|
Hoveyda–Grubbs Catalyst
Grubbs catalysts are a series of transition metal carbene complexes used as catalysts for olefin metathesis. They are named after Robert H. Grubbs, the chemist who supervised their synthesis. Several generations of the catalyst have also been developed. Grubbs catalysts tolerate many functional groups in the alkene substrates, are air-tolerant, and are compatible with a wide range of solvents. For these reasons, Grubbs catalysts have become popular in synthetic organic chemistry. Grubbs, together with Richard R. Schrock and Yves Chauvin, won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in recognition of their contributions to the development of olefin metathesis. First-generation Grubbs catalyst In the 1960s, ruthenium trichloride was found to catalyze olefin metathesis. Processes were commercialized based on these discoveries. These ill-defined but highly active homogeneous catalysts remain in industrial use. The first well-defined ruthenium catalyst was reported in 1992. It was prepared fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Metal Carbene Complex
A transition metal carbene complex is an organometallic compound featuring a divalent carbon ligand, itself also called a carbene. Carbene complexes have been synthesized from most transition metals and f-block metals, using many different synthetic routes such as nucleophilic addition and alpha-hydrogen abstraction. The term carbene ligand is a formalism since many are not directly derived from carbenes and most are much less reactive than lone carbenes. Described often as , carbene ligands are intermediate between alkyls and carbynes . Many different carbene-based reagents such as Tebbe's reagent are used in synthesis. They also feature in catalytic reactions, especially alkene metathesis, and are of value in both industrial heterogeneous and in homogeneous catalysis for laboratory- and industrial-scale preparation of fine chemicals. Classification Metal carbene complexes are often classified into two types. The Fischer carbenes, named after Ernst Otto Fischer, feature s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
One-pot Synthesis
In chemistry a one-pot synthesis is a strategy to improve the efficiency of a chemical reaction in which a reactant is subjected to successive chemical reactions in just one reactor. This is much desired by chemists because avoiding a lengthy separation process and purification of the intermediate chemical compounds can save time and resources while increasing chemical yield. An example of a one-pot synthesis is the total synthesis of tropinone or the Gassman indole synthesis. Sequential one-pot syntheses can be used to generate even complex targets with multiple stereocentres, such as oseltamivir, which may significantly shorten the number of steps required overall and have important commercial implications. A sequential one-pot synthesis with reagents added to a reactor one at a time and without work-up is also called a telescoping synthesis. In one such procedure the reaction of 3-N-tosylaminophenol I with acrolein II affords a hydroxyl substituted quinoline III thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ACS Catalysis
''ACS Catalysis'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal established in 2011 by the American Chemical Society. The journal covers research on all aspects of heterogeneous, homogeneous, and biocatalysis. The editor-in-chief is Cathleen Crudden, who assumed the position in early 2021. The journal received the Association of American Publishers’ PROSE Award for "Best New Journal in Science, Technology & Medicine" in 2013. Types of content The journal publishes the following types of articles: Letters, Articles, Reviews, Perspectives, and Viewpoints. Reviews, Perspectives, and Viewpoints appear mostly on invitation. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: *Chemical Abstracts Service *Current Contents/Physical, Chemical & Earth Sciences *Ei Compendex *Science Citation Index Expanded *Scopus According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor of 11.3. References External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Acs Catalysis Cata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siegfried Blechert
Siegfried Blechert (born 1 March 1946 in Aalborg, Denmark) is a German chemist. Blechert studied chemistry at the University of Hannover, Germany and completed his PhD under the supervision of Ekkehard Winterfeldt in 1974. After a research stay with Pierre Potier in Gif-sur-Yvette, France, in 1981, he finished his habilitation at the University of Hannover in 1982 and there became lecturer in organic chemistry. In 1986 he took up a professorship at the University of Bonn. In 1990 he accepted the Chair of the Organic Chemistry Department at Technische Universität Berlin. His research interests include the development of new catalysts for olefin metathesis In organic chemistry, Olefin Metathesis or Alkene Metathesis is an organic reaction that entails the redistribution of fragments of alkenes (olefins) by the Bond cleavage, scission and regeneration of carbon-carbon double bonds. Because of the ..., novel synthetic methods, and the stereoselective synthesis of natural produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amir H
Emir (; ' (), also transliterated as amir, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or ceremonial authority. The title has a history of use in West Asia, East Africa, West Africa, Central Asia, and South Asia. In the modern era, when used as a formal monarchical title, it is roughly synonymous with "prince", applicable both to a son of a hereditary monarch, and to a reigning monarch of a sovereign principality, namely an emirate. The feminine form is emira ( '), with the same meaning as "princess". Prior to its use as a monarchical title, the term "emir" was historically used to denote a "commander", "general", or "leader" (for example, Amir al-Mu'min). In contemporary usage, "emir" is also sometimes used as either an honorary or formal title for the head of an Islamic, or Arab (regardless of religion) organisation or movement. Qatar and Kuwait are the only i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphine
Phosphine (IUPAC name: phosphane) is a colorless, flammable, highly toxic compound with the chemical formula , classed as a pnictogen hydride. Pure phosphine is odorless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphane (). With traces of present, is spontaneously flammable in air ( pyrophoric), burning with a luminous flame. Phosphine is a highly toxic respiratory poison, and is immediately dangerous to life or health at 50 ppm. Phosphine has a trigonal pyramidal structure. Phosphines are compounds that include and the organophosphines, which are derived from by substituting one or more hydrogen atoms with organic groups. They have the general formula . Phosphanes are saturated phosphorus hydrides of the form , such as triphosphane. Phosphine () is the smallest of the phosphines and the smallest of the phosphanes. History Philippe Gengembre (1764–1838), a student of Lavoisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-heterocyclic Carbene
A persistent carbene (also known as stable carbene) is an organic molecule whose natural resonance structure has a carbon atom with octet rule, incomplete octet (a carbene), but does not exhibit the tremendous instability typically associated with such moieties. The best-known examples and by far largest subgroup are the ''N''-heterocyclic carbenes (NHC) (sometimes called Arduengo carbenes), in which nitrogen atoms flank the formal carbene. Modern theoretical analysis suggests that the term "persistent carbene" is in fact a misnomer. Persistent carbenes do not in fact have a carbene electronic structure in their ground state, but instead an ylide stabilized by Aromaticity, aromatic resonance or steric shielding. Excitation to a carbene structure then accounts for the carbene-like dimerization that some persistent carbenes undergo over the course of days. Persistent carbenes in general, and Arduengo carbenes in particular, are popular ligands in organometallic chemistry. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis acids and bases, Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent bond, covalent to ionic bond, ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acids and bases, Lewis acidic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity (chemistry), reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection requires critical consideration in many practical are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Letters
''Organic Letters'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in organic chemistry. It was established in 1999 and is published by the American Chemical Society. In 2014, the journal moved to a hybrid open access publishing model. The founding editor-in-chief was Amos Smith. The current editor-in-chief is Marisa C. Kozlowski. The journal is abstracted and indexed in: the Science Citation Index Expanded, Scopus, Academic Search Premier, BIOSIS Previews, Chemical Abstracts Service, EMBASE, and MEDLINE MEDLINE (Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online, or MEDLARS Online) is a bibliographic database of life sciences and biomedical information. It includes bibliographic information for articles from academic journals covering medic .... References External links * American Chemical Society academic journals Biweekly journals Organic chemistry journals Academic journals established in 1999 English-language journals {{chem-journal-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
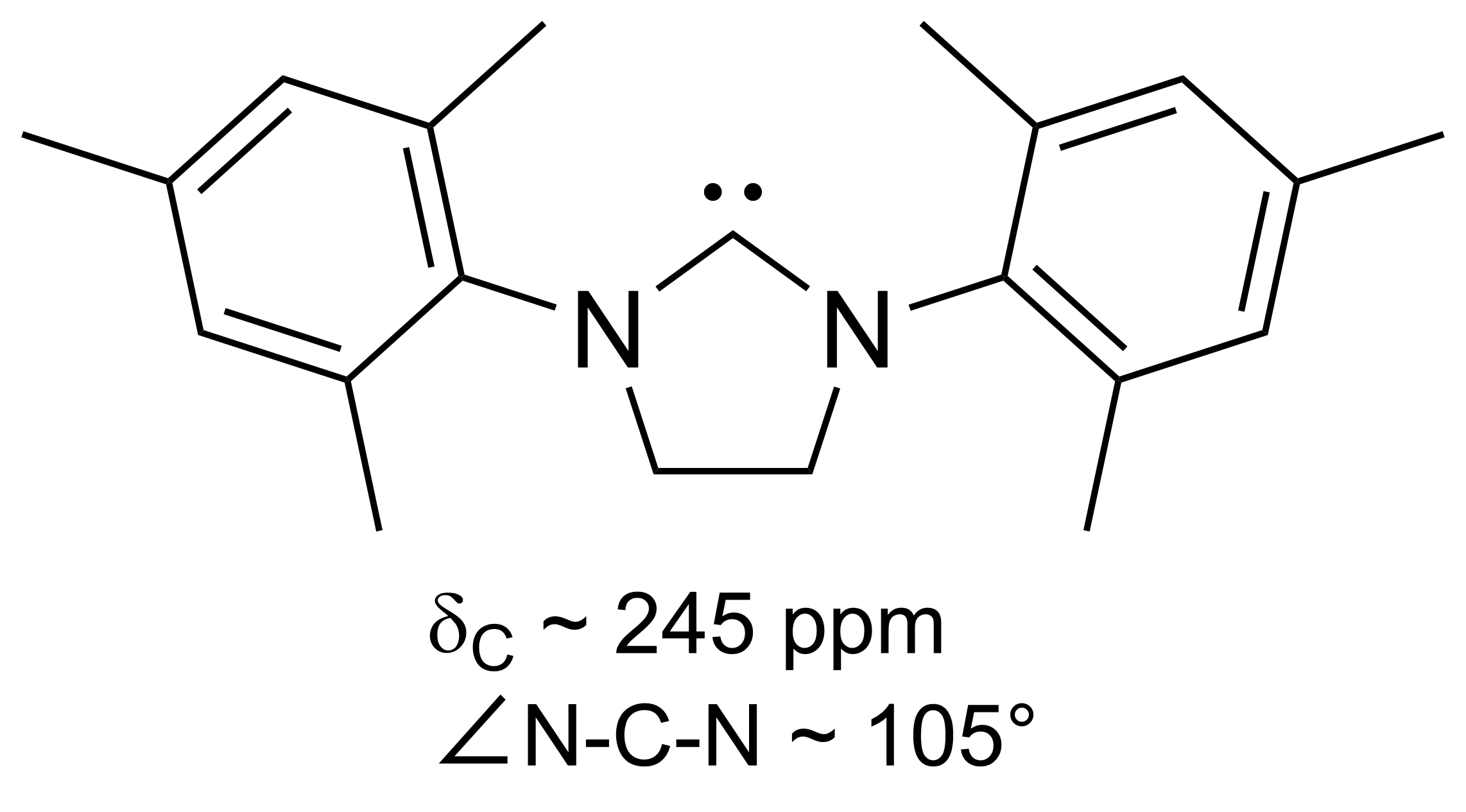
H₂IMes
SIMes (or H2Imes) is an ''N''-heterocyclic carbene. It is a white solid that dissolves in organic solvents. The compound is used as a ligand in organometallic chemistry. It is structurally related to the more common ligand IMes IMes is an abbreviation for an organic compound that is a common ligand in organometallic chemistry. It is an ''N''-heterocyclic carbene (NHC). The compound, a white solid, is often not isolated but instead is generated upon attachment to the me ... but with a saturated backbone (the S of SIMes indicates a saturated backbone). It is slightly more flexible and is a component in Grubbs II. It is prepared by alkylation of trimethylaniline by dibromoethane followed by ring closure and dehydrohalogenation. References {{organic-compound-stub Carbenes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedron Letters
''Tetrahedron Letters'' is a weekly international journal for rapid publication of full original research papers in the field of organic chemistry. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2022 impact factor of 1.8 Indexing ''Tetrahedron Letters'' is indexed in: References See also *''Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron (: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular Face (geometry), faces, six straight Edge (geometry), edges, and four vertex (geometry), vertices. The tet ...'' *'' Tetrahedron: Asymmetry'' Chemistry journals Weekly journals Academic journals established in 1959 Elsevier academic journals {{chem-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |