|
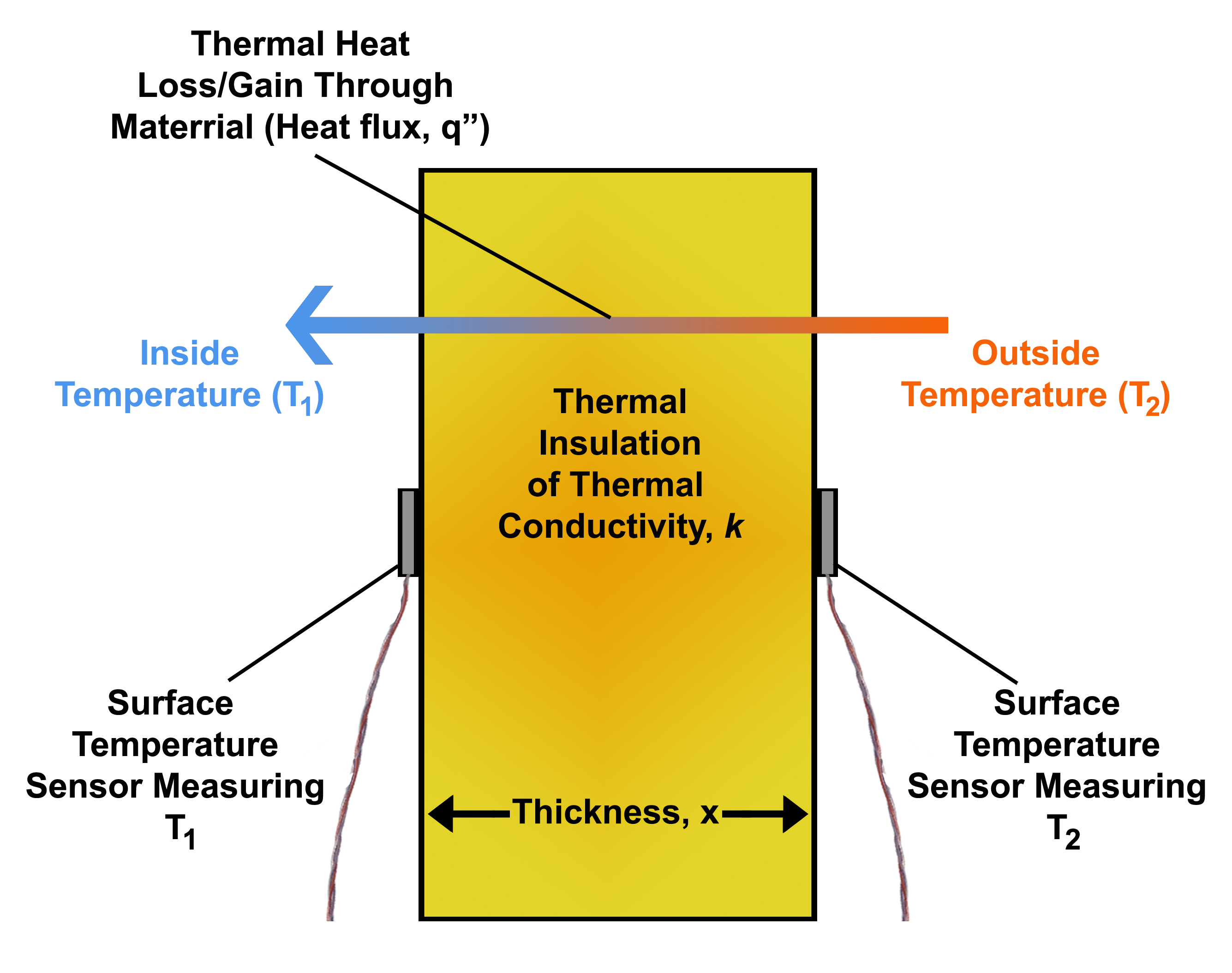
Heat Flux
In physics and engineering, heat flux or thermal flux, sometimes also referred to as heat flux density, heat-flow density or heat-flow rate intensity, is a flow of energy per unit area per unit time (physics), time. Its SI units are watts per square metre (W/m2). It has both a direction and a magnitude, and so it is a Vector (geometric), vector quantity. To define the heat flux at a certain point in space, one takes the Limiting case (mathematics), limiting case where the size of the surface becomes infinitesimally small. Heat flux is often denoted \vec_\mathrm, the subscript specifying ''heat'' flux, as opposed to ''Mass flux, mass'' or Transport phenomena, ''momentum'' flux. Heat conduction#Fourier's law, Fourier's law is an important application of these concepts. Fourier's law For most solids in usual conditions, heat is transported mainly by thermal conduction, conduction and the heat flux is adequately described by Fourier's law. Fourier's law in one dimension \phi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." It is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. (...) You will come to see physics as a towering achievement of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to heat conduction, conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa and is measured in W·m−1·K−1. Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal conductivity. For instance, metals typically have high thermal conductivity and are very efficient at conducting heat, while the opposite is true for insulating materials such as mineral wool or Styrofoam. Metals have this high thermal conductivity due to free electrons facilitating heat transfer. Correspondingly, materials of high thermal conductivity are widely used in heat sink applications, and materials of low thermal conductivity are used as thermal insulation. The reciprocal of thermal conductivity is called thermal resistivity. The defining equation for thermal conductivity is \mathbf = - k \nabla T, where \mathbf is the heat flux, k is the thermal conductivity, and \nabla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rate Of Heat Flow
The rate of heat flow is the amount of heat that is transferred per unit of time in some material, usually measured in watts (joules per second). Heat is the flow of thermal energy driven by thermal non-equilibrium, so the term 'heat flow' is a redundancy (i.e. a pleonasm). Heat must not be confused with stored thermal energy, and moving a hot object from one place to another must not be called heat transfer. However, it is common to say ‘heat flow’ to mean ‘heat content’. The equation of heat flow is given by Fourier's law of heat conduction. Rate of heat flow = - (heat transfer coefficient) * (area of the body) * (variation of the temperature) / (length of the material) The formula for the rate of heat flow is: :\frac = -kA \frac where * Q is the net heat (energy) transfer, * \Delta t is the time taken, * \Delta T is the difference in temperature between the cold and hot sides, * \Delta x is the thickness of the material conducting heat (distance between hot and col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latent Heat Flux
Latent heat (also known as latent energy or heat of transformation) is energy released or absorbed, by a body or a thermodynamic system, during a constant-temperature process—usually a first-order phase transition, like melting or condensation. Latent heat can be understood as hidden energy which is supplied or extracted to change the state of a substance without changing its temperature or pressure. This includes the latent heat of fusion (solid to liquid), the latent heat of vaporization (liquid to gas) and the latent heat of sublimation (solid to gas). The term was introduced around 1762 by Scottish chemist Joseph Black. Black used the term in the context of calorimetry where a heat transfer caused a volume change in a body while its temperature was constant. In contrast to latent heat, sensible heat is energy transferred as heat, with a resultant temperature change in a body. Usage The terms ''sensible heat'' and ''latent heat'' refer to energy transferred between a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiant Flux
In radiometry, radiant flux or radiant power is the radiant energy emitted, reflected, transmitted, or received per unit time, and spectral flux or spectral power is the radiant flux per unit frequency or wavelength, depending on whether the spectrum is taken as a function of frequency or of wavelength. The SI unit of radiant flux is the watt (W), one joule per second (), while that of spectral flux in frequency is the watt per hertz () and that of spectral flux in wavelength is the watt per metre ()—commonly the watt per nanometre (). Mathematical definitions Radiant flux Radiant flux, denoted ('e' for "energetic", to avoid confusion with photometric quantities), is defined as \begin \Phi_\mathrm &= \frac \\ ptQ_\mathrm &= \int_ \int_ \mathbf\cdot \hat\mathbf\, dA dt \end where * is the time; * is the radiant energy passing out of a closed surface ; * is the Poynting vector, representing the current density of radiant energy; * is the normal vector of a point on ; * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monte Carlo Integration
In mathematics, Monte Carlo integration is a technique for numerical integration using random numbers. It is a particular Monte Carlo method that numerically computes a definite integral. While other algorithms usually evaluate the integrand at a regular grid, Monte Carlo randomly chooses points at which the integrand is evaluated. This method is particularly useful for higher-dimensional integrals. There are different methods to perform a Monte Carlo integration, such as uniform sampling, stratified sampling, importance sampling, sequential Monte Carlo (also known as a particle filter), and mean-field particle methods. Overview In numerical integration, methods such as the trapezoidal rule use a deterministic approach. Monte Carlo integration, on the other hand, employs a non-deterministic approach: each realization provides a different outcome. In Monte Carlo, the final outcome is an approximation of the correct value with respective error bars, and the correct value ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Law Of Thermodynamics
The first law of thermodynamics is a formulation of the law of conservation of energy in the context of thermodynamic processes. For a thermodynamic process affecting a thermodynamic system without transfer of matter, the law distinguishes two principal forms of energy transfer, heat and thermodynamic work. The law also defines the internal energy of a system, an extensive property for taking account of the balance of heat transfer, thermodynamic work, and matter transfer, into and out of the system. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be transformed from one form to another. In an externally isolated system, with internal changes, the sum of all forms of energy is constant. An equivalent statement is that perpetual motion machines of the first kind are impossible; work done by a system on its surroundings requires that the system's internal energy be consumed, so that the amount of internal energy lost by that work must be resupplied as heat by an external e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoelectric Effect
The thermoelectric effect is the direct conversion of temperature differences to electric voltage and vice versa via a thermocouple. A thermoelectric device creates a voltage when there is a different temperature on each side. Conversely, when a voltage is applied to it, heat is transferred from one side to the other, creating a temperature difference. This effect can be used to generate electricity, measure temperature or change the temperature of objects. Because the direction of heating and cooling is affected by the applied voltage, thermoelectric devices can be used as temperature controllers. The term "thermoelectric effect" encompasses three separately identified effects: the Seebeck effect (temperature differences cause electromotive forces), the Peltier effect (thermocouples create temperature differences), and the Thomson effect (the Seebeck coefficient varies with temperature). The Seebeck and Peltier effects are different manifestations of the same physical proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermopile
A thermopile is an electronic device that converts thermal energy into electrical energy. It is composed of several thermocouples connected usually in series or, less commonly, in parallel. Such a device works on the principle of the thermoelectric effect, i.e., generating a voltage when its dissimilar metals (thermocouples) are exposed to a temperature difference. Operation Thermocouples operate by measuring the temperature differential from their junction point to the point in which the thermocouple output voltage is measured. Once a closed circuit is made up of more than one metal and there is a difference in temperature between junctions and points of transition from one metal to another, a current is produced as if generated by a difference of potential between the hot and cold junction. Thermocouples can be connected in series as thermocouple pairs with a junction located on either side of a thermal resistance layer. The output from the thermocouple pair will be a vol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Flux Sensor
] A heat flux sensor is a transducer that generates an electrical signal proportional to the total heat transfer, heat rate applied to the surface of the sensor. The measured heat rate is divided by the surface area of the sensor to determine the heat flux. The heat flux can have different origins; in principle convective, Thermal radiation, radiative as well as Thermal conduction, conductive heat can be measured. Heat flux sensors are known under different names, such as heat flux transducers, heat flux gauges, or heat flux plates. Some instruments are actually single-purpose heat flux sensors, like pyranometers for solar radiation measurement. Other heat flux sensors include Gardon gauges (also known as a circular-foil gauge), thin-film thermopiles, and Schmidt-Boelter gauges. Usage Heat flux sensors are used for a variety of applications. Common applications are studies of building envelope thermal resistance, studies of the effect of fire and flames or laser power measurem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electronic component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity. Resistors are common elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in electronic equipment. Practical resistors as discrete components can be composed of various compounds and forms. Resisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), work needed per unit of Electric charge, charge to move a positive Test particle#Electrostatics, test charge from the first point to the second point. In the SI unit, International System of Units (SI), the SI derived unit, derived unit for voltage is the ''volt'' (''V''). The voltage between points can be caused by the build-up of electric charge (e.g., a capacitor), and from an electromotive force (e.g., electromagnetic induction in a Electric generator, generator). On a macroscopic scale, a potential difference can be caused by electrochemical processes (e.g., cells and batteries), the pressure-induced piezoelectric effect, and the thermoelectric effect. Since it is the difference in electric potential, it is a physical Scalar (physics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |