|
Heart Block
Heart block (HB) is a disorder in the heart's rhythm due to a fault in the natural pacemaker. This is caused by an obstruction – a block – in the electrical conduction system of the heart. Sometimes a disorder can be inherited. Despite the severe-sounding name, heart block may cause no symptoms at all in some cases, or occasional missed heartbeats in other cases (which can cause light-headedness, syncope (fainting), and palpitations), or may require the implantation of an artificial pacemaker, depending upon exactly where in the heart conduction is being impaired and how significantly it is affected. Heart block should not be confused with other conditions, which may or may not be co-occurring, relating to the heart and/or other nearby organs that are or can be serious, including angina (heart-related chest pain), heart attack (myocardial infarction), any type of heart failure, cardiogenic shock or other types of shock, different types of abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrioventricular Node
The atrioventricular node (AV node, or Aschoff-Tawara node) electrically connects the heart's atria and ventricles to coordinate beating in the top of the heart; it is part of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The AV node lies at the lower back section of the interatrial septum near the opening of the coronary sinus, and conducts the normal electrical impulse from the atria to the ventricles. The AV node is quite compact (~1 x 3 x 5 mm).Full Size Picture triangle of-Koch.jpg Retrieved on 2008-12-22 Structure Location The AV node lies at the lower back section of the i ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daily Life
Everyday life, daily life or routine life comprises the ways in which people typically act, think, and feel on a daily basis. Everyday life may be described as mundane, routine, natural, habitual, or normal. Human diurnality means most people sleep at least part of the night and are active in daytime. Most eat two or three meals in a day. Working time (apart from shift work) mostly involves a daily schedule, beginning in the morning. This produces the daily rush hours experienced by many millions, and the drive time focused on by radio broadcasters. Evening is often leisure time. Bathing every day is a custom for many. Beyond these broad similarities, lifestyles vary and different people spend their days differently. For example, nomadic life differs from sedentism, and among the sedentary, urban people live differently from rural folk. Differences in the lives of the rich and the poor, or between laborers and intellectuals, may go beyond their working ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is awareness of a state or object, either internal to oneself or in one's external environment. However, its nature has led to millennia of analyses, explanations, and debate among philosophers, scientists, and theologians. Opinions differ about what exactly needs to be studied or even considered consciousness. In some explanations, it is synonymous with the mind, and at other times, an aspect of it. In the past, it was one's "inner life", the world of introspection, of private thought, imagination, and volition (psychology), volition. Today, it often includes any kind of cognition, experience, feeling, or perception. It may be awareness, awareness of awareness, metacognition, or self-awareness, either continuously changing or not. The disparate range of research, notions, and speculations raises a curiosity about whether the right questions are being asked. Examples of the range of descriptions, definitions or explanations are: ordered distinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woldemar Mobitz
Woldemar Mobitz (31 May 1889 – 11 April 1951) was a Russian-German physician. The forms of second degree AV block are named after him for him. Mobitz was born on 31 May 1889 in St. Petersburg, Russia. He attended the local high school in Meiningen (Saxony, Germany) from which he graduated in 1908. He then studied medicine at the Universities of Freiburg and Munich, where he earned his doctorate in 1914 (“Contributions to Basedow disease”). He then worked at the Surgical Hospitals in Berlin and Halle (Saale), Halle as well as in internal medicine at the University Hospitals of Munich and Freiburg. In Munich, Mobitz was promoted to the position of a senior lecturer thanks to his research on heart block. In 1928, after a 4-year tenure, he accepted a post in Freiburg as Associate Professor and Chief of Staff of the Clinic of Internal Medicine. In 1943, he became Director of the Medical Hospital in Magdeburg-Sudenburg Municipal Hospital until the occupation by the Soviet army in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karel Frederik Wenckebach
Karel Frederik Wenckebach (; March 24, 1864 – November 11, 1940) was a Dutch anatomist who was a native of the Hague. He studied medicine in Utrecht, and in 1901 become a professor of medicine at the University of Groningen. Later he was a professor at the Universities of Strasbourg (1911–14) and Vienna (1914–29). Contributions in cardiology Wenckebach is primarily remembered for his work in cardiology. In 1899 he provided a description of irregular pulses due to partial blockage of atrioventricular conduction, creating a progressive lengthening of conduction time in cardiac tissue. The condition was referred to as a " second degree AV block" and later named the "Wenckebach phenomenon" and reclassified as Mobitz type I block in Mobitz's 1924 paper. A similar phenomenon can also occur in the sinoatrial node where it gives rise to type I second degree SA block, and this is also known as a Wenckebach block; the two have distinct features on an ECG however. Wenckebach i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemiblock
Heart block (HB) is a disorder in the heart's rhythm due to a fault in the natural pacemaker. This is caused by an obstruction – a block – in the electrical conduction system of the heart. Sometimes a disorder can be inherited. Despite the severe-sounding name, heart block may cause no symptoms at all in some cases, or occasional missed heartbeats in other cases (which can cause light-headedness, syncope (fainting), and palpitations), or may require the implantation of an artificial pacemaker, depending upon exactly where in the heart conduction is being impaired and how significantly it is affected. Heart block should not be confused with other conditions, which may or may not be co-occurring, relating to the heart and/or other nearby organs that are or can be serious, including angina (heart-related chest pain), heart attack (myocardial infarction), any type of heart failure, cardiogenic shock or other types of shock, different types of abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundle Branch Block
A bundle branch block is a partial or complete interruption in the flow of electrical impulses in either of the bundle branches of the heart's electrical system. Anatomy and physiology The heart's electrical activity begins in the sinoatrial node (the heart's natural pacemaker), which is situated on the upper right atrium. The impulse travels next through the left and right atria and summates at the atrioventricular node. From the AV node the electrical impulse travels down the bundle of His and divides into the right and left bundle branches. The right bundle branch contains one fascicle. The left bundle branch subdivides into two fascicles: the left anterior fascicle, and the left posterior fascicle. Other sources divide the left bundle branch into three fascicles: the left anterior, the left posterior, and the left septal fascicle. The thicker left posterior fascicle bifurcates, with one fascicle being in the septal aspect. Ultimately, the fascicles divide into mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
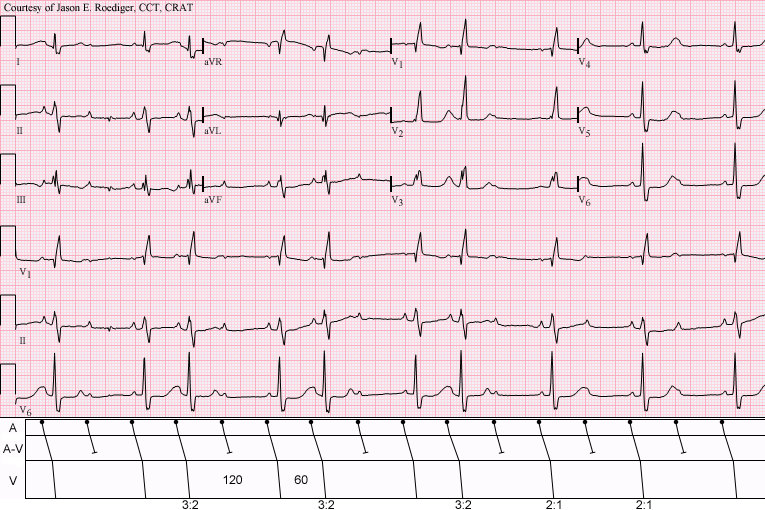
AV Block
AV, Av or A.V. may refer to: Arts and entertainment * The abbreviation of audiovisual, possessing both a sound and a visual component * ''A.V.'' (film), a 2005 Hong Kong film directed by Pang Ho-Cheung * Adult video, an alternative name/synonym of a pornographic film * ''AV The Hunt'', a 2020 Turkish thriller film directed by Emre Akay Businesses and organizations * America Votes, an American 501(c)4 organization that promotes progressive causes * Ambulance Victoria, an ambulance service operated in the Australian state of Victoria * Anonymous for the Voiceless, a grassroots animal rights organization specializing in street activism * Aston Villa F.C., an English professional football club * AV Akademikerverlag GmbH & Co. KG an imprint of the German group VDM Publishing (''now'' OmniScriptum) * Avaya, a technology company formerly listed on the New York Stock Exchange with symbol "AV" * Avianca (IATA airline code AV) * Aviva, British insurance company, listed on the New York Sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AV Node
The atrioventricular node (AV node, or Aschoff-Tawara node) electrically connects the heart's atria and ventricles to coordinate beating in the top of the heart; it is part of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The AV node lies at the lower back section of the interatrial septum near the opening of the coronary sinus, and conducts the normal electrical impulse from the atria to the ventricles. The AV node is quite compact (~1 x 3 x 5 mm).Full Size Picture triangle of-Koch.jpg Retrieved on 2008-12-22 Structure Location The AV node lies at the lower back section of the |
Sinoatrial Block
A sinoatrial block (also spelled sinuatrial block) is a disorder in the normal rhythm of the heart, known as a heart block, that is initiated in the sinoatrial node. The initial action impulse in a heart is usually formed in the sinoatrial node (SA node) and carried through the atria, down the internodal atrial pathways to the atrioventricular node The atrioventricular node (AV node, or Aschoff-Tawara node) electrically connects the heart's atria and ventricles to coordinate beating in the top of the heart; it is part of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The AV node lies at the ... (AV) node. In normal conduction, the impulse would travel across the bundle of His (AV bundle), down the bundle branches, and into the Purkinje fibers. This would depolarize the ventricles and cause them to contract. In an SA block, the electrical impulse is delayed or blocked on the way to the atria, thus delaying the atrial beat. (An AV block, occurs in the AV node and delays ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |