|
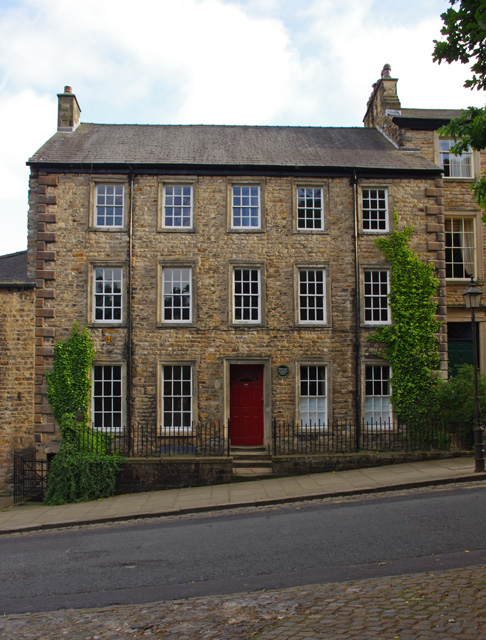
Hornby Castle, Lancashire
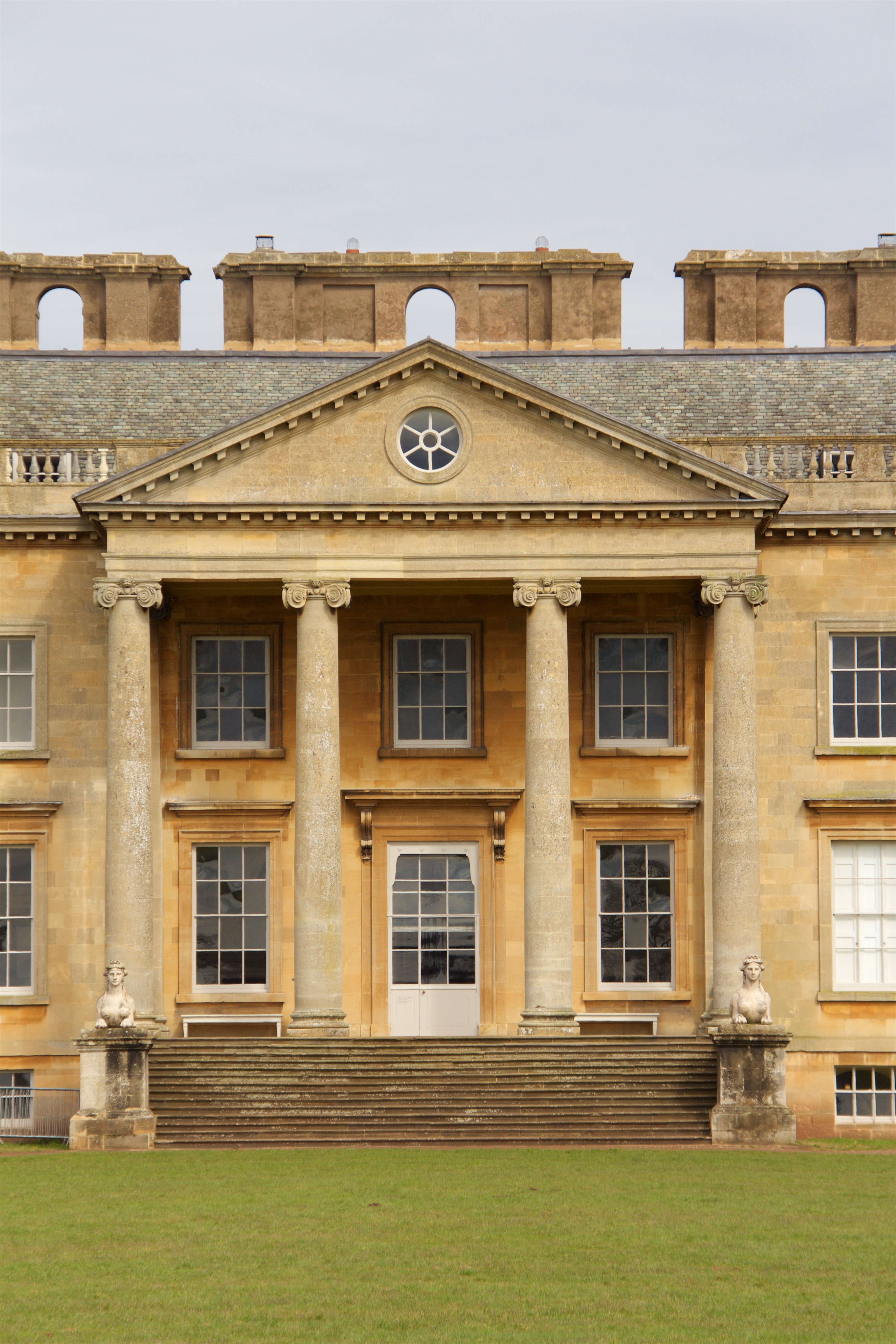
Hornby Castle is a country house, developed from a medieval castle, standing to the east of the village of Hornby in the Lune Valley, Lancashire, England. It occupies a position overlooking the village in a curve of the River Wenning. The house is recorded in the National Heritage List for England as a designated Grade I listed building. History It is thought that the castle was originally built for the Neville family in the 13th century; this is the most likely date of the base of the tower at the back of the castle. In 1285, Margaret de Neville was the owner and "had writ for livery" at Hornby Castle. The polygonal tower rising from this base dates from the 16th century, and was probably built for Sir Edward Stanley, 1st Baron Monteagle. His son, the second Baron Monteagle, took part in suppressing the Rising of the North in 1536. The third Baron Monteagle sold off a lot of the land and on his death in 1581 was succeeded by an only daughter, Elizabet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hornby-with-Farleton
Hornby-with-Farleton is a civil parish in the City of Lancaster in Lancashire Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated ''Lancs'') is a ceremonial county in North West England. It is bordered by Cumbria to the north, North Yorkshire and West Yorkshire to the east, Greater Manchester and Merseyside to the south, and the Irish Sea to ..., England. It had a population of 729 recorded in the 2001 census, increasing marginally to 730 at the 2011 census. The parish is about north-east of Lancaster and consists of two villages: Hornby and Farleton, both on the A683 road. The parish was formed 24 March 1887 from the parishes of "Hornby" and "Farleton". See also * Listed buildings in Hornby-with-Farleton * Hornby Priory References External links Hornby-with-Farleton Parish Council website [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rising Of The North
The Rising of the North of 1569, also called the Revolt of the Northern Earls, Northern Rebellion or the Rebellion of the Earls, was an unsuccessful attempt by Catholicism, Catholic nobles from Northern England to depose Queen Elizabeth I of England and replace her with Mary, Queen of Scots. Background Elizabeth I of England, Elizabeth I succeeded her half-sister Mary I as queen of England in 1558. Elizabeth's accession was disputed due to the questioned legitimacy of the marriage of her parents (Henry VIII and Anne Boleyn), and Elizabeth's own questioned legitimacy due to the Second Succession Act, Act of Succession 1536. Under Henry VIII and his advisor Thomas Cromwell, power was gradually shifted from regional institutions to royal control. This course was encouraged by Elizabeth's counsellors such as William Cecil, 1st Baron Burghley, William Cecil and a policy of centralization was the approach favoured by Elizabeth herself at least in regards to the northern border region. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bradford
Bradford is a city status in the United Kingdom, city in West Yorkshire, England. It became a municipal borough in 1847, received a city charter in 1897 and, since the Local Government Act 1972, 1974 reform, the city status in the United Kingdom, city status has belonged to the larger City of Bradford metropolitan borough. It had a population of 349,561 at the 2011 Census for England and Wales, 2011 census, making it the second-largest subdivision of the West Yorkshire Built-up Area after Leeds, which is approximately to the east. The borough had a population of , making it the List of English districts by population, most populous district in England. Historic counties of England, Historically part of the West Riding of Yorkshire, the city grew in the 19th century as an international centre of Textile manufacture during the Industrial Revolution, textile manufacture, particularly wool. It was a boomtown of the Industrial Revolution, and amongst the earliest Industrialisation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paley And Austin
Sharpe, Paley and Austin are the surnames of architects who practised in Lancaster, England, Lancaster, Lancashire, England, between 1835 and 1946, working either alone or in partnership. The full names of the principals in their practice, which went under various names during its life, are Edmund Sharpe (1809–77); Edward Graham Paley (1823–95), who practised as E. G. Paley; Hubert Austin, Hubert James Austin (1841–1915); Henry Paley, Henry Anderson Paley (1859–1946), son of Edward, usually known as Harry Paley; and, for a very brief period, Geoffrey Langshaw Austin (1884–1971), son of Hubert. The firm's commissions were mainly for buildings in Lancashire and what is now Cumbria, but also in Yorkshire, Cheshire, the West Midlands (region), West Midlands, North Wales, and Hertfordshire. The practice specialised in work on churches; the design of new churches, Victorian restoration, restoring older churches, and making additions or alterations. They also des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Foster (textile Manufacturer)
John Foster (1798–1879) was a British manufacturer of worsted cloth. He was the son of a colliery owner and farmer in Bradford, West Yorkshire. In 1819 he married Ruth Briggs, daughter of a landowner from Queensbury, on the outskirts of Bradford. He set up in business the same year in a warehouse in Queensbury on what would later be the site of the Black Dyke Mills. Initially he would buy yarn and distribute it to handloom weavers who would sell back the finished cloth. By 1827 he was successful enough to build Prospect House as a family home. In 1828 he rented Cannon Mill for wool spinning, prior to erecting the first part of Black Dyke Mills in 1835 on land acquired from his father-in-law. By 1851 Black Dyke Mills was dominating the Queensbury landscape and at the Great Exhibition of that year he was awarded first prize for alpaca and mohair fabrics and the gold medal for yarns. In the 1870s he bought and renovated Hornby Castle, Lancashire, to which he retired. On his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Heritage
English Heritage (officially the English Heritage Trust) is a charity that manages over 400 historic monuments, buildings and places. These include prehistoric sites, a battlefield, medieval castles, Roman forts, historic industrial sites, Listed building, listed ruins, and architecturally notable English country houses. The charity states that it uses these properties to "bring the story of England to life for over 10 million people each year". Within its portfolio are Stonehenge, Dover Castle, Tintagel Castle, and the "best-preserved" parts of Hadrian's Wall. English Heritage also manages the London blue plaque scheme, which links influential historical figures to particular buildings. When originally formed in 1983, English Heritage was the operating name of an executive non-departmental public body of the Her Majesty's Government, British Government, officially titled the Historic Buildings and Monuments Commission for England, that ran the national system of heritage prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portico
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cultures, including most Western cultures. Porticos are sometimes topped with pediments. Palladio was a pioneer of using temple-fronts for secular buildings. In the UK, the temple-front applied to The Vyne, Hampshire, was the first portico applied to an English country house. A pronaos ( or ) is the inner area of the portico of a Greek or Roman temple, situated between the portico's colonnade or walls and the entrance to the '' cella'', or shrine. Roman temples commonly had an open pronaos, usually with only columns and no walls, and the pronaos could be as long as the ''cella''. The word ''pronaos'' () is Greek for "before a temple". In Latin, a pronaos is also referred to as an ''anticum'' or ''prodomus''. The pronaos of a Greek a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
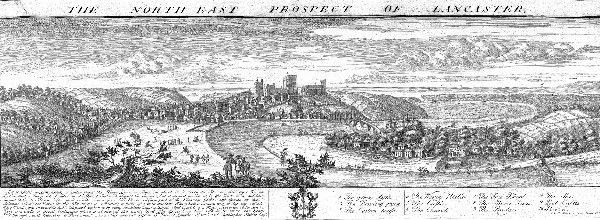
Lancaster, Lancashire
Lancaster (, ) is a city in Lancashire, England, and the main cultural hub, economic and commercial centre of City of Lancaster district. The city is on the River Lune, directly inland from Morecambe Bay. Lancaster is the county town, although Lancashire County Council has been based at County Hall, Preston, County Hall in Preston, Lancashire, Preston since its formation in 1889. The city's long history is marked by Lancaster Roman Fort, Lancaster Castle, Lancaster Priory, Lancaster Priory Church, Lancaster Cathedral and the Ashton Memorial. It is the seat of Lancaster University and has a campus of the University of Cumbria. It had a population of 52,234 in the 2011 census, compared to the district, which had a population of 138,375. The House of Lancaster was a branch of the List of English monarchs, English royal family. The Duchy of Lancaster still holds large estates on behalf of Charles III, who is the Duke of Lancaster. The Port of Lancaster and the 18th-century Lancas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Sheriff Of Lancashire
The High Sheriff of Lancashire is an ancient office, now largely ceremonial, granted to Lancashire, a county in North West England. High Shrievalties are the oldest secular titles under the Crown, in England and Wales. The High Sheriff of Lancashire is the representative of the monarch in the county, and is the "Keeper of The King's Peace" in the county, executing judgements of the High Court through an Under Sheriff. Throughout the Middle Ages, the High Sheriff was a powerful political position; the sheriffs were responsible for the maintenance of law and order and various other roles. Some of its powers were relinquished in 1547 as the Lord Lieutenant of Lancashire was instated to deal with military duties. It was in 1908 under King Edward VII of the United Kingdom that the Lord Lieutenant position became more senior than the High Sheriff. Since that time the High Sheriff has broadly become an honorific title, with many of its previous roles having been taken up by High Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wennington Hall
Wennington Hall is a former country house in Wennington, a village in the City of Lancaster district in Lancashire, England. The house is a Grade II listed building and from 1940 until 2022 was used as a school, at first by the Quaker boarding school Wennington School before its move to Yorkshire, then by Lancashire County Council. History In its early history, Wennington Hall was the seat of William de Wennington. and in the 14th century, it passed to the Morley family. In 1674 the hall was sold to Henry Marsden, MP for Clitheroe. It descended to Henry Marsden, who lived at the hall with his younger brother John, known as "Silly Marsden", and their aunt. Henry died in 1780 from alcoholism and John was induced by his guardian aunt and her ambitious husband to sell the hall and buy Hornby Castle, Lancashire. Wennington was bought in 1788 by the Rev Anthony Lister, who took the surname Marsden. The hall was later sold to Richard Saunders in 1841. The present building on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Wemyss, 5th Earl Of Wemyss
James Wemyss, 5th Earl of Wemyss (30 August 169921 March 1756), was the son of David Wemyss, 4th Earl of Wemyss. In Edinburgh Wemyss lived in Riddles Court off the Royal Mile which retains much of its 17th century interior.Grant's Old and New Edinburgh vol.2 p.282 On 17 September 1720, he married Janet Charteris, heiress of the great Francis Charteris (rake), Colonel Francis Charteris, and they had four children: *David Wemyss, 6th Earl of Wemyss (1721–1787) *Francis Charteris, 7th Earl of Wemyss (1723–1808) *James Wemyss (1726–1786), James Wemyss (1726–1786) *Frances Wemyss (died 1789) In 1730, he was key to securing the release his father-in-law from Newgate Prison after he was sentenced to hang for the capital felony of rape. His second son, Francis, the seventh Earl, legally changed his name to Charteris, his mother's maiden name, on his inheritance of Colonel Charteris's estates and fortune built upon gambling. References 1699 births 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Charteris (rake)
Colonel Francis Charteris (''baptised'' 4 April 1675 – 24 February 1732), nicknamed "The Rape-Master General",Antony E. Simpson (2004). was a Scottish soldier and adventurer who earned a substantial sum of money through gambling and the South Sea Bubble. He was convicted of raping a servant in 1730 and sentenced to death, but was subsequently pardoned, before dying of natural causes shortly afterwards. Early life Charteris was born at Edinburgh in about 1675, the son of John Charteris (died 1691 dead by 1702), a magistrate, and his wife, Mary, who was possibly the daughter of Sir Francis Kinloch, 1st Baronet. His family were land-holders and owned property in Amisfield, near Dumfries. Even before his conviction, he was notorious and despised by many in London as an archetypal rake. He had a serial military career, being dismissed from service four times; the third time in the Southern Netherlands by the Duke of Marlborough, for cheating at cards, and the fourth time by Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |