|
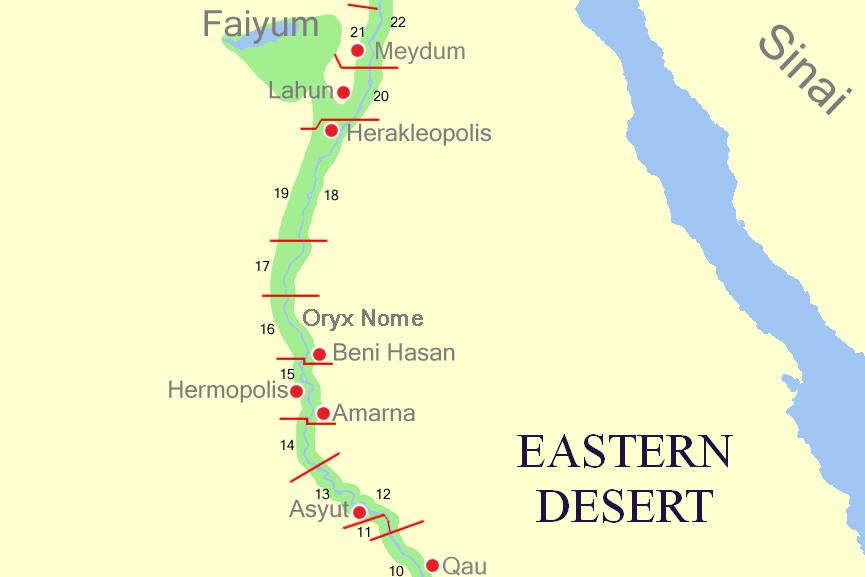
Hermopolis
Hermopolis (or ''Hermopolis Magna'') was a major city in antiquity, located near the boundary between Lower and Upper Egypt. Its Egyptian name ''Khemenu'' derives from the eight deities (the Ogdoad) said to reside in the city. A provincial capital since the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Hermopolis developed into a major city of Roman Egypt, and an early Christian center from the third century. It was abandoned after the Muslim conquest of Egypt but was restored as both a Latin Catholic (meanwhile suppressed) and a Coptic Orthodox titular see. Its remains are located near the modern town of el-Ashmunein (from the Coptic name) in Mallawi, Minya Governorate, Egypt. Name The common English name is Hermopolis ( ''Hermoúpolis'' "the City of Hermes", also ''Hermopolis Magna'', ''Hermoû pólis megálẽ'', (reconstructed pronunciation), Egyptological pronunciation: "Khemenu"; ''Shmūn'', and thus ). ''Khemenu'' (), the Egyptian language name of the city, means "Eight-Town", afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damanhur
Damanhur ( ', ) is a city in Lower Egypt, and the capital of the Beheira Governorate. It is located northwest of Cairo, and E.S.E. of Alexandria, in the middle of the western Nile Delta. Damanhur is a historic city, whose history can be dated back to the Old Kingdom of Egypt. The modern city has also absorbed the ancient villages ''Shubra al-Jadida'' (, ), ''Tāmus'' (), ''Askanida'' () and ''Chortaso'' (, ). Etymology The city's modern Arabic name comes from Coptic p-Timinhor (, ), which in turn is derived from , also attested in Aramaic (). The Greeks called the city Hermopolis Mikra (). The name of the city suggests that Horus, whom Greeks equated with Apollo, was worshipped as the chief deity. However, the Greek name for the town, Hermopolis Mikra, suggests that Hermes/ Thoth was the local god. This discrepancy is possibly due to a misinterpretation that persisted even after the Greeks had gained a better understanding of Egypt. History In ancient Egypt, the city was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nome (Egypt)
A nome (, from , ''nomós'', "district") was a territorial division in ancient Egypt. Each nome was ruled by a nomarch (, "Great Chief"). The number of nomes changed through the various periods of the history of ancient Egypt. Etymology The term ''nome'' comes from Ancient Greek νομός ''nomós'' meaning "pasture" extended to "dwelling" and "district"; the Ancient Egyptian term was ( /sɛpɑt/). Today's use of the Ancient Greek rather than the Ancient Egyptian term came about during the Ptolemaic period, when the use of Greek was widespread in Egypt. The availability of Greek records on Egypt influenced the adoption of Greek terms by later historians. History Dynastic Egypt The division of ancient Egypt into nomes can be traced back to prehistoric Egypt (before 3100 BC). These nomes originally existed as autonomous city-states, but later began to unify. According to ancient tradition, the ruler Menes completed the final unification. Not only did the division into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minya Governorate
Minya ( ') is one of the governorates of Upper Egypt. Its capital city, Minya, is located on the left bank of the Nile River. Etymology The name originates from the chief city of the governorate, originally known in Sahidic Coptic as ''Tmoone'' and in Bohairic as ''Thmonē'', meaning “the residence”, in reference to a monastery formerly in the area. The name may also originate from the city's name in Egyptian ''Men'at Khufu''. Overview The rate of poverty is more than 60% in this governorate, where the total population is nearly 6 million. Recently the government has provided some assistance via social safety networks, specifically, some financial assistance to residents with disabilities, and job opportunities for them and others. The funding has been coordinated by the country's Ministry of Finance and with assistance from international organizations. Municipal divisions The governorate is divided into municipal divisions with a total estimated population as of Janua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoth
Thoth (from , borrowed from , , the reflex of "[he] is like the ibis") is an ancient Egyptian deity. In art, he was often depicted as a man with the head of an African sacred ibis, ibis or a baboon, animals sacred to him. His feminine counterpart was Seshat, and his wife was Maat. He was the god of the Moon, wisdom, knowledge, writing, hieroglyphs, science, magic, art and judgment. Thoth's chief Egyptian temple, temple was located in the city of Hermopolis ( , Egyptological pronunciation: Khemenu, ). Later known as in Egyptian Arabic, the Temple of Thoth was mostly destroyed before the beginning of the Christian era. Its very large pronaos was still standing in 1826, but was demolished and used as fill for the foundation of a sugar factory by the mid-19th century. Thoth played many vital and prominent roles in Egyptian mythology, such as maintaining the universe, and being one of the two deities (the other being Maat, Ma'at) who stood on either side of Ra, Ra's solar barq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heptanomis
Middle Egypt () is the section of land between Lower Egypt (the Nile Delta) and Upper Egypt, stretching upstream from Asyut in the south to Memphis in the north. At the time, Ancient Egypt was divided into Lower and Upper Egypt, though Middle Egypt was technically a subdivision of Upper Egypt. It was not until the 19th century that archaeologists felt the need to divide Upper Egypt in two. As a result, they coined the term "Middle Egypt" for the stretch of river between Cairo and the Qena Bend. It was also associated with a region termed " Heptanomis" (; Greek: , in Ptol. iv. 5. § 55; more properly or , in Dionysius Periegetes 251; and sometimes ; meaning "Seven Nomes", a " nome" being a subdivision of ancient Egypt), generally as the district which separates the Thebaïd from the Delta. Middle Egypt today can be identified as the part of the Nile Valley that, while geographically part of Upper Egypt, is culturally closer to Lower Egypt. For instance, in terms of language, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Egypt
Roman Egypt was an imperial province of the Roman Empire from 30 BC to AD 642. The province encompassed most of modern-day Egypt except for the Sinai. It was bordered by the provinces of Crete and Cyrenaica to the west and Judaea, later Arabia Petraea, to the East. Egypt was conquered by Roman forces in 30 BC and became a province of the new Roman Empire upon its formation in 27 BC. Egypt came to serve as a major producer of grain for the empire and had a highly developed urban economy. It was by far the wealthiest Roman province outside of Italy. The population of Roman Egypt is unknown, although estimates vary from . Alexandria, its capital, was the largest port and second largest city of the Roman Empire. Three Roman legions garrisoned Egypt in the early Roman imperial period, with the garrison later reduced to two, alongside formations of the Roman army. The major town of each '' nome'' (administrative region) was known as a metropolis and gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Egypt
Lower Egypt ( ') is the northernmost region of Egypt, which consists of the fertile Nile Delta between Upper Egypt and the Mediterranean Sea, from El Aiyat, south of modern-day Cairo, and Dahshur. Historically, the Nile River split into seven branches of the delta in Lower Egypt. Lower Egypt was divided into nomes and began to advance as a civilization after 3600 BC. Today, it contains two major channels that flow through the delta of the Nile River – Mahmoudiyah Canal (ancient Agathos Daimon) and Muways Canal (, "waterway of Moses"). Name In Ancient Egyptian, Lower Egypt was known as ''mḥw'' which means "north". Later on, during Antiquity and the Middle Ages, Greeks and Romans called it ''Κάτω Αἴγυπτος'' or ''Aegyptus Inferior'' both meaning "Lower Egypt", but Copts carried on using the old name related to the north – ''Tsakhet'' () or ''Psanemhit'' () meaning the "Northern part". It was further divided into a number of regions or nomes () – '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ogdoad (Egyptian)
In Egyptian mythology, the Ogdoad ( "the Eightfold"; , a plural nisba of "eight") were eight primordial deities worshiped in Hermopolis. The earliest certain reference to the Ogdoad is from the Eighteenth Dynasty, in a dedicatory inscription by Hatshepsut at the Speos Artemidos. Texts of the Late Period describe them as having the heads of frogs (male) and serpents (female), and they are often depicted in this way in reliefs of the last dynasty, the Ptolemaic Kingdom. Names The eight deities were arranged in four male–female pairs. The names have the same meanings and differ only slightly. Attributes File:Kek god.svg, Kek and other male members File:Kauket.svg, Kauket and other female members File:Heh as chaos.svg, Nu File:Heh.svg, Ḥeḥ File:Amun post Amarna (azure skin color).svg, Amun File:Amunet.svg, Amunet The names of Nu and Naunet are written with the determiners for sky and water, and it seems clear that they represent the primordial waters. � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermes
Hermes (; ) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology considered the herald of the gods. He is also widely considered the protector of human heralds, travelers, thieves, merchants, and orators. He is able to move quickly and freely between the worlds of the mortal and the divine aided by his winged sandals. Hermes plays the role of the psychopomp or "soul guide"—a conductor of souls into the afterlife. In myth, Hermes functions as the emissary and messenger of the gods, and is often presented as the son of Zeus and Maia, the Pleiad. He is regarded as "the divine trickster", about which the '' Homeric Hymn to Hermes'' offers the most well-known account. Hermes's attributes and symbols include the herma, the rooster, the tortoise, satchel or pouch, talaria (winged sandals), and winged helmet or simple petasos, as well as the palm tree, goat, the number four, several kinds of fish, and incense. However, his main symbol is the ''caduceus'', a wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hare Nome
The Hare nome, also called the Hermopolite nome ( "Cape hare") was one of the 42 '' nomoi'' (administrative divisions) in ancient Egypt; more precisely, it was the 15th nome of Upper Egypt. Wolfram Grajetzki, ''The Middle Kingdom of ancient Egypt: history, archaeology and society''. London, Duckworth Egyptology, 2006, pp. 109-11 The Hare nome's main city was Khemenu (later Hermopolis Magna, and the modern el-Ashmunein) in Middle Egypt. The local main deity was Thoth, though the inscriptions on the White Chapel of Senusret I links this nome with the cult of Bes and Unut. History The Hare nome was already recognized during the 4th Dynasty of the Old Kingdom as shown by the triad statue of pharaoh Menkaure, Hathor, and an anthropomorphized-deified depiction of the nome. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Egypt
Upper Egypt ( ', shortened to , , locally: ) is the southern portion of Egypt and is composed of the Nile River valley south of the delta and the 30th parallel North. It thus consists of the entire Nile River valley from Cairo south to Lake Nasser (formed by the Aswan High Dam). Name In ancient Egypt, Upper Egypt was known as ''tꜣ šmꜣw'', literally "the Land of Reeds" or "the Sedgeland", named for the sedges that grow there. In Biblical Hebrew it was known as and in Akkadian it was known as . Both names originate from the Egyptian '' pꜣ- tꜣ- rsj'', meaning "the southern land". In Arabic, the region is called Sa'id or Sahid, from صعيد meaning "uplands", from the root صعد meaning to go up, ascend, or rise. Inhabitants of Upper Egypt are known as Sa'idis and they generally speak Sa'idi Egyptian Arabic. Geography Upper Egypt is between the Cataracts of the Nile beyond modern-day Aswan, downriver (northward) to the area of El-Ayait, which places modern- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebaid
The Thebaid or Thebais (, ''Thēbaïs'') was a region in ancient Egypt, comprising the 13 southernmost nome (Egypt), nomes of Upper Egypt, from Abydos, Egypt, Abydos to Aswan. Pharaonic history The Thebaid acquired its name from its proximity to the ancient Egyptian capital of Thebes, Egypt, Thebes (Luxor). During the Ancient Egyptian dynasties this region was dominated by Thebes and its priesthood at the temple of Amun at Karnak. In Ptolemaic dynasty, Ptolemaic Egypt, the Thebaid formed a single administrative district under the ''Epistrategos'' of Thebes, who was also responsible for overseeing navigation in the Red Sea and the Indian Ocean. The capital of Ptolemais in Thebaide, Ptolemaic Thebaid was Ptolemais Hermiou, a Hellenistic colony on the Nile which served as the center of royal political and economic control in Upper Egypt. Roman province(s) During the Roman Empire, Diocletian created the province of ''Thebais'', guarded by the Roman legion, legions Legio I Maxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |