|
Hand-loom
A loom is a device used to weaving, weave cloth and tapestry. The basic purpose of any loom is to hold the Warp (weaving), warp threads under tension (mechanics), tension to facilitate the interweaving of the weft threads. The precise shape of the loom and its mechanics may vary, but the basic function is the same. Etymology and usage The word "loom" derives from the Old English ''geloma'', formed from ''ge-'' (perfective prefix) and ''loma'', a root of unknown origin; the whole word ''geloma'' meant a utensil, tool, or machine of any kind. In 1404 "lome" was used to mean a machine to enable weaving thread into cloth. By 1838 "loom" had gained the additional meaning of a machine for interlacing thread. Components and actions Basic structure File:Simple_treadle_floorloom,_line_drawing.png, upright=1.5, left, A simple treadle floor loom. Mouse over components for pop-up links. The warp runs horizontally. On the left the warp beam, held from turning by with a weighted trough t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankara 4P5C4752 (27616736687)
Ankara is the capital city of Turkey and the largest capital by area in the world. Located in the central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5,290,822 in its urban center ( Etimesgut, Yenimahalle, Çankaya, Keçiören, Altındağ, Pursaklar, Mamak, Gölbaşı, Sincan) and 5,864,049 in Ankara Province (total of 25 districts). Ankara is Turkey's second-largest city by population after Istanbul, first by urban land area, and third by metro land area after Konya and Sivas. Ankara was historically known as Ancyra and Angora. Serving as the capital of the ancient Celtic state of Galatia (280–64 BC), and later of the Roman province with the same name (25 BC–7th century), Ankara has various Hattian, Hittite, Lydian, Phrygian, Galatian, Greek, Persian, Roman, Byzantine, and Ottoman archeological sites. The Ottomans made the city the capital first of the Anatolia Eyalet (1393 – late 15th century) and then the Angora Eyalet (1827–1864) and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peg Loom
A peg loom is a simple weaving loom. Handheld weaving sticks use the same principle. A peg loom is a board, usually wooden, with one or more rows of holes, and a set of wooden or nylon pegs which fit into these holes. Each peg is a dowel with a hole drilled along its diameter near one end. Handheld weaving sticks are similar to the pegs, but tapered at the hole end and pointed at the other end. Plastic looms are also made for the educational market. Double-length warp threads are threaded through the hole in each peg or stick, and the loose ends knotted. The pegs are inserted into the loom, or the sticks are handheld, and the weft thread is woven around the pegs or sticks. As the work progresses, it is slid off the pegs or sticks onto the trailing warp threads. Different yarns can be used to create patterns, and when using sticks a curved piece of work can be created by weaving less often round certain sticks. Looms are made in a range of sizes. As an example, one English compan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pin Loom
Pin weaving is a form of small-scale weaving traditionally done on a frame made of pins; the warp and weft are wrapped around the pins. Pin-woven textiles have a selvage edge all the way around. Pin looms were popular from the 1930s to the 1960s. Quite elaborate patterns were published, especially in the 1930s. 21st-century designs often focus more on the fiber than on elaborate patterning; for instance, yarns with precisely repeating colours can be used to make plaids. Equipment The equipment needed is minimal, consisting of pins, a pinnable board, and a bodkin needle. It can also be done on some types of knitting frame. There are also commercial looms made for pin weaving. Smooth, rounded pin tops are desirable; they don't snag the yarn or fingers. Pins are usually spaced apart. 4-8 pins per inch (3-6 pins every two centimeters), The pins may be numbered (with numbers written beside the pins), and the lower-left corner may be marked, for ease of reference when working pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WEAVING WITH A PIN (cropped)
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal threads are called the warp and the lateral threads are the weft, woof, or filling. The method in which these threads are interwoven affects the characteristics of the cloth. Cloth is usually woven on a loom, a device that holds warp threads in place while filling threads are woven through them. A fabric band that meets this definition of cloth (warp threads with a weft thread winding between) can also be made using other methods, including tablet weaving, back strap loom, or other techniques that can be done without looms. The way the warp and filling threads interlace with each other is called the weave. The majority of woven products are created with one of three basic weaves: plain weave, satin weave, or twill weave. Woven cloth c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
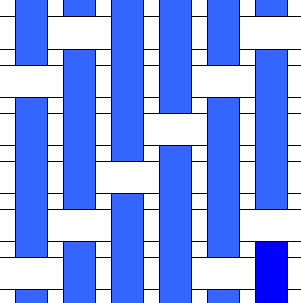
Twill Weave
Twill is a type of textile weave with a pattern of parallel, diagonal ribs. It is one of three fundamental types of weave, along with plain weave and satin. It is made by passing the weft thread over one or more warp threads then under two or more warp threads and so on, with a "step", or offset, between rows to create the characteristic diagonal pattern. Due to this structure, twill generally drapes well. Classification Twill weaves can be classified from four points of view: # According to the stepping: #* ''Warp-way'': 3/1 warp way twill, etc. #* ''Weft-way'': 2/3 weft way twill, etc. # According to the direction of twill lines on the face of the fabric: #* ''S-twill'', or ''left-hand twill weave'': 2/1 S, etc. #* ''Z-twill'', or ''right-hand twill weave'': 3/2 Z, etc. # According to the face yarn (warp or weft): #* ''Warp face twill weave'': 4/2 S, etc. #* ''Weft face twill weave'': 1/3 Z, etc. #* ''Double face'' twill weave'': 3/3 Z, etc. # According to the natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabby Weave
Plain weave (also called tabby weave, linen weave or taffeta weave) is the most basic of three fundamental types of textile weaves (along with satin weave and twill). It is strong and hard-wearing, and is used for fashion and furnishing fabrics. Fabrics with a plain weave are generally strong, durable, and have a smooth surface. They are often used for a variety of applications, including clothing, home textiles, and industrial fabrics. In plain weave cloth, the warp and weft threads cross at right angles, aligned so they form a simple criss-cross pattern. Each weft thread crosses the warp threads by going over one, then under the next, and so on. The next weft thread goes under the warp threads that its neighbor went over, and vice versa. * Balanced plain weaves are fabrics in which the warp and weft are made of threads of the same weight (size) and the same number of ends per inch as picks per inch. * Basketweave is a variation of plain weave in which two or more thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shed (weaving)
In weaving, the shed is the temporary separation between upper and lower warp yarns through which the weft is woven. The shed is created to make it easy to interlace the weft into the warp and thus create woven fabric. Most types of looms have some sort of device which separates some of the warp threads from the others. This separation is called the shed, and allows for a shuttle carrying the weft thread to move through the shed perpendicular to the warp threads. Which threads are raised and which are lowered are changed after each pass of the shuttle. The process of weaving can be simplified to a series of four steps: the shed is raised, the shuttle is passed through, the shed is closed, and the weft thread is beaten into place. These steps are then repeated, with a different set of threads being raised so as to interlace the warp and weft. The term ''shedding'' refers to the action of creating a shed. A ''shedding device'' is the device used to raise or open the shed. Cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warp (weaving)
In the manufacture of cloth, warp and weft are the two basic components in weaving to transform thread and yarn into textile fabrics. The vertical ''warp'' yarns are held stationary in tension on a loom (frame) while the horizontal ''weft'' (also called the ''woof'') is drawn through (inserted over and under) the warp thread. In the terminology of weaving, each warp thread is called a ''warp end''; a ''pick'' is a single weft thread that crosses the warp thread (synonymous terms are ''fill yarn'' and ''filling yarn'').Burnham (1980), pp. 170, 179Barber (1991), p. 79. In the 18th century, the Industrial Revolution facilitated the industrialisation of the production of textile fabrics with the "picking stick" and the " flying shuttle", the latter of which was invented by John Kay, in 1733. The mechanised power loom was patented by Edmund Cartwright in 1785, which allowed sixty picks per minute. Etymology The word ''weft'' derives from the Old English word , to weave. ''Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belarus Weaving
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an area of with a population of . The country has a hemiboreal climate and is administratively divided into six regions. Minsk is the capital and largest city; it is administered separately as a city with special status. For most of the medieval period, the lands of modern-day Belarus was ruled by independent city-states such as the Principality of Polotsk. Around 1300 these lands came fully under the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and subsequently by the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth; this period lasted for 500 years until the 1792-1795 partitions of Poland-Lithuania placed Belarus within the Russian Empire for the first time. In the aftermath of the Russian Revolution in 1917, different states arose competing for legitimacy amid the Civil W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leiden
Leiden ( ; ; in English language, English and Archaism, archaic Dutch language, Dutch also Leyden) is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of South Holland, Netherlands. The municipality of Leiden has a population of 127,046 (31 January 2023), but the city forms one densely connected agglomeration with its suburbs Oegstgeest, Leiderdorp, Voorschoten and Zoeterwoude with 215,602 inhabitants. The Statistics Netherlands, Netherlands Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS) further includes Katwijk in the agglomeration which makes the total population of the Leiden urban agglomeration 282,207 and in the larger Leiden urban area also Teylingen, Noordwijk, and Noordwijkerhout are included with in total 365,913 inhabitants. Leiden is located on the Oude Rijn (Utrecht and South Holland), Oude Rijn, at a distance of some from The Hague to its south and some from Amsterdam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museum Het Leids Wevershuis
Museum Het Leids Wevershuis consists of one of the last remaining "weavers' homes" in Leiden, Netherlands. Built around 1560, the exterior, the large antique loom (1830) and the interior, are testimony of the once flourishing textile industry (and trade) around Leiden, in particular during the 16th and 17th century, when many home weavers supplied the draper's guild with high quality woolen cloth. Museum The building and its antique interior are the museum. There is a small collection of modern hand-woven textiles. The museum has a weaver available most days to demonstrate the craft on a large loom A loom is a device used to weaving, weave cloth and tapestry. The basic purpose of any loom is to hold the Warp (weaving), warp threads under tension (mechanics), tension to facilitate the interweaving of the weft threads. The precise shape of .... Products made during demonstrations are for sale. The museum is a short walking distance from the old Draper's guild, part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |