|
Hejazi Arabic
Hejazi Arabic or Hijazi Arabic (HA) (, Hejazi Arabic: , ), also known as West Arabian Arabic, is a Varieties of Arabic, variety of Arabic spoken in the Hejaz region in Saudi Arabia. Strictly speaking, there are two main groups of dialects spoken in the Hejaz region, one by the urban population, originally spoken mainly in the cities of Jeddah, Mecca, Medina and partially in Ta'if and another dialect by the urbanized rural and bedouin populations. However, the term most often applies to the urban variety which is discussed in this article. In antiquity, the Hejaz was home to the Old Higazi, Old Hejazi dialect of Arabic recorded in the consonantal text of the Qur'an. Old Hejazi is distinct from modern Hejazi Arabic, and represents an older linguistic layer wiped out by centuries of migration, but which happens to share the imperative prefix vowel /a-/ with the modern dialect. Classification Also referred to as the sedentary Hejazi dialect, this is the form most commonly associated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hejazi Arabic Phonology
The phonological system of the Hejazi Arabic consists of approximately 26 to 28 native consonant phonemes and 8 vowel phonemes: . Consonant length and vowel length are both distinctive in Hejazi. Strictly speaking, there are two main groups of dialects spoken in the Hejaz region, one by the urban population originally spoken in the cities of Jeddah, Medina and Mecca where they constitute the majority and partially in Ta'if, and another dialect spoken by the rural or Bedouin populations which is also currently spoken as well in the mentioned cities. However, the term most often applies to the urban variety which is discussed in this article. * phonemes will be (written inside slashes ) and allophones (written inside brackets ). Consonants Hejazi consonant inventory depends on the speaker. Most speakers use 26 to 28 consonant phonemes in addition to the marginal phoneme , with the phonemes and being used partially due to the influence of Modern Standard Arabic and neighbori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries by area, fifth-largest country in Asia, the largest in the Middle East, and the List of countries and dependencies by area, 12th-largest in the world. It is bordered by the Red Sea to the west; Jordan, Iraq, and Kuwait to the north; the Persian Gulf, Bahrain, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates to the east; Oman to the southeast; and Yemen to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the south. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northwest separates Saudi Arabia from Egypt and Israel. Saudi Arabia is the only country with a coastline along both the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf, and most of Geography of Saudi Arabia, its terrain consists of Arabian Desert, arid desert, lowland, steppe, and List of mountains in Saudi Arabia, mountains. The capital and List of cities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vowel Reduction
In phonetics, vowel reduction is any of various changes in the acoustic ''quality'' of vowels as a result of changes in stress, sonority, duration, loudness, articulation, or position in the word (e.g. for the Muscogee language), and which are perceived as "weakening". It most often makes the vowels shorter as well. Vowels which have undergone vowel reduction may be called ''reduced'' or ''weak''. In contrast, an unreduced vowel may be described as ''full'' or ''strong''. The prototypical reduced vowel in English is schwa. In Australian English, that is the only reduced vowel, though other dialects have additional ones. Transcription There are several ways to distinguish full and reduced vowels in transcription. Some English dictionaries indicate full vowels by marking them for secondary stress even when they are not stressed, so that e.g. is a unstressed full vowel while is a reduced ''schwi''. Or the vowel quality may be portrayed as distinct, with reduced vowels centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Najdi Arabic
Najdi Arabic (, Najdi Arabic: , ) is the group of Arabic varieties originating from the Najd region of Saudi Arabia. Outside of Saudi Arabia, it is also the main Arabic variety spoken in the Syrian Desert of Iraq, Jordan, and Syria (with the exception of Palmyra oasis and settlements dotting the Euphrates, where Mesopotamian Arabic is spoken) as well as the westernmost part of Kuwait. Najdi Arabic can be divided into four region-based groups: #Northern Najdi, spoken by the tribe of Shammar and surrounding tribes in Ha'il Region in Najd and the Syrian Desert. #Mixed northern-central Najdi of Al-Qassim, Northern Riyadh region of Sudair, and the tribe of Dhafeer around Kuwait. #Central Najdi, spoken in the city of Riyadh and surrounding towns and farming communities, and by the tribe of Anazah in the Syrian Desert. This dialect group includes the modern urban dialect of Riyadh, which has become the prestige dialect of Saudi Arabia. #Southern Najdi, spoken by the tribes of Qah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
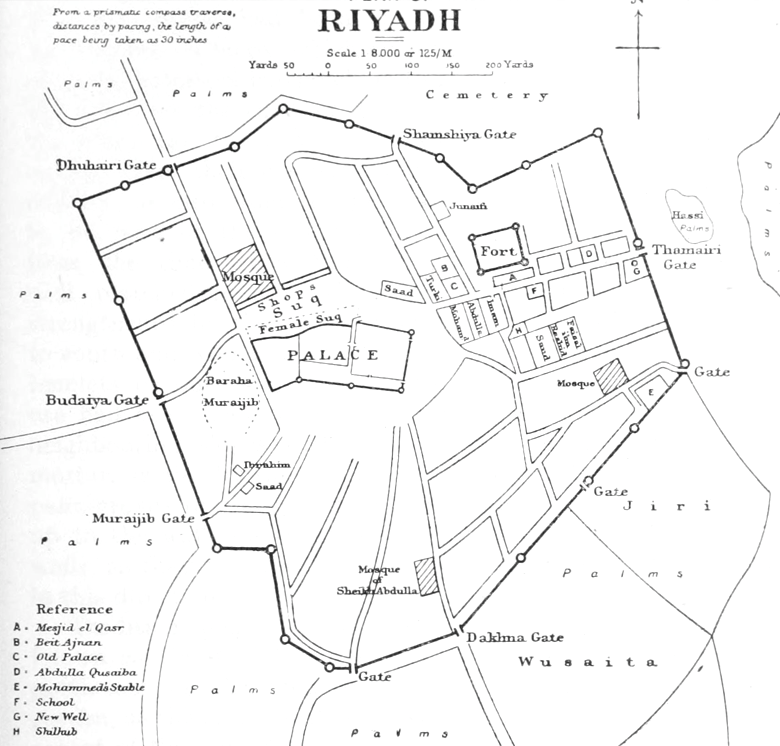
Riyadh
Riyadh is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyadh Province and the centre of the Riyadh Governorate. Located on the eastern bank of Wadi Hanifa, the current form of the metropolis largely emerged in the 1950s as an offshoot of the 18th century Walled town of Riyadh, walled town following the dismantling of its Riyadh city fortifications, defensive fortifications. It is the List of Arabian cities by population, largest city on the Arabian Peninsula, and is situated in the center of the An Nafud, an-Nafud desert, on the eastern part of the Najd plateau. The city sits at an average of above sea level, and receives around 5 million Tourism in Saudi Arabia, tourists each year, making it the List of cities by international visitors, forty-ninth most visited city in the world and the 6th in the Middle East. Riyadh had a population of 7.0 million people in 2022, making it the List of cities in Saudi Arabia, most-populous city in Saudi Arabia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Modern Standard Arabic
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Modern Written Arabic (MWA) is the variety of Standard language, standardized, Literary language, literary Arabic that developed in the Arab world in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and in some usages also the variety of spoken Arabic that approximates this written standard. MSA is the language used in literature, academia, print media, print and mass media, law and legislation, though it is generally not spoken as a first language, similar to Contemporary Latin. It is a Pluricentric language, pluricentric standard language taught throughout the Arab world in formal education, differing significantly from many vernacular varieties of Arabic that are commonly spoken as mother tongues in the area; these are only partially mutually intelligible with both MSA and with each other depending on their proximity in the Dialect continuum#Arabic, Arabic dialect continuum. Many linguists consider MSA to be distinct from Classical Arabic (CA; ) – t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Habitual Aspect
In linguistics, the aspect of a verb is a grammatical category that defines the temporal flow (or lack thereof) in a given action, event, or state. As its name suggests, the habitual aspect (abbreviated ), not to be confused with iterative aspect or frequentative aspect, specifies an action as occurring habitually: the subject performs the action usually, ordinarily, or customarily. As such, the habitual aspect provides structural information on the nature of the subject referent, "John smokes" being interpretable as "John is a smoker", "Enjoh habitually gets up early in the morning" as "Enjoh is an early bird". The habitual aspect is a type of imperfective aspect, which does not depict an event as a single entity viewed only as a whole but instead specifies something about its internal temporal structure. Östen Dahl found that the habitual past, the most common tense context for the habitual, occurred in only seven of 60 languages sampled, including English. Especially in Tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Palestinian Arabic
Palestinian Arabic (also known as simply Palestinian) is part of a dialect continuum comprising various mutually intelligible varieties of Levantine Arabic spoken by Palestinians in Palestine, which includes the State of Palestine, Israel, and the Palestinian diaspora. The Arabic dialects spoken in the region of Palestine and Transjordan do not form a homogeneous linguistic unit; rather, they encompass a diverse range of dialects influenced by geographical, historical, and socioeconomic factors. Comparative studies of Arabic dialects indicate that Palestinian Arabic is among the closest dialects to Modern Standard Arabic, particularly the dialect spoken in the Gaza Strip. Additional distinctions can be made within Palestinian Arabic, such as the dialects spoken in the northern West Bank and the Hebron area, which exhibit similarities to those spoken by descendants of Palestinian refugees. Palestinian Arabic dialects reflect a historical layering of languages previously spoken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Egyptian Arabic
Egyptian Arabic, locally known as Colloquial Egyptian, or simply as Masri, is the most widely spoken vernacular Arabic variety in Egypt. It is part of the Afro-Asiatic language family, and originated in the Nile Delta in Lower Egypt. The estimated 111 million Egyptians speak a continuum of dialects, among which Cairene is the most prominent. It is also understood across most of the Arabic-speaking countries due to broad Egyptian influence in the region, including through Egyptian cinema and Egyptian music. These factors help make it the most widely spoken and by far the most widely studied variety of Arabic. While it is primarily a spoken language, the written form is used in novels, plays and poems (vernacular literature), as well as in comics, advertising, some newspapers and transcriptions of popular songs. In most other written media and in radio and television news reporting, literary Arabic is used. Literary Arabic is a standardized language based on the langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Double Negative
A double negative is a construction occurring when two forms of grammatical negation are used in the same sentence. This is typically used to convey a different shade of meaning from a strictly positive sentence ("You're not unattractive" vs "You're attractive"). Multiple negation is the more general term referring to the occurrence of more than one negative in a clause. In some languages, double negatives cancel one another and produce an affirmative; in other languages, doubled negatives intensify the negation. Languages where multiple negatives affirm each other are said to have negative concord or emphatic negation. Lithuanian, Portuguese, Persian, French, Russian, Polish, Bulgarian, Greek, Spanish, Icelandic, Old English, Italian, Afrikaans, and Hebrew are examples of negative-concord languages. This is also true of many vernacular dialects of modern English. Chinese, Latin, German (with some exceptions in various High German dialects), Dutch, Japanese, Swedis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arabic Verbs
Arabic verbs ( '; '), like the verbs in other Semitic languages, and the entire vocabulary in those languages, are based on a set of two to five (but usually three) consonants called a Semitic root, root (''triliteral'' or ''quadriliteral'' according to the number of consonants). The root communicates the basic meaning of the verb, e.g. ' 'write', ' 'read', ' 'eat'. Changes to the vowels in between the consonants, along with prefixes or suffixes, specify grammatical functions such as person, gender, number, tense, mood, and voice. Various categories are marked on verbs: * Three Grammatical tense, tenses (present, past; future tense is indicated by the prefix ' or the particle ' and the present tense). * Two Grammatical voice, voices (active, passive) * Two Grammatical gender, genders (masculine, feminine) * Three Grammatical person, persons (first, second, third) * Three Grammatical number, numbers (singular, dual (grammatical number), dual, plural) * Six Grammatical mood, mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |