|
Healabhal Mhòr
Healabhal Mhòr (471 m), is a hill in the north of the Isle of Skye, Scotland. It is also known as MacLeod's Table North, as it lies close the fellow flat-topped hill of Healabhal Bheag, or MacLeod's Table South. Despite its lower height, it has a greater bulk than its neighbour. The more commonly climbed of the two peaks, walks usually start from the coastal village of Dunvegan. The summit plateau provides an outstanding view to the Outer Hebrides The Outer Hebrides ( ) or Western Isles ( , or ), sometimes known as the Long Isle or Long Island (), is an Archipelago, island chain off the west coast of mainland Scotland. It is the longest archipelago in the British Isles. The islan ... on a clear day. References Marilyns of Scotland Mountains and hills of the Isle of Skye {{SkyeLochalsh-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
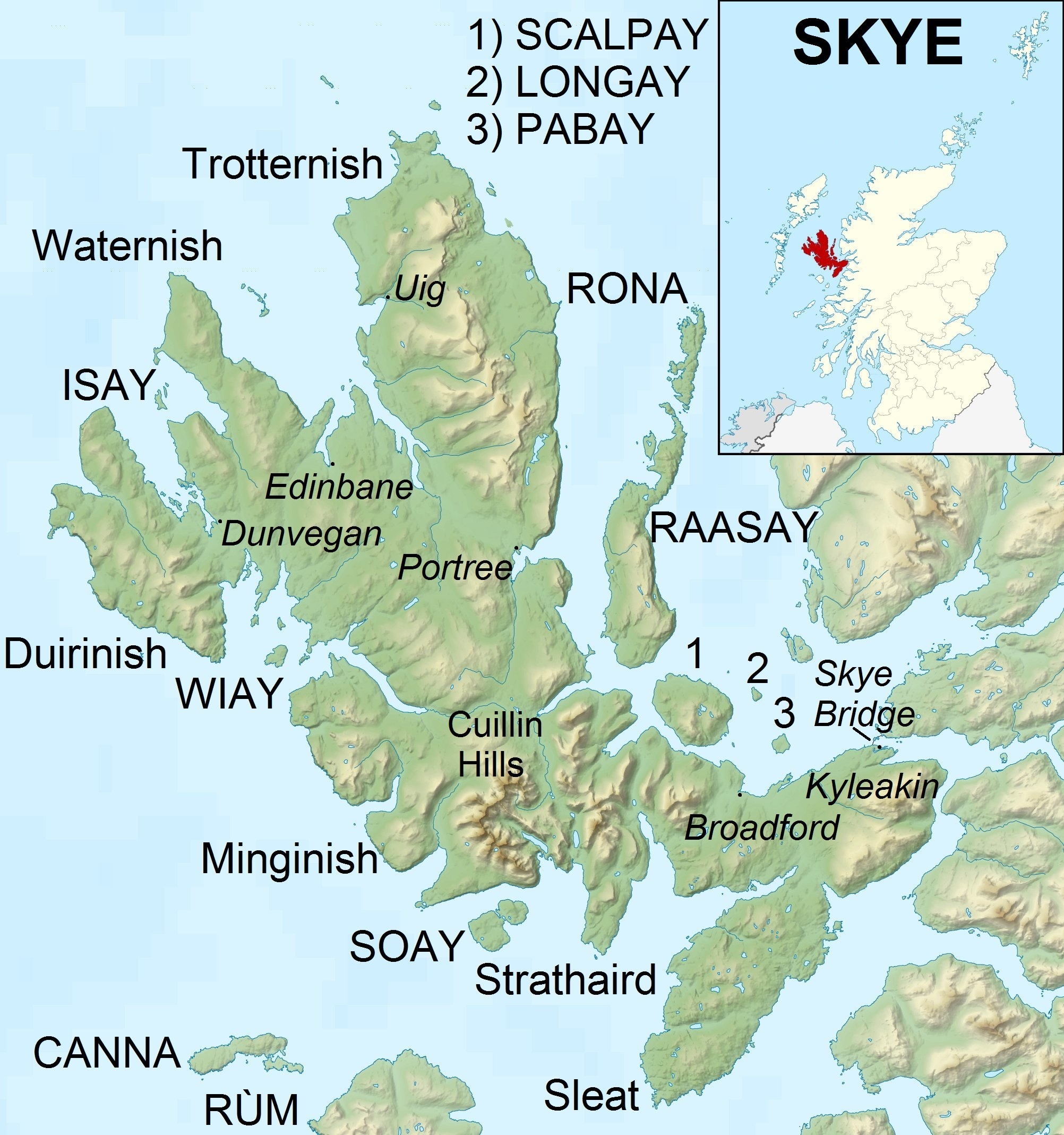
Skye
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye, is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated by the Cuillin, the rocky slopes of which provide some of the most dramatic mountain scenery in the country. Slesser (1981) p. 19. Although has been suggested to describe a winged shape, no definitive agreement exists as to the name's origin."Gaelic Culture" . VisitScotland. Retrieved 5 January 2013. The island has been occupied since the period, and over its history has been occupied at various times by Celtic tribes includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjacent Islands of Scotland, islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. To the south-east, Scotland has its Anglo-Scottish border, only land border, which is long and shared with England; the country is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the north-east and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. The population in 2022 was 5,439,842. Edinburgh is the capital and Glasgow is the most populous of the cities of Scotland. The Kingdom of Scotland emerged as an independent sovereign state in the 9th century. In 1603, James VI succeeded to the thrones of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, forming a personal union of the Union of the Crowns, three kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marilyn (hill)
This is a list of Marilyn hills and mountains in the United Kingdom, Republic of Ireland, Ireland and surrounding islands and Stack (geology), sea stacks. Lists of mountains and hills in the British Isles#Marilyns, Marilyns are defined as peaks with a topographic prominence, prominence of or more, regardless of height or any other merit (e.g. topographic isolation, as used in Lists of mountains and hills in the British Isles#Munros, Munros). Thus, Marilyns can be mountains, with a height above , or relatively small hills. there were 2,010 recorded Marilyns. Definition The Marilyn classification was created by Alan Dawson in his 1992 book ''The Relative Hills of Britain''. The name Marilyn was coined by Dawson as a punning contrast to the ''Munro'' classification of Scottish mountains above , but which has no explicit prominence threshold, being homophone, homophonous with (Marilyn) ''Marilyn Monroe, Monroe''. The list of Marilyns was extended to Ireland by Clem Clements. Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordnance Survey
The Ordnance Survey (OS) is the national mapping agency for Great Britain. The agency's name indicates its original military purpose (see Artillery, ordnance and surveying), which was to map Scotland in the wake of the Jacobite rising of 1745. There was also a more general and nationwide need in light of the potential threat of invasion during the Napoleonic Wars. Since 1 April 2015, the Ordnance Survey has operated as Ordnance Survey Ltd, a state-owned enterprise, government-owned company, 100% in public ownership. The Ordnance Survey Board remains accountable to the Secretary of State for Science, Innovation and Technology. It was also a member of the Public Data Group. Paper maps represent only 5% of the company's annual revenue. It produces digital map data, online route planning and sharing services and mobile apps, plus many other location-based products for business, government and consumers. Ordnance Survey mapping is usually classified as either "Scale (map), lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isle Of Skye
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye, is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated by the Cuillin, the rocky slopes of which provide some of the most dramatic mountain scenery in the country.#Slesser70, Slesser (1981) p. 19. Although has been suggested to describe a winged shape, no definitive agreement exists as to the name's origin."Gaelic Culture" . VisitScotland. Retrieved 5 January 2013. The island has been occupied since the Mesolithic period, and over its history has been occupied at various times by Celtic tribes including the Picts and the Gaels, Scandinavian Vikings, and most notably the powerful integrated Norse-Gaels clans of Clan MacLeod, MacLeod and Clan Donald, MacDonald. The island was considered to be under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Healabhal Bheag
Healabhal Bheag is a hill located on the Duirinish peninsula of the Isle of Skye in the Inner Hebrides The Inner Hebrides ( ; ) is an archipelago off the west coast of mainland Scotland, to the south east of the Outer Hebrides. Together these two island chains form the Hebrides, which experience a mild oceanic climate. The Inner Hebrides compri ..., Scotland. It is also known as MacLeod's Table South and is part of the prominent pair of peaks known as MacLeod's Tables that dominate the views to the west of Dunvegan and to the north of Harlosh.Slesser (1970) p. 178. Notes References * {{Coord, 57.3844, N, 6.6210, W, type:landmark_region:GB, display=title Mountains and hills of the Isle of Skye Marilyns of Scotland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunvegan
Dunvegan () is a village on the Isle of Skye in Scotland. It is famous for Dunvegan Castle, seat of the chiefs of Clan MacLeod. Dunvegan is within the parish of Duirinish, Skye, Duirinish. In 2011, it had a population of 386. Name In ''The Norse Influence on Gaelic Scotland'' (1910), George Henderson suggests that the name ''Dùn Bheagain'' derives from Old Gaelic ''Dùn Bheccáin'' ([the] fort of Beccán), Beccán being a Gaelic personal name. ''Dùn Bheagain'' would not mean 'little fort' as this would be ''Dùn Beag'' in Scottish Gaelic, Gaelic. Geography Dunvegan sits on the shores of the large Loch Dunvegan, and the Old School Restaurant in the village is noted for its fish, caught freshly from the loch itself. Dunvegan is situated at the junction of the A850 road (Great Britain), A850 and the A863 road (Great Britain), A863. The B884 road also has a junction with the A863, at the eastern end of Dunvegan. Demography Dunvegan's permanent population is declining. However, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outer Hebrides
The Outer Hebrides ( ) or Western Isles ( , or ), sometimes known as the Long Isle or Long Island (), is an Archipelago, island chain off the west coast of mainland Scotland. It is the longest archipelago in the British Isles. The islands form part of the archipelago of the Hebrides, separated from the Scottish mainland and from the Inner Hebrides by the waters of the Minch, the Little Minch, and the Sea of the Hebrides. The Outer Hebrides are considered to be the traditional heartland of the Gaelic language. The islands form one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, which since 1998 has used only the Gaelic form of its name, including in English language contexts. The council area is called Na h-Eileanan an Iar ('the Western Isles') and its council is ('Council of the Western Isles'). Most of the islands have a bedrock formed from ancient metamorphic rocks, and the climate is mild and oceanic. The 15 inhabited islands had a total population of in and there are more th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marilyns Of Scotland
This is a list of Marilyn hills and mountains in the United Kingdom, Ireland and surrounding islands and sea stacks. Marilyns are defined as peaks with a prominence of or more, regardless of height or any other merit (e.g. topographic isolation, as used in Munros). Thus, Marilyns can be mountains, with a height above , or relatively small hills. there were 2,010 recorded Marilyns. Definition The Marilyn classification was created by Alan Dawson in his 1992 book ''The Relative Hills of Britain''. The name Marilyn was coined by Dawson as a punning contrast to the ''Munro'' classification of Scottish mountains above , but which has no explicit prominence threshold, being homophonous with (Marilyn) '' Monroe''. The list of Marilyns was extended to Ireland by Clem Clements. Marilyn was the first of several subsequent British Isles classifications that rely solely on prominence, including the P600s, the HuMPs, and the TuMPs. Topographic prominence is more difficult to es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |