|
Holašovice
Holašovice (, or ''Holschowitz'') is a small historic village located in the south of the Czech Republic, 16 kilometres west of České Budějovice. Village belongs to the municipality Jankov. To the south lies the protected landscape area of Blanský Forest. The village was deserted after the Second World War, allowing its medieval plan and vernacular buildings in the South Bohemian Folk or Rural Baroque style to remain intact. It was restored and repopulated from 1990, and it was designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1998 because of its exceptional preservation of a traditional Baroque-era village. History Holašovice is first mentioned in 1263. In 1292, King Wenceslaus II gave the village and several others to the Cistercian monastery of Vyšší Brod. It remained the property of the monastery until 1848. Between 1520 and 1525, Holašovice was nearly wiped out by the bubonic plague. Only two of its inhabitants survived. A column erected over the plague grave a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jankov (České Budějovice District)
Jankov is a municipality and village in České Budějovice District in the South Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 400 inhabitants. The village of Holašovice within the municipality is protected as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Administrative division Jankov consists of two municipal parts (in brackets population according to the 2021 census): *Jankov (173) * Holašovice (204) Etymology The name is derived from the personal name Janek (a diminutive of Jan), meaning "Janek's (court)". Geography Jankov is located about west of České Budějovice. It lies in the Bohemian Forest Foothills. The highest point is the Švelhán hill at above sea level. There are several fishponds in the northern part of the municipal territory. Most of the municipality lies within the Blanský les Protected Landscape Area. History The first written mention of Jankov is from 1379. Until 1850, it belonged to the Český Krumlov estate and shared its owners. Until the end World W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Heritage Sites In The Czech Republic
The first UNESCO World Heritage Sites on the territory of the present Czech Republic were inscribed at the 16th Session of the World Heritage Committee, held in Santa Fe, United States in 1992, when the country was part of the Czech and Slovak Federative Republic (also known as Czechoslovakia). At this session, three sites were added: the Historic Centre of Prague, the Historic Centre of Český Krumlov and the Historic Centre of Telč. With the dissolution of Czechoslovakia on 1 January 1993, the country was split into the Czech Republic and Slovakia. The Czech Republic officially adopted the convention on 26 March 1993, inheriting those three sites. , there are 17 sites inscribed on the list and a further 13 on the tentative list. The most recent addition is Žatec and the Landscape of Saaz Hops, added in 2023. The Erzgebirge/Krušnohoří Mining Region, the three spa towns in the Great Spa Towns of Europe site and the Jizera Mountains forest as an extension to the Anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
České Budějovice District
České Budějovice District () is a Okres, district in the South Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. Its capital is the city of České Budějovice. Administrative division České Budějovice District is divided into three Districts of the Czech Republic#Municipalities with extended competence, administrative districts of municipalities with extended competence: České Budějovice, Trhové Sviny and Týn nad Vltavou. List of municipalities Cities and towns are marked in bold and market towns in ''italics'': Adamov (České Budějovice District), Adamov - Bečice (České Budějovice District), Bečice - Borek (České Budějovice District), Borek - Borovany - Borovnice (České Budějovice District), Borovnice - Boršov nad Vltavou - Bošilec - Branišov - Břehov - Čakov (České Budějovice District), Čakov - Čejkovice (České Budějovice District), Čejkovice - Čenkov u Bechyně - České Budějovice - Chotýčany - Chrášťany (České Budějovice District), Chrá� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Bohemian Region
The South Bohemian Region () is an administrative unit (''Regions of the Czech Republic, kraj'') of the Czech Republic, located mostly in the southern part of its historical land of Bohemia, with a small part in southwestern Moravia. The western part of the South Bohemian Region is former Prácheňsko, a huge archaic region with distinctive features with its capital, Písek. In 2011, there were 624 municipalities in the region, whereof 54 had a status of a town. The region borders (from the west clockwise) the regions of Plzeň Region, Plzeň, Central Bohemian Region, Central Bohemian, Vysočina Region, Vysočina and South Moravian Region, South Moravian. To the south, it borders Austria (Lower Austria and Upper Austria) and Germany (Bavaria). Until 30 May 2001, the region was named as or , after its capital, České Budějovice. Due to its geographical location and natural surroundings the region belongs to the first settlements that appeared in the distant past. Over the past ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cistercian
The Cistercians (), officially the Order of Cistercians (, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint Benedict, as well as the contributions of the highly influential Bernard of Clairvaux, known as the Latin Rule. They are also known as Bernardines, after Bernard of Clairvaux, Saint Bernard, or as White Monks, in reference to the colour of their cowl, as opposed to the black cowl worn by Benedictines. The term ''Cistercian'' derives from ''Cistercium,'' the Latin name for the locale of Cîteaux, near Dijon in eastern France. It was here that a group of Benedictine monks from the monastery of Molesme Abbey, Molesme founded Cîteaux Abbey in 1098. The first three abbots were Robert of Molesme, Alberic of Cîteaux and Stephen Harding. Bernard helped launch a new era when he entered the monastery in the early 1110s with 30 companions. By the end of the 12th century, the ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Of Nepomuk
John of Nepomuk (or John Nepomucene) (; ; ) ( 1345 – 20 March 1393) was a saint of Bohemia (a western part of what is now the Czech Republic) who was drowned in the Vltava river at the behest of King Wenceslaus IV of Bohemia. Later accounts state that he was the confessor of the queen of Bohemia and refused to divulge the secrets of the confessional. On the basis of this account, John of Nepomuk is considered the first martyr of the Seal of the Confessional and the Catholic Church, Seal of the Confessional, a patron against defamation, calumnies and, because of the manner of his death, a protector from floods and drowning. Basic biographical information Jan z Pomuku came from the small market town of ''Pomuk'' (later renamed Nepomuk) in Bohemia, now in the Czech Republic, which belonged to the nearby Cistercian abbey. Born in the 1340s, his father was called ''Velflín,'' while his mother is unknown. His father's name was probably derived from the German name ''Wolfgang''. Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech Language
Czech ( ; ), historically known as Bohemian ( ; ), is a West Slavic language of the Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script. Spoken by over 12 million people including second language speakers, it serves as the official language of the Czech Republic. Czech is closely related to Slovak, to the point of high mutual intelligibility, as well as to Polish to a lesser degree. Czech is a fusional language with a rich system of morphology and relatively flexible word order. Its vocabulary has been extensively influenced by Latin and German. The Czech–Slovak group developed within West Slavic in the high medieval period, and the standardization of Czech and Slovak within the Czech–Slovak dialect continuum emerged in the early modern period. In the later 18th to mid-19th century, the modern written standard became codified in the context of the Czech National Revival. The most widely spoken non-standard variety, known as Common Czech, is based on the vernacular of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
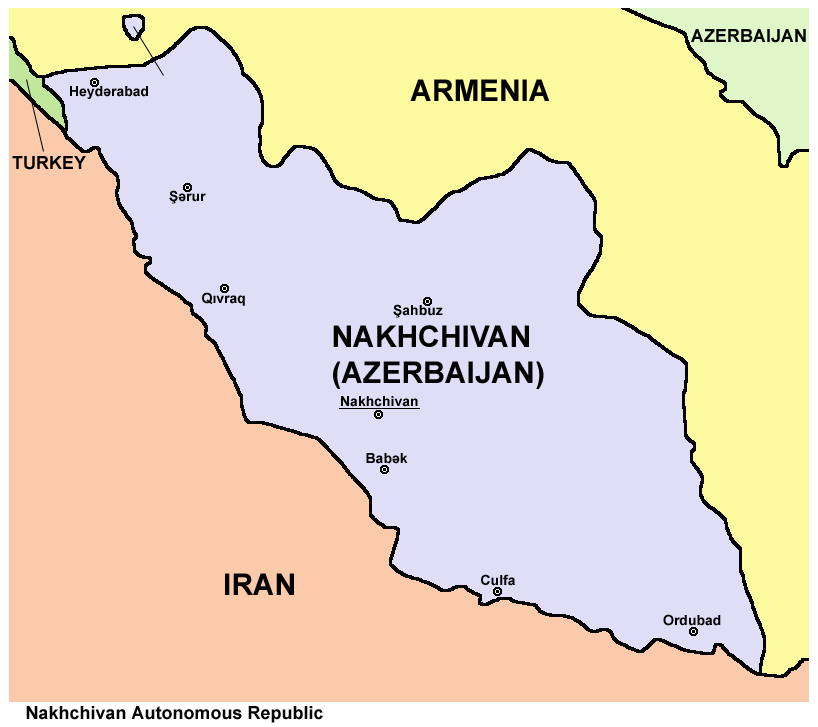
Enclave
An enclave is a territory that is entirely surrounded by the territory of only one other state or entity. An enclave can be an independent territory or part of a larger one. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to denote a territory that is only partly surrounded by another state. Enclaves that are not part of a larger territory are not exclaves, for example Lesotho (enclaved by South Africa), and San Marino and Vatican City (both enclaved by Italy) are enclaved sovereign states. An exclave is a portion of a state or district geographically separated from the main part, by some surrounding alien territory. Many exclaves are also enclaves, but an exclave surrounded by the territory of more than one state is not an enclave. The Azerbaijani exclave of Nakhchivan is an example of an exclave that is not an enclave, as it borders Armenia, Iran, and Turkey. Semi-enclaves and semi-exclaves are areas that, except for possessing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Language
German (, ) is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, mainly spoken in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe. It is the majority and Official language, official (or co-official) language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein. It is also an official language of Luxembourg, German-speaking Community of Belgium, Belgium and the Italian autonomous province of South Tyrol, as well as a recognized national language in Namibia. There are also notable German-speaking communities in other parts of Europe, including: Poland (Upper Silesia), the Czech Republic (North Bohemia), Denmark (South Jutland County, North Schleswig), Slovakia (Krahule), Germans of Romania, Romania, Hungary (Sopron), and France (European Collectivity of Alsace, Alsace). Overseas, sizeable communities of German-speakers are found in the Americas. German is one of the global language system, major languages of the world, with nearly 80 million native speakers and over 130 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city and state. Austria is bordered by Germany to the northwest, the Czech Republic to the north, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The country occupies an area of and has Austrians, a population of around 9 million. The area of today's Austria has been inhabited since at least the Paleolithic, Paleolithic period. Around 400 BC, it was inhabited by the Celts and then annexed by the Roman Empire, Romans in the late 1st century BC. Christianization in the region began in the 4th and 5th centuries, during the late Western Roman Empire, Roman period, followed by the arrival of numerous Germanic tribes during the Migration Period. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total land area of Germany, and with over 13.08 million inhabitants, it is the list of German states by population, second most populous German state, behind only North Rhine-Westphalia; however, due to its large land area, its population density is list of German states by population density, below the German average. Major cities include Munich (its capital and List of cities in Bavaria by population, largest city, which is also the list of cities in Germany by population, third largest city in Germany), Nuremberg, and Augsburg. The history of Bavaria includes its earliest settlement by Iron Age Celts, Celtic tribes, followed by the conquests of the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of Ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |