|
Hudson, Wisconsin
Hudson is a city in and the county seat of St. Croix County, Wisconsin, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, its population was 14,755. It is part of the Minneapolis–St. Paul metropolitan area. History Several List of burial mounds in the United States, Native American burial mounds dated to the Middle Woodland period, Middle or Late Woodland period have been found in what is now Birkmose Park in Hudson. Hudson was settled in 1840 by Louis Massey and his brother in-law, Peter Bouchea. William Streets arrived at about the same time. Later that year, Joseph Sauperson (commonly known as Joe LaGrue) took up residence. These four are considered Hudson's original inhabitants. Massey and Bouchea settled at the mouth of the Willow River (St. Croix River tributary), Willow River, near the present-day First and St. Croix Streets. They had been part of a group that lived for some time along the river below Fort Snelling, which appears on some old maps as "Mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
City
A city is a human settlement of a substantial size. The term "city" has different meanings around the world and in some places the settlement can be very small. Even where the term is limited to larger settlements, there is no universally agreed definition of the lower boundary for their size. In a narrower sense, a city can be defined as a permanent and Urban density, densely populated place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, Public utilities, utilities, land use, Manufacturing, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organisations, government organizations, and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving the efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
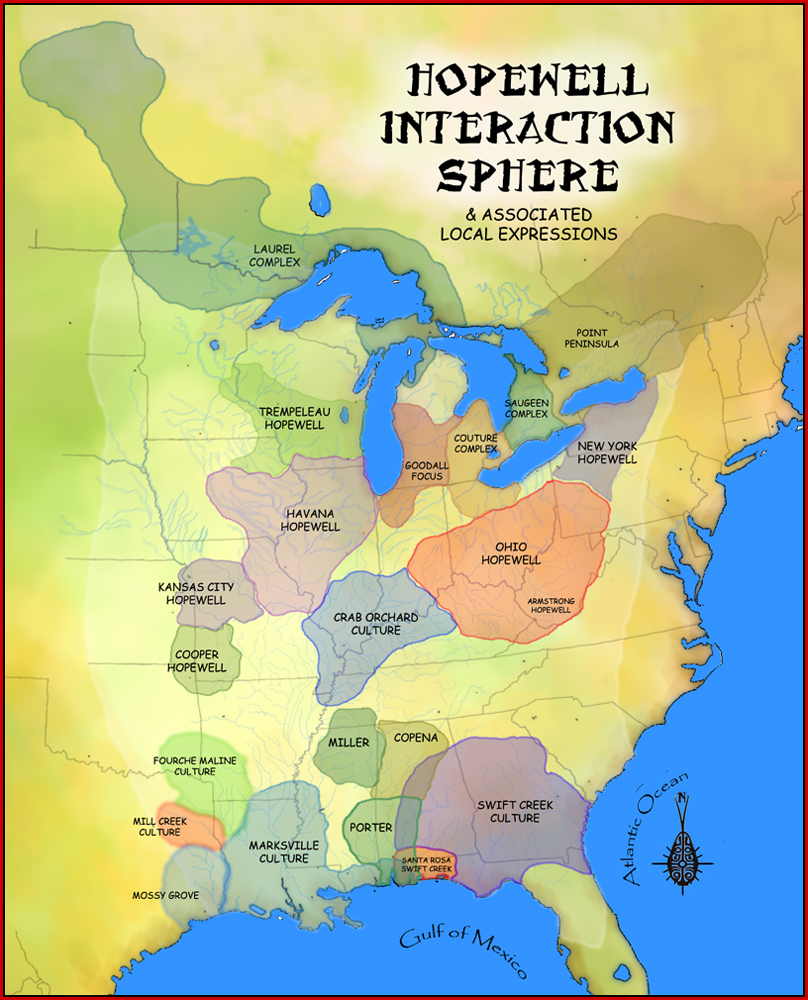
Middle Woodland Period
In the classification of :category:Archaeological cultures of North America, archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 BC to European contact in the eastern part of North America, with some archaeologists distinguishing the Mississippian period, from 1000 AD to European contact as a separate period. The term "Woodland Period" was introduced in the 1930s as a generic term for prehistoric, prehistoric sites falling between the Archaic period in the Americas, Archaic hunter-gatherers and the agriculturalist Mississippian cultures. The Eastern Woodlands cultural region covers what is now eastern Canada south of the Subarctic region, the Eastern United States, along to the Gulf of Mexico. This period is variously considered a developmental stage, a time period, a suite of technological adaptations or "traits", and a "family tree" of cultures related to earlier Archaic cultures. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Causeway
A causeway is a track, road or railway on the upper point of an embankment across "a low, or wet place, or piece of water". It can be constructed of earth, masonry, wood, or concrete. One of the earliest known wooden causeways is the Sweet Track in the Somerset Levels, England, which dates from the Neolithic age. Timber causeways may also be described as both boardwalks and bridges. Etymology When first used, the word ''causeway'' appeared in a form such as "causey way", making clear its derivation from the earlier form "causey". This word seems to have come from the same source by two different routes. It derives ultimately, from the Latin for heel, , and most likely comes from the trampling technique to consolidate earthworks. Originally, the construction of a causeway used earth that had been trodden upon to compact and harden it as much as possible, one layer at a time, often by slaves or flocks of sheep. Today, this work is done by machines. The same technique w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Interstate 94
Interstate 94 (I-94) is an east–west Interstate Highway connecting the Great Lakes and northern Great Plains regions of the United States. Its western terminus is just east of Billings, Montana, at a junction with I-90; its eastern terminus is in Port Huron, Michigan, where it meets with I-69 and crosses the Blue Water Bridge into Sarnia, Ontario, Canada, where the route becomes Ontario Highway 402. It thus lies along the primary overland route from Seattle (via I-90) to Toronto (via Ontario Highway 401) and is the only east–west Interstate Highway to have a direct connection to Canada. It is the longest Interstate whose route number is not divisible by 5. I-94 intersects with I-90 several times: at its western terminus; Tomah to Madison in Wisconsin; in Chicago, Illinois; and in Lake Station, Indiana. Major cities that I-94 connects to are Billings, Bismarck, Fargo, Minneapolis–Saint Paul, Madison, Milwaukee, Chicago, and Detroit. Route description , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
People's Council Of America
The People's Council of America for Democracy and the Terms of Peace, commonly known as the "People's Council," was an American pacifist political organization established in New York City in May 1917. Organized in opposition to the decision of the Woodrow Wilson administration's decision to enter World War I, the People's Council attempted to mobilize American workers and intellectuals against the war effort through publication of literature and the conduct of mass meetings and public demonstrations. The organization's dissident views made it a target of federal, state, and local authorities, who disrupted its meetings and arrested a number of its leading participants under provisions of the Espionage Act. The People's Council was succeeded in 1919 by a new group based in the same New York City headquarters, the People's Freedom Union. Organizational history Forerunners The eruption of World War I in August 1914 saw its response in the United States of America with the emergence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pacifist
Pacifism is the opposition to war or violence. The word ''pacifism'' was coined by the French peace campaigner Émile Arnaud and adopted by other peace activists at the tenth Universal Peace Congress in Glasgow in 1901. A related term is ''ahimsa'' (to do no harm), which is a core philosophy in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism. While modern connotations are recent, having been explicated since the 19th century, ancient references abound. In modern times, interest was revived by Leo Tolstoy in his late works, particularly in ''The Kingdom of God Is Within You''. Mahatma Gandhi propounded the practice of steadfast nonviolent resistance, nonviolent opposition which he called "satyagraha", instrumental in its role in the Indian independence movement. Its effectiveness served as inspiration to Martin Luther King Jr., James Lawson (activist), James Lawson, Charles and Mary Beard, Mary and Charles Beard, James Bevel, Thích Nhất Hạnh,"Searching for the Enemy of Man", in Nhat Nanh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
New York (state)
New York, also called New York State, is a U.S. state, state in the northeastern United States. Bordered by New England to the east, Canada to the north, and Pennsylvania and New Jersey to the south, its territory extends into both the Atlantic Ocean and the Great Lakes. New York is the List of U.S. states and territories by population, fourth-most populous state in the United States, with nearly 20 million residents, and the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 27th-largest state by area, with a total area of . New York has Geography of New York (state), a varied geography. The southeastern part of the state, known as Downstate New York, Downstate, encompasses New York City, the List of U.S. cities by population, most populous city in the United States; Long Island, with approximately 40% of the state's population, the nation's most populous island; and the cities, suburbs, and wealthy enclaves of the lower Hudson Valley. These areas are the center of the expansive New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hudson River
The Hudson River, historically the North River, is a river that flows from north to south largely through eastern New York (state), New York state. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains at Henderson Lake (New York), Henderson Lake in the town of Newcomb, New York, Newcomb, and flows south to the New York Bay , New York Bay, a tidal estuary between New York City, New York and Jersey City, Jersey City, before draining into the Atlantic Ocean , Atlantic Ocean. The river marks boundaries between several County (New York), New York counties and the eastern border between the U.S. states of New York and New Jersey , New Jersey. The lower half of the river is a tidal estuary, deeper than the body of water into which it flows, occupying the Hudson Fjord, an inlet that formed during the most recent period of North American Quaternary glaciation, glaciation, estimated at 26,000 to 13,300 years ago. Even as far north as the city of Troy, New York, Troy, the flow of the river chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Buena Vista
The Battle of Buena Vista (February 22–23, 1847), known as the Battle of La Angostura in Mexico, and sometimes as Battle of Buena Vista/La Angostura, was a battle of the Mexican–American War. It was fought between U.S. forces, largely volunteers, under General Zachary Taylor, and the much larger Mexican Army under General Antonio López de Santa Anna. It took place near Buena Vista, a village in the state of Coahuila, about south of Saltillo, Mexico. ''La Angostura'' ("the narrow place") was the local name for the site. The outcome of the battle was ambiguous, with both sides claiming victory. Santa Anna's forces withdrew with war trophies of cannons and flags and left the field to the surprised U.S. forces, who had expected there to be another day of hard fighting. Background U.S. president James K. Polk had decided that an invasion into central Mexico via the Gulf Coast port of Veracruz would make the Mexicans come to the negotiating table. He told Major General ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
River Falls, Wisconsin
River Falls is a city in Pierce and St. Croix counties in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. It is located mostly within the town of River Falls, and adjacent to the town of Kinnickinnic in St. Croix County. River Falls is the most populous city in Pierce County. The population was 16,182 at th2020 census with 12,546 residing in Pierce County and 3,636 in St. Croix County. It is part of the Minneapolis–St. Paul metropolitan area and located approximately east of the center of that region. River Falls is the home of the University of Wisconsin–River Falls. History The city's first settlers were Joel Foster and his indentured servant, Dick, in 1848. The village was started as Kinnickinnic in 1854 by brothers Nathaniel N. and Oliver S. Powell, who were from St. Lawrence County, New York. At the time, the town and village were also known as Greenwood, but this was changed, as another Greenwood, Wisconsin already existed. The present name comes from the Kinnickinnic River r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Joel Foster
Joel Foster (December 15, 1814August 9, 1885) was an American pioneer farmer, judge and local politician in River Falls, Wisconsin. Background Foster was born the youngest of eleven at Meriden, Connecticut, December 15, 1814. He was liberally educated. He came to Alton, Illinois, in 1830 where he became the ferry master. In 1848 he traveled to what would become Hudson, Wisconsin, then only a few structures at the mouth of the Willow River. After a careful exploration of the surrounding area he settled in the fall of 1848, at the junction of the two branches of the Kinnickinnic River, just upstream from its falls. His first winter was spent in a walled-in overhang cave below the falls of the river with "Dick" an orphan who had been indentured to the family. That same year they began building a small cabin known as Fort Foster. Foster was the first white settler of River Falls, a city which grew at the location of the falls of the Kinnickinnic. He built the first dwelling h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |