|
Haywards Heath Railway Station
Haywards Heath railway station is on the Brighton Main Line in England, serving the town of Haywards Heath, West Sussex. It is 37 miles 59 chains (60.7 km) down the line from via and is situated between and . It is managed by Southern. Trains calling at Haywards Heath are operated by Southern, Thameslink and Gatwick Express. Until 2008 a small number of CrossCountry services also stopped here. History The London and Brighton Railway opened its main line from a junction with the London and Croydon Railway at Norwood as far as Haywards Heath on 12 July 1841, with a coach service to take passengers on the remainder of their journey towards Brighton. This was the result of a roof fall during the construction of Haywards Heath Tunnel just south of the station on 2 January 1841, which killed three men. The remainder of the line to Brighton opened shortly after on 21 September of the same year. The original station was designed by the architect David Mocatta and inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haywards Heath
Haywards Heath ( ) is a town in West Sussex, England, south of London, north of Brighton, south of Gatwick Airport and northeast of the county town, Chichester. Nearby towns include Burgess Hill to the southwest, Horsham to the northwest, Crawley northwest and East Grinstead northeast. With a decently small number of jobs available in the immediate vicinity, mostly in the agricultural or service sector, residents work remotely or commute daily via road or rail to London, Brighton, Crawley or Gatwick Airport. Etymology The first element of the place-name Haywards Heath is derived from the Old English ''hege'' + ''worð'', meaning hedge enclosure, with the later addition of ''hǣð''. The place-name was first recorded in 1261 as ''Heyworth'', then in 1359 as ''Hayworthe'', in 1544 as ''Haywards Hoth'' (i.e. 'heath by the enclosure with a hedge'), and in 1607 as ''Hayworths Hethe''. There is a local legend that the name comes from a highwayman who went under the name of Jac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And Brighton Railway
The London and Brighton Railway (L&BR) was a railway company in England which was incorporated in 1837 and survived until 1846. Its railway ran from a junction with the London and Croydon Railway (L&CR) at Norwood – which gives it access from London Bridge, just south of the River Thames in central London. It ran from Norwood to the South Coast at Brighton, together with a branch to Shoreham-by-Sea. Background During the English Regency, and particularly after the Napoleonic Wars, Brighton rapidly became a fashionable social resort, with more than 100,000 passengers being carried there each year by coach. Early schemes A proposal by William James in 1823 to connect London "with the ports of Shoreham (Brighton), Rochester (Chatham) and Portsmouth by a line of Engine Railroad" was largely ignored. However, about 1825 a company called The Surrey, Sussex, Hants, Wilts & Somerset Railway employed John Rennie to survey a route to Brighton, but again the proposal came to nothin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croydon
Croydon is a large town in South London, England, south of Charing Cross. Part of the London Borough of Croydon, a Districts of England, local government district of Greater London; it is one of the largest commercial districts in Greater London, with an extensive shopping area. The entire town had a population of 192,064 as of 2011, whilst the wider borough had a population of 384,837. Historically an ancient parish in the Wallington Hundred of Surrey, at the time of the Norman conquest of England Croydon had a church, a mill, and around 365 inhabitants, as recorded in the Domesday Book of 1086. Croydon expanded in the Middle Ages as a market town and a centre for charcoal production, leather tanning and brewing, with the brewing industry in particular remaining strong for hundreds of years. The Surrey Iron Railway from Croydon to Wandsworth opened in 1803 and was an early public railway. Later 19th century railway building facilitated Croydon's growth as a commuter town for L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
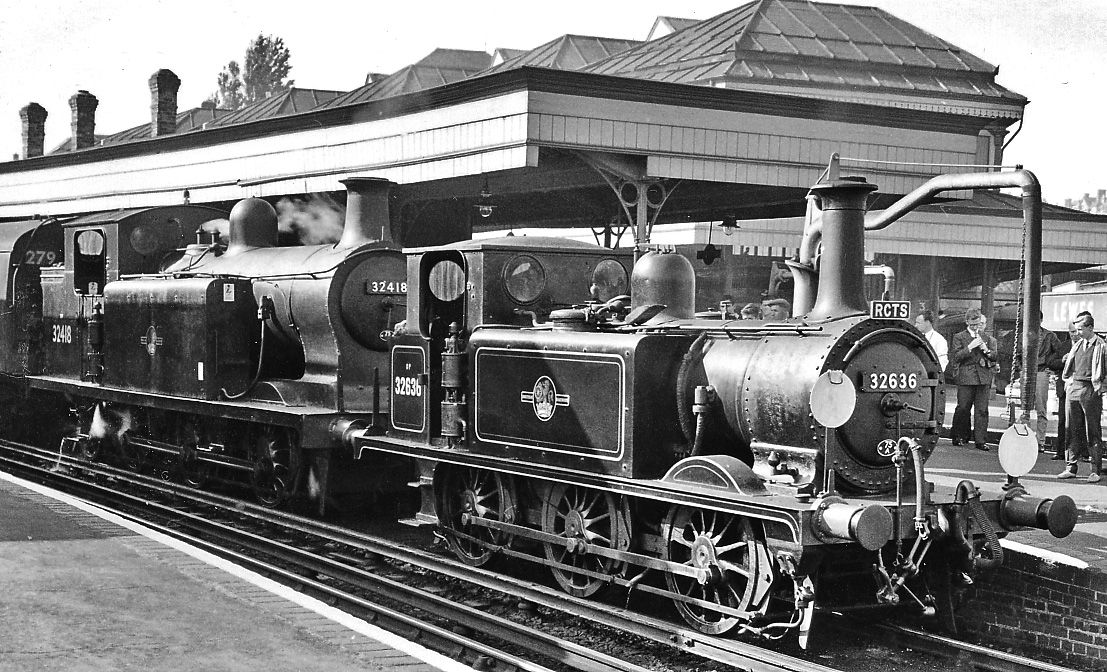
Bluebell Railway
The Bluebell Railway is an heritage line in West Sussex in England. It is managed by the Bluebell Railway Preservation Society. It uses steam trains which operate between and , with intermediate stations at and . It is the first preserved standard gauge steam-operated passenger railway in the world to operate a public service. The society ran its first train on 7 August 1960, less than three years after the line from East Grinstead to Lewes had been closed by British Railways. On 23 March 2013, the Bluebell Railway started to run through to its new terminus station. At East Grinstead there is a connection to the national rail network, the first connection of the Bluebell Railway to the national network in 50 years, since the Horsted Keynes – line closed in 1963. Today the railway is managed and run largely by volunteers. Having preserved a number of steam locomotives even before steam stopped running on British mainline railways in 1968, today it has over 30 steam l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horsted Keynes Railway Station
Horsted Keynes railway station is a preserved railway station on the Bluebell Railway in Sussex. The station has been used as a shooting location in several film and TV productions. History The station was closed by British Railways under the Beeching Axe on 28 October 1963 with the cessation of trains from Seaford via Haywards Heath railway station, Haywards Heath (trains over the Lewes railway station, Lewes to East Grinstead railway station, East Grinstead line having ceased in 1958). However, the first Bluebell Railway The Bluebell Railway is an heritage line in West Sussex in England. It is managed by the Bluebell Railway Preservation Society. It uses steam trains which operate between and , with intermediate stations at and . It is the first preserv ... trains had run on the last day of the 1962 season using the disused eastern side (electrified services only used Platform 2). Between 1960 and 1962, Bluebell Railway services had terminated at Bluebell Halt, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewes And East Grinstead Railway
The Bluebell Railway is an heritage line in West Sussex in England. It is managed by the Bluebell Railway Preservation Society. It uses steam trains which operate between and , with intermediate stations at and . It is the first preserved standard gauge steam-operated passenger railway in the world to operate a public service. The society ran its first train on 7 August 1960, less than three years after the line from East Grinstead to Lewes had been closed by British Railways. On 23 March 2013, the Bluebell Railway started to run through to its new terminus station. At East Grinstead there is a connection to the national rail network, the first connection of the Bluebell Railway to the national network in 50 years, since the Horsted Keynes – line closed in 1963. Today the railway is managed and run largely by volunteers. Having preserved a number of steam locomotives even before steam stopped running on British mainline railways in 1968, today it has over 30 steam loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Brighton And South Coast Railway
The London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR (known also as the Brighton line, the Brighton Railway or the Brighton)) was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1846 to 1922. Its territory formed a rough triangle, with London at its apex, practically the whole coastline of Sussex as its base, covering a large part of Surrey. It was bounded on its western side by the London and South Western Railway (L&SWR), which provided an alternative route to Portsmouth. On its eastern side the LB&SCR was bounded by the South Eastern Railway (SER)—later one component of the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SE&CR)—which provided an alternative route to Bexhill, St Leonards-on-Sea, and Hastings. The LB&SCR had the most direct routes from London to the south coast seaside resorts of Brighton, Eastbourne, Worthing, Littlehampton and Bognor Regis, and to the ports of Newhaven and Shoreham-by-Sea. It served the inland towns and cities of Chichester, Horsham, East Grinstead an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keymer
Keymer is a village in the civil parish of Hassocks, in the Mid Sussex District, Mid Sussex district of West Sussex, England. It lies on the B2116 road south of Burgess Hill. In 1971 the parish had a population of 5303. On 1 April 2000 the parish was abolished to form Hassocks. Both Keymer and Clayton, West Sussex, Clayton's records go back as far as the Domesday Book. Keymer is situated just to the east of Hassocks and is only a matter of a few hundred yards from the boundary with East Sussex. It has a fine parish church, St Cosmas and St Damian Church, Keymer, St Cosmas and St Damian Church. The oldest part of Keymer can be found in the area of this church and the Greyhound public house. Several buildings in this area are listed as being of Listed building, special architectural or historic interest and the oldest dates from the 15th century. To the north-east of Keymer can be found Oldland Mill dating from the 18th century. It is one of the few remaining post mills still st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewes Railway Station
Lewes railway station serves the town of Lewes in East Sussex, England. It has five platforms and is on the East Coastway Line, from via . Train services are provided by Southern. The station has a café and there is a taxi office on the main forecourt. There is a small taxi rank outside. History The first station in Friars Walk opened on 8 June 1846 was originally built as a terminus on the Brighton line. However, this station became inconvenient after an extension to opened on 27 June 1846. The new railway met the Brighton line at a junction just west of Lewes Station (i.e. towards Brighton), requiring trains serving Lewes to reverse. The director of the London, Brighton & South Coast Railway called the station "the most incomplete and injudicious station ever erected". On 2 October 1847, the Keymer Junction to Lewes line opened. New platforms (called Pinwell) were built opposite the terminus, west of the Hastings line branch. On 1 November 1857, a new station was b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batsford
Batsford is a village and Civil parishes in England, civil parish in the Cotswold (district), Cotswold district of Gloucestershire, England. The village is about north-west of Moreton-in-Marsh. There is a falconry centre close to the village and Batsford Arboretum is nearby, situated on the Cotswold escarpment. Moreton-in-Marsh and Batsford War Memorial, on the High Street in Moreton-in-Marsh, commemorates the village's dead of two World Wars. Civil parish The civil parish of Batsford extends east from the village, and includes the hamlets of Dorn, Gloucestershire, Dorn and Lower Lemington. According to the 2001 census the parish had a population of 99. Batsford was an ancient parish, which became a civil parish in 1866. In 1935 the civil parish more than doubled in size, when Dorn was transferred from the parish of Blockley and the civil parish of Lower Lemington was abolished and merged into Batsford. Religious sites The Church of St Leonard, Lower Lemington, Church of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Mocatta
David Alfred Mocatta (1806–1882) was a British architect and a member of the Anglo-Jewish Mocatta family. Early career David Alfred Mocatta was born to a Sephardic Jewish family in 1806, the son of the licensed bullion broker Moses Mocatta (1768–1857) and Abigail Lindo (1775–1824). He also was a grandson of the prominent financier Abraham Lumbroso de Matos Mocatta (1730–1800). He studied in London from 1821 to 1827 under Sir John SoaneBrodie, 2001, page 194 and then travelled in Italy during 1829–30. By 1839 he was in practice together with W.J. Mocatta at 32 Brunswick Square in Bloomsbury where he remained until 1846, before moving to 57 Old Broad Street in the City of London. His synagogue in Ramsgate for Moses Montefiore (1833) was possibly the first in England to be designed by a Jewish architect. The West London Synagogue of British Jews commissioned Mocatta to design both their temporary premises in Burton Street (1841) and their building in Margaret Street ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |