|
Hepatic Artery Proper
The hepatic artery proper (also proper hepatic artery) is the artery that supplies the liver and gallbladder. It raises from the common hepatic artery, a branch of the celiac artery. Structure The hepatic artery proper arises from the common hepatic artery and runs alongside the portal vein and the common bile duct to form the portal triad. A branch of the common hepatic arterythe gastroduodenal artery gives off the small supraduodenal artery to the duodenal bulb. Then the right gastric artery comes off and runs to the left along the lesser curvature of the stomach to meet the left gastric artery, which is a branch of the celiac trunk. It subsequently bifurcates into the right and left hepatic arteries. Variant anatomy Of note, the right and left hepatic arteries may demonstrate variant anatomy. A misplaced right hepatic artery may arise from the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) and a misplaced left hepatic artery may arise from the left gastric artery. The cystic artery g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Hepatic Artery
The common hepatic artery is a short blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, pylorus of the stomach, duodenum, pancreas, and gallbladder. It arises from the celiac artery and has the following branches: Additional images File:Common hepatic artery.jpg, Common hepatic artery and its branches including hepatic artery proper and right gastric artery (pyloric artery) References External links * - "Stomach, Spleen and Liver The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...: Contents of the Hepatoduodenal ligament" * {{Authority control Arteries of the abdomen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duodenal Bulb
The duodenal bulb (also ampulla of duodenum, duodenal ampulla, or duodenal cap) is the initial, dilated portion of (the superior part of) the duodenum just distal to the stomach; it begins at the pylorus and ends at the neck of the gallbladder. It is normally about 5 centimeters long. Structure Relations It is located posterior to the liver and the gallbladder and superior to the pancreatic head. The gastroduodenal artery, portal vein, and common bile duct are situated posterior to the duodenal bulb. The distal part of the bulb is located retroperitoneally. It is located immediately distal to the pyloric sphincter The pylorus ( or ) connects the stomach to the duodenum. The pylorus is considered as having two parts, the ''pyloric antrum'' (opening to the body of the stomach) and the ''pyloric canal'' (opening to the duodenum). The ''pyloric canal'' ends a .... Clinical significance The duodenal bulb is the site of duodenal ulcer occurrence. Duodenal ulcers are more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
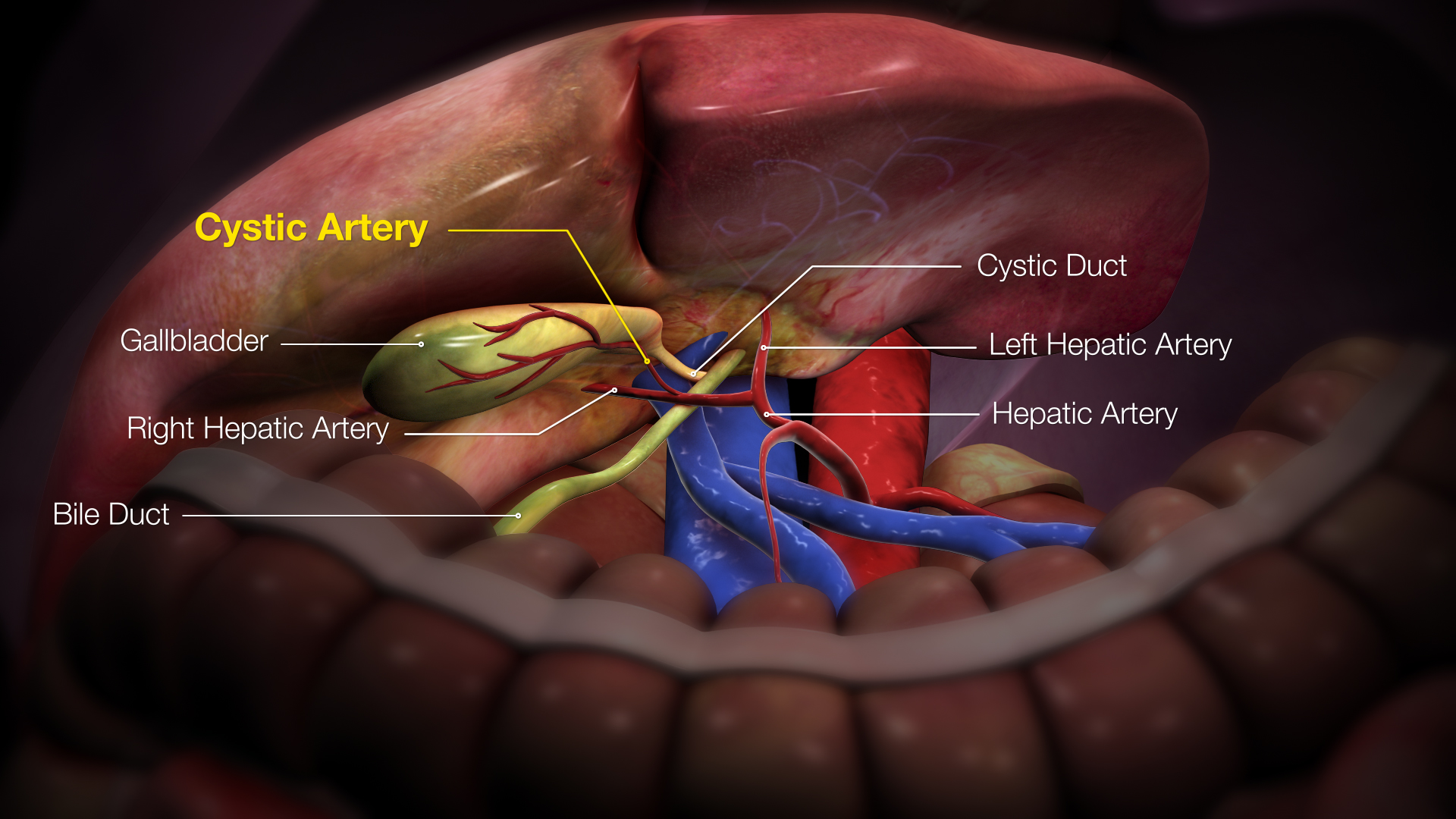
Cystic Artery
The cystic artery (also known as bachelor artery) is (usually) a branch of the right hepatic artery that provides arterial supply to the gallbladder and contributes arterial supply to the extrahepatic bile ducts. Anatomy The cystic artery usually has a diameter of less than 3mm. Origin The cystic artery arises from the right hepatic artery in about 80% of cases. Course It usually passes posterior to the common hepatic duct within the cystohepatic triangle. Within the triangle, it is usually superior to the cystic duct (if it does not pass superior to the cystic duct, it may be situated outside the triangle). Branches Upon reaching the superior aspect of the neck of the gallbladder, it splits into superficial and deep branches. These branches then form an anastomotic network over the surface of the body and fundus of the gallbladder. It produces 2 to 4 minor branches (known as ''Calot’s arteries'') that supply part of the cystic duct and cervix of the gallbladder before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Mesenteric Artery
In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) is an artery which arises from the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta, just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk, and supplies blood to the intestine from the lower part of the duodenum through two-thirds of the transverse colon, as well as the pancreas. Structure Origin In the adult, the SMA arises anterior to inferior border of vertebra L1 ( transpyloric plane). It is usually 1 cm lower than the celiac trunk. Course and relations It initially travels in an anterior/inferior direction, passing behind/under the neck of the pancreas and the splenic vein. Located under this portion of the superior mesenteric artery, between it and the aorta, are the following: * left renal vein - travels between the left kidney and the inferior vena cava (can be compressed between the SMA and the abdominal aorta at this location, leading to nutcracker syndrome). * the third part of the duodenum, a segment of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Body
The human body is the entire structure of a Human, human being. It is composed of many different types of Cell (biology), cells that together create Tissue (biology), tissues and subsequently Organ (biology), organs and then Organ system, organ systems. The external human body consists of a human head, head, hair, neck, torso (which includes the thorax and abdomen), Sex organ, genitals, arms, Hand, hands, human leg, legs, and Foot, feet. The internal human body includes organs, Human tooth, teeth, bones, muscle, tendons, ligaments, blood vessels and blood, lymphatic vessels and lymph. The study of the human body includes anatomy, physiology, histology and embryology. The body Anatomical variation, varies anatomically in known ways. Physiology focuses on the systems and organs of the human body and their functions. Many systems and mechanisms interact in order to maintain homeostasis, with safe levels of substances such as sugar, iron, and oxygen in the blood. The body is st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celiac Trunk
The celiac () artery (also spelled coeliac in British English), also known as the celiac trunk or truncus coeliacus, is the first major branch of the abdominal aorta. It is about 1.25 cm in length. Branching from the aorta at thoracic vertebra 12 (T12) in humans, it is one of three anterior/ midline branches of the abdominal aorta (the others are the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries). Structure The celiac artery is the first major branch of the descending abdominal aorta, branching at a 90° angle. This occurs just below the crus of the diaphragm. This is around the first lumbar vertebra. There are three main divisions of the celiac artery, and each in turn has its own named branches: The celiac artery may also give rise to the inferior phrenic arteries. Function The celiac artery supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, stomach, abdominal esophagus, spleen, and the superior half of both the duodenum and the pancreas. These structures correspond to the em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Gastric Artery
In human anatomy, the left gastric artery arises from the celiac artery and runs along the superior portion of the lesser curvature of the stomach before anastomosing with the right gastric artery (which runs right to left). It also issues esophageal branches that supply lower esophagus and ascend through the esophageal hiatus to form anastomoses with the esophageal branches of thoracic part of aorta. Anatomy Origin The LGA usually arises from (the superior aspect of) the coeliac trunk - sometimes as a terminal branch of a trifurcation, and more rarely as a side branch of the splenic artery or of common hepatic artery. Sometimes it originates directly from aorta or from arteria phrenica inferior. Course From the crus of diaphragm, the LGA arches obliquely anterior-ward and to the left to reach the left curvature of the stomach just inferior to the gastric cardia (thus erecting the gastropancreatic (peritoneal) fold). Fate Upon reaching the cardia, the LGA splits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Gastric Artery
The right gastric artery usually arises from the proper hepatic artery. It descends to the pyloric end of the stomach The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ... before passing from right to left along its lesser curvature, supplying it with branches, and finally anastomosing with the left gastric artery. Anatomy Variation Origin In most (53%) individuals, the RGA arises from the proper hepatic artery. It can also arise from the region of division of the common hepatic artery (20%), the left branch of the hepatic artery (15%), the gastroduodenal artery (8%), and - most rarely - the common hepatic artery itself (4%). Additional images File:Gray532.png, The celiac artery and its branches; the liver has been raised, and the lesser omentum and anterior layer of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraduodenal Artery
The supraduodenal artery are 1-2 small arteries which usually arise from the gastroduodenal artery, and sometimes from the posterior superior pancreaticoduodenal arteries, or common hepatic artery The common hepatic artery is a short blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, pylorus of the stomach, duodenum, pancreas, and gallbladder. It arises from the celiac artery and has the following branches: Additional images .... They provide arterial supply to the anterosuperior portion of the proximal duodenum. References Arteries of the abdomen {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Hepatic Artery
The common hepatic artery is a short blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, pylorus of the stomach, duodenum, pancreas, and gallbladder. It arises from the celiac artery and has the following branches: Additional images File:Common hepatic artery.jpg, Common hepatic artery and its branches including hepatic artery proper and right gastric artery (pyloric artery) References External links * - "Stomach, Spleen and Liver The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...: Contents of the Hepatoduodenal ligament" * {{Authority control Arteries of the abdomen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastroduodenal Artery
In anatomy, the gastroduodenal artery is a small blood vessel in the abdomen. It supplies blood directly to the pylorus (distal part of the stomach) and proximal part of the duodenum. It also indirectly supplies the pancreatic head (via the anterior and posterior superior pancreaticoduodenal arteries). Structure The gastroduodenal artery most commonly originates from the common hepatic artery, which is a branch of the celiac trunk. Occasionally, it may arise from the proper hepatic artery or from the right or left hepatic arteries, but these are less common anatomical variations. It first gives rise to the supraduodenal artery, followed by the posterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery. It terminates in a bifurcation when it splits into the right gastroepiploic artery and the anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery ( superior pancreaticoduodenal artery). These branches form functional anastomoses with the anterior and posterior inferior pancreaticoduodenal arteries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portal Triad
In histology (microscopic anatomy), the lobules of liver, or hepatic lobules, are small divisions of the liver defined at the microscopic scale. The hepatic lobule is a building block of the liver tissue, consisting of portal triads, hepatocytes arranged in linear cords between a capillary network, and a central vein. Lobules are different from the lobes of liver: they are the smaller divisions of the lobes. The two-dimensional microarchitecture of the liver can be viewed from different perspectives: The term "hepatic lobule", without qualification, typically refers to the classical lobule. Structure The hepatic lobule can be described in terms of metabolic "zones", describing the hepatic acinus (terminal acinus). Each zone is centered on the line connecting two portal triads and extends outwards to the two adjacent central veins. The periportal zone I is nearest to the entering vascular supply and receives the most oxygenated blood, making it least sensitive to ischemic i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |