Yarkand in English language, English, was the seat of an ancient Buddhism, Buddhist kingdom on the southern branch of the Silk Road and the Yarkand Khanate. The county sits at an altitude of and had a population of . The fertile oasis is fed by the Yarkand River, which flows north down from the Karakorum Mountains, Karakorum mountains and passes through the Kunlun Mountains, known historically as the Congling mountains (lit. 'Onion Mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Grant
A land grant is a gift of real estate—land or its use privileges—made by a government or other authority as an incentive, means of enabling works, or as a reward for services to an individual, especially in return for military service. Grants of land are also awarded to individuals and companies as incentives to develop unused land in relatively unpopulated countries; the process of awarding land grants are not limited to the countries named below. The United States historically gave out numerous land grants as homesteads to individuals desiring to make a farm. The American Industrial Revolution was guided by many supportive acts of legislatures (for example, the Main Line of Public Works legislation of 1863) promoting commerce or transportation infrastructure development by private companies, such as the Cumberland Road turnpike, the Lehigh Canal, the Schuylkill Canal and the many railroads that tied the young United States together. Ancient Rome Roman soldiers were giv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jagir
A jagir (), ( Hindustani: जागीर/جاگیر, ''Jāgīr''), ( Marathi: जहागीर, ''Jahāgīrá'') also spelled as jageer, was a type of feudal land grant in the Indian subcontinent at the foundation of its Jagirdar ( Zamindar) system. It developed during the Islamic era of the Indian subcontinent, starting in the early 13th century, wherein the powers to govern and collect tax from an estate was granted to an appointee of the state. 13th-century origin and successors This feudal system of land ownership is referred to as the ''jagirdar'' system. The system was introduced by the Sultans of Delhi from the 13th century onwards, was later adopted by the Mughal Empire, the Maratha Empire and continued under the British East India Company. Some Hindu jagirdars were converted into Muslim vassal states under Mughal imperial sway, such as the nawabs of Kurnool. Most princely states of India during the colonial British Raj era were jagirdars such as Mohrampur Jagi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarkand (town)
Yarkant County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also Shache County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also transliterated from Uyghur as Yakan County, is a county in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, China, located on the southern rim of the Taklamakan Desert in the Tarim Basin. It is one of 11 counties administered under Kashgar Prefecture. The county, usually referred to as Yarkand in English, was the seat of an ancient Buddhist kingdom on the southern branch of the Silk Road and the Yarkand Khanate. The county sits at an altitude of and had a population of . The fertile oasis is fed by the Yarkand River, which flows north down from the Karakorum mountains and passes through the Kunlun Mountains, known historically as the Congling mountains (lit. 'Onion Mountains' - from the abundance of wild onions found there). The oasis now covers , but was likely far more extensive before a period of desiccation affected the reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afaqi Khoja Revolts
In 1759, the Qing dynasty of China defeated the Dzungar Khanate and completed the conquest of Dzungaria. Concurrent with this conquest, the Qing occupied the Altishahr region in modern southern Xinjiang, which had been settled by Muslims who followed the political and religious leadership of Afaq Khoja. After the Qing conquest, the Chinese began to incorporate Altishahr and the Tarim Basin into their empire. The territory along with Dzungaria came to be known as Xinjiang. Although the followers of Afaq Khoja known as the Āfāqī Khojas resisted Qing rule, their rebellion was put down and the khojas were removed from power. Beginning at that time and lasting for approximately one hundred years, the Āfāqī Khojas waged numerous military campaigns in an effort to retake Altishahr from the Qing. Khoja background and rivalries The Khoja (Turkestan), Khojas of Central Asia were a Naqshbandī Sufi lineage founded by Ahmad Kāsānī (1461-1542), known as Makhdūm-i-Azam or the "G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xaidulla
Shahidulla, also spelt Xaidulla from Mandarin Chinese, (altitude ca. 3,646 m or 11,962 ft), was a nomad camping ground and historical caravan halting place in the Karakash River valley, close to Khotan, in the southwestern part of Xinjiang Autonomous Region, China. The site contains the ruins of a historical fort which was demolished by the Chinese administration of Xinjiang between 1890 and 1892. The site lies next to the Chinese National Highway G219 between Kashgar and Tibet, 25 km east of Mazar and 115 km west of Dahongliutan. The modern town of Saitula (Xeyidula) is located next to the old fort of Suget Karaul built by the Qing administration (of China) about 10 km (30 " Chinese miles") southeast of the original site. A modern People's Liberation Army barracks named Sanshili Yingfang or Sanshili Barracks () is also located here. "Sanshili Barracks" is a more common name used by motorists along the G219 highway. Etymology The Uyghur name ''Shahidulla' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kunlun Mountains
The Kunlun Mountains constitute one of the longest mountain chains in Asia, extending for more than . In the broadest sense, the chain forms the northern edge of the Tibetan Plateau south of the Tarim Basin. Located in Western China, the Kunlun Mountains have been known as the "Forefather of Mountains" in China. The exact definition of the Kunlun Mountains varies over time. Older sources used Kunlun to mean the mountain belt that runs across the center of China, that is, Altyn Tagh along with the Qilian and Qin Mountains. Recent sources have the Kunlun range forming most of the south side of the Tarim Basin and then continuing east, south of the Altyn Tagh. Sima Qian ('' Records of the Grand Historian'', scroll 123) says that Emperor Wu of Han sent men to find the source of the Yellow River and gave the name Kunlun to the mountains at its source. The name seems to have originated as a semi-mythical location in the classical Chinese text '' Classic of Mountains and Seas''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzerainty
A suzerain (, from Old French "above" + "supreme, chief") is a person, state (polity)">state or polity who has supremacy and dominant influence over the foreign policy">polity.html" ;"title="state (polity)">state or polity">state (polity)">state or polity who has supremacy and dominant influence over the foreign policy and economic relations of another subordinate party or polity, but allows internal autonomy to that subordinate. Where the subordinate polity is called a vassal, vassal state or tributary state, the dominant party is called the suzerain. The rights and obligations of a vassal are called ''vassalage'', and the rights and obligations of a suzerain are called suzerainty. Suzerainty differs from sovereignty in that the dominant power does not exercise centralized governance over the vassals, allowing tributary states to be technically self-ruling but enjoy only limited independence. Although the situation has existed in a number of historical empires, it is con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thum (title)
Mir of Hunza was the title of rulers of Hunza in the Hunza Valley in the Northern Areas, Pakistan. Etymology The Mir used to have the Burushaski title of Thum (also ''Tham'' or ''Thom''), later changed to Mir, Persianform of the Arabic title ''Emir''. Timeline ** Mir Salim Khan I ** Mir Shah Sultan Khan ** Mir Shahbaz Khan (1710 – Unknown) ** Mir Shahbeg Khan ** Mir Shah Khisrow Khan (1750 – 1790) ** Mir Mirza Khan (1790) ** Mir Salim Khan II (1790 – 1825) ** Mir Ghazanfar Ali Khan I (1825 – 1864) ** Mir Muhammad Ghazan Khan I (1864 – 1886) ** Mir Safdar Ali Khan (1886 – 1891) *** Mir Safdar fled to China after conquest of Hunza and Nagar States by British Forces in December 1891.Prince Muhammad Nafis Khan was the main contender of Mir-ship of Hunza on the grounds that he was the elder son of Mir Muhammad Ghazan Khan-I and has the legitimate right to be appointed as Mir of Hunza but His younger brother Nazim Khan was placed in his position by British Raj in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |