|
Huamán
{{for, the fictional Three Kingdoms character, Huaman (Three Kingdoms) Huaman (Quechua language, ''waman'' falcon /sup> or variable hawk /sup>) is a Quechuan surname. It may refer to: People * Felipe Huaman Poma de Ayala, colonial Quechua Quechua may refer to: *Quechua people, several Indigenous ethnic groups in South America, especially in Peru *Quechuan languages, an Indigenous South American language family spoken primarily in the Andes, derived from a common ancestral language ... nobleman and Peruvian chronist. * Dr. Augusto Huaman Velasco, Peruvian physician and scientist. *Benjamin Huaman de los Heros, Peruvian lawyer and politician. During the Oncenio de Leguía he was Minister of War (1922-1924), Minister of Finance and Trade (1924-1925), and Prime Minister (1929-1930). He was also a national deputy (1911-1918 and 1920–1925) and deputy of the National Constituent Assembly of 1919. *Vilchez Huaman, the ''stage name'' adopted by ''Ricardo Wiesse Hamann'', Peruvian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santiago De Huamán
Santiago de Huamán, simply known as Huaman (from meaning 'hawk') is a traditional village in Trujillo, Peru; it is located in the western part of the city in Víctor Larco Herrera. Currently its main attractions are the Baroque-style church and the Patron Festivities that are held every year in May or June. History Located in southwest Trujillo city, its territory was part of the Moche and Chimu cultures. It was later conquered by the Inca, who presumably gave it its name of Huaman, and subsequently seized by the Spanish. The church of Santiago de Huamán, erected at the beginning of the 17th century, is without a doubt the oldest standing Catholic church in Trujillo. In the past it was dedicated to the Virgin of Mercy and was maintained by the Mercedarian friars. Festivals * Patron Lord of Huaman The origin of this tradition dates back more than 300 years. It is a religious festival that attracts pilgrims and tourists who visit the historic church of Santiago de Huaman. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felipe Guaman Poma De Ayala
Felipe Guamán Poma de Ayala (Fane, 165after 1616), also known as Huamán Poma or Waman Poma, was a Quechua nobleman known for chronicling and denouncing the ill treatment of the natives of the Andes by the Spanish Empire after their conquest of Peru.Adorno, RolenaFelipe Guamán Poma de Ayala's ''Nueva crónica y buen gobierno'' (''New Chronicle and Good Government'').''Early Ibero/Anglo Americanist Summit: New World Antiquities and Histories.'' (retrieved 8 Sept 2009) Today, Guaman Poma is noted for his illustrated chronicle, '' El primer nueva corónica y buen gobierno''.Fane, 166 Biography The son of a noble family of the Indigenous (but non-Inca) Yarowilca dynasty of Guánuco in the north Peruvian cordillera, he was a direct descendant of the eminent Indigenous conqueror and ruler Huaman-Chava-Ayauca Yarovilca-Huanuco.Hamilton, RolandTable of Contents and Excerpt, Guaman Poma de Ayala, the First New Chronicle and Good Government.''University of Texas Press.'' 2009 (retriev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vilcashuamán
Vilcashuamán or Vilcasguaman (from Quechua language, Quechua Willka Waman, "sacred hawk") is the capital of Vilcas Huamán Province, Ayacucho region, Peru. It is located at an altitude of 3,490 m on the eastern slopes of the Andes. It is located on an ancient archaeological site. Vilcashuamán was an Inca administrative center, established after the Incas conquered the Chancas and the Pocras. According to the Chronicler Pedro Cieza de León, Vilcashuamán was home to 40,000 people.Cieza de León, Pedro (2005 [1553]). Crónica del Perú - El señorío de los Incas - edited by Franklin Pease G.Y. - Fundación Biblioteca Ayacucho - Caracas - Venezuela The city was located around a large plaza where ceremonies involving sacrifices were performed, usually camelids or libation of chicha, corn wine. Around this plaza were the city's two most important buildings: the Sun Temple (Templo del Sol) and the Ushnu which remain to this day. It is believed that the city had the shape of a falco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quechua People
Quechua people (, ; ) , Quichua people or Kichwa people may refer to any of the Indigenous peoples of South America who speak the Quechua languages, which originated among the Indigenous people of Peru. Although most Quechua speakers are native to Peru, there are some significant populations in Ecuador, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, and Argentina. The most common Quechua dialect is Southern Quechua. The Kichwa people of Ecuador speak the Kichwa language, Kichwa dialect; in Colombia, the Inga people speak Inga Kichwa. The Quechua word for a Quechua speaker is ''runa'' or ''nuna'' ("person"); the plural is ''runakuna'' or ''nunakuna'' ("people"). "Quechua speakers call themselves Runa -- simply translated, "the people". Some historical Quechua people are: * The Chanka people lived in the Huancavelica Region, Huancavelica, Ayacucho Region, Ayacucho, and Apurímac Region, Apurímac regions of Peru. * The Huanca people of the Junín Region of Peru spoke Quechua before the Incas did. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quechua Language
Quechua (, ), also called (, 'people's language') in Southern Quechua, is an Indigenous languages of the Americas, indigenous language family that originated in central Peru and thereafter spread to other countries of the Andes. Derived from a common ancestral "Proto-Quechuan language, Proto-Quechua" language, it is today the most widely spoken Pre-Columbian era, pre-Columbian language family of the Americas, with the number of speakers estimated at 8–10 million speakers in 2004,Adelaar 2004, pp. 167–168, 255. and just under 7 million from the most recent census data available up to 2011. Approximately 13.9% (3.7 million) of Peruvians speak a Quechua language. Although Quechua began expanding many centuries before the Inca Empire, Incas, that previous expansion also meant that it was the primary language family within the Inca Empire. The Spanish also tolerated its use until the Peruvian War of Independence, Peruvian struggle for independence in the 1780s. As a result, var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
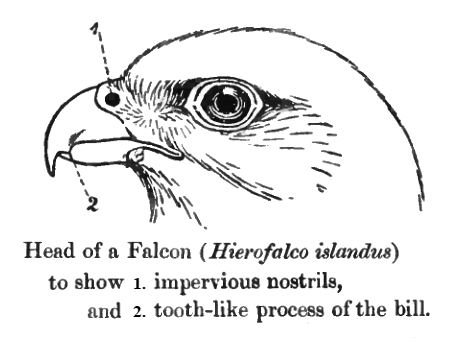
Falcon
Falcons () are birds of prey in the genus ''Falco'', which includes about 40 species. Some small species of falcons with long, narrow wings are called hobbies, and some that hover while hunting are called kestrels. Falcons are widely distributed on all continents of the world except Antarctica, though closely related raptors did occur there in the Eocene. Adult falcons have thin, tapered wings, which enable them to fly at high speed and change direction rapidly. Fledgling falcons, in their first year of flying, have longer flight feathers, which make their configuration more like that of a general-purpose bird such as a broadwing. This makes flying easier while still learning the aerial skills required to be effective hunters like the adults. The falcons are the largest genus in the Falconinae subfamily of Falconidae, which also includes two other subfamilies comprising caracaras and a few other species of "falcons". All these birds kill prey with their beaks, using a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Hawk
The variable hawk (''Geranoaetus polyosoma'') is a polymorphic species of bird of prey in the family Accipitridae. It is widespread and often common in open habitats in western and southern South America, including the Falkland Islands. Its taxonomy is disputed, with some splitting it into the widespread red-backed hawk (''G. polyosoma'') and the Puna hawk or Gurney's hawk (''G. poecilochrous'') of the central and north Andean highlands, but the differences between the two are unclear. Most recent authorities have supported the lumping together of the two hawks although the issue still is controversial.South American Classification Committee (2007). Merge Buteo poecilochrous into B. polyosoma.'. Accessed 10-07-2009South American Classification Committee (2009). '. Accessed 10-07-2009 On the contrary, the rare taxon from the Juan Fernández Islands is relatively distinctive, and possibly worthy of species recognition as the Juan Fernández hawk (''B. exsul'').Jaramillo, A. Burke, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quechuan Languages
Quechua (, ), also called (, 'people's language') in Southern Quechua, is an indigenous language family that originated in central Peru and thereafter spread to other countries of the Andes. Derived from a common ancestral " Proto-Quechua" language, it is today the most widely spoken pre-Columbian language family of the Americas, with the number of speakers estimated at 8–10 million speakers in 2004,Adelaar 2004, pp. 167–168, 255. and just under 7 million from the most recent census data available up to 2011. Approximately 13.9% (3.7 million) of Peruvians speak a Quechua language. Although Quechua began expanding many centuries before the Incas, that previous expansion also meant that it was the primary language family within the Inca Empire. The Spanish also tolerated its use until the Peruvian struggle for independence in the 1780s. As a result, various Quechua languages are still widely spoken today, being co-official in many regions and the most spoken language in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augusto Huaman Velasco
Augusto Huaman Velasco (September 1, 1924 in Lima, Peru – July 20, 1998) was a physician, philanthropist, humanitarian, statesman, lecturer and scientist. Early life Huaman was the son of Gil Huaman who was known as a jurist, landowner and avid traveler. He studied at Nuestra Señora de Guadalupe High School in Lima. He graduated with honors from the Escuela San Fernando and medical school of the Universidad de San Marcos. He followed this with specialization studies in Spain and Germany. In 1942, he received a specialization in tropical diseases at Complutense University in Madrid. Career At Complutense, Huaman met Gregorio Marañon. This meeting interested Huaman in mental illness. Huaman became involved in the recently created Institute of Medical Pathology and grew interested in tropical diseases. During the mid-1980s, Huaman earned a special denomination after an active cooperation at Universitäts Frauenklinik, Kiel, Germany, on pioneer work with laparoscopic appe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jorge Huaman
Jorge is the Spanish and Portuguese form of the given name George. While spelled alike, this name is pronounced very differently in each of the two languages: Spanish ; Portuguese . It is derived from the Greek name Γεώργιος (''Georgios'') via Latin ''Georgius''; the former is derived from (''georgos''), meaning "farmer" or "earth-worker". The Latin form ''Georgius'' had been rarely given in Western Christendom since at least the 6th century. The popularity of the name however develops from around the 12th century, in Occitan in the form '' Jordi'', and it becomes popular at European courts after the publication of the ''Golden Legend'' in the 1260s. The West Iberian form ''Jorge'' is on record in Portugal as the name of Jorge de Lencastre, Duke of Coimbra (1481–1550). List of people with the given name Jorge * Jorge (footballer, born 1939), Brazilian footballer * Jorge (footballer, born 1946), Brazilian footballer * Jorge (Brazilian singer), Brazilian musician and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
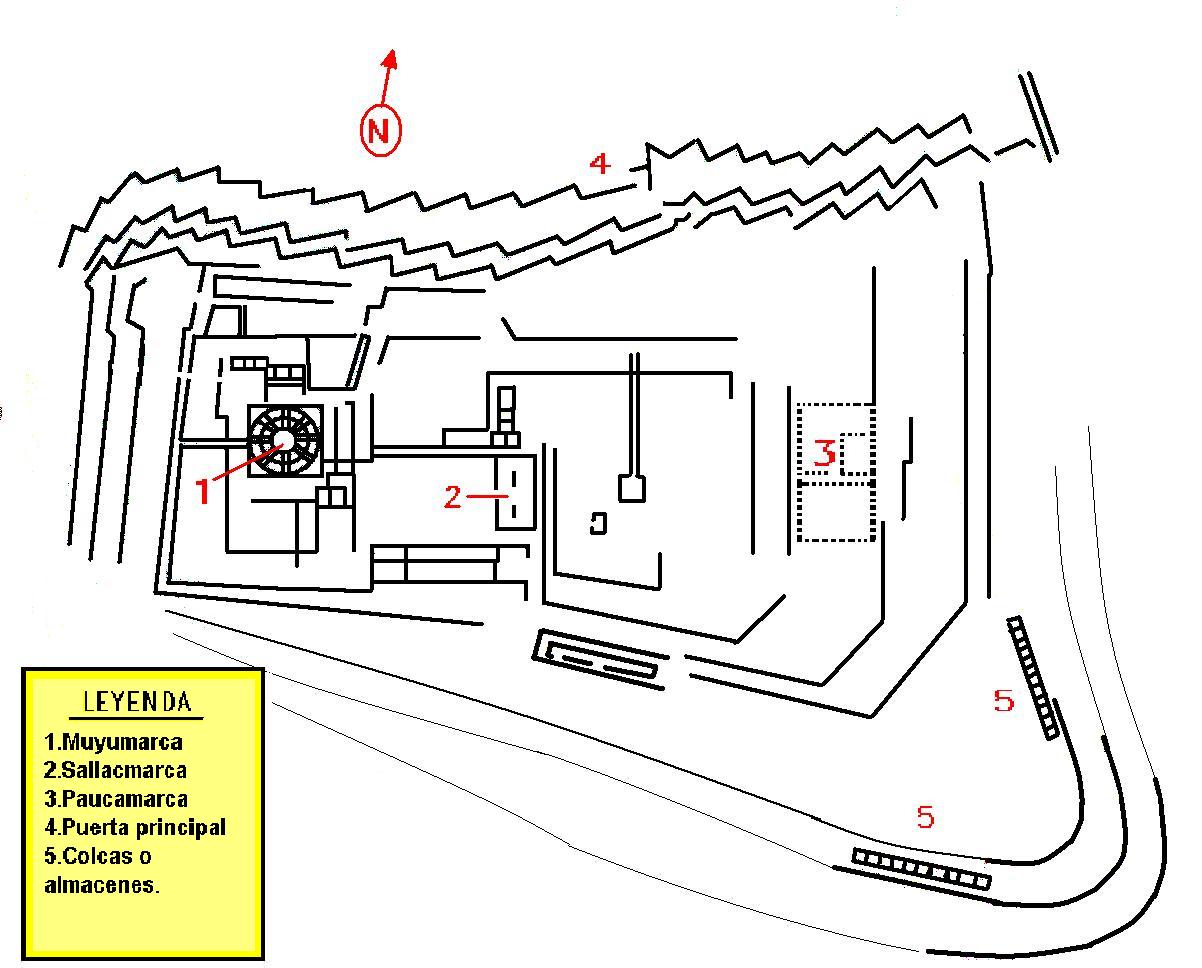
Sacsayhuamán
Sacsayhuamán ( ; ) or Saksaywaman (from Quechuan languages, Quechua , , ) is a citadel on the northern outskirts of the city of Cusco, Peru, the historic capital of the Inca Empire. The site is at an altitude of . The complex was built by the Incas in the 15th century, particularly under Sapa Inca Pachacuti and his successors. Dry stone walls constructed of huge stones were built on the site, with the workers carefully cutting the boulders to fit them together tightly. In 1983, Cusco and Sacsayhuamán together were designated as sites on the UNESCO World Heritage List, for international recognition and protection. The archeological site is now a tourist destination. Description Located on a steep hill that overlooks the city, the fortified complex has a wide view of the valley to the southeast. Archeological studies of surface collections of pottery at Sacsayhuamán indicate that the earliest occupation of the hilltop dates to about 900 CE. According to Inca oral history, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |